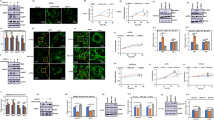
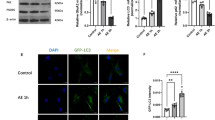
Abstract
EGb-761 is commonly used as a treatment for ischemic brain injury, neurodegenerative diseases and some types of tumors (Christen and Maixent, in Cell Mol Biol 48(6):601–611, 2002). However, it is unclear whether EGb-761 affects the proliferation of cells exposed to fluoride. In this study, the proliferation and apoptosis of PC-12 cells exposed to fluoride were investigated and EGb-761 was used to protect PC-12 cells against the effects of fluoride. We found that the canonical Wnt signaling pathway was involved in the anti-proliferation of PC-12 cells exposed to fluoride. Furthermore, the results also showed that EGb-761 could attenuate the anti-proliferative activity of fluoride via DDK1 in PC-12 cells. This study may provide a new method for protecting against the inhibition of cell proliferation induced by fluoride.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christen Y, Maixent JM (2002) What is Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761? An overview–from molecular biology to clinical medicine. Cell Mol Biol 48(6):601–611
Ersoy IH et al (2011) Serum copper, zinc, and magnesium levels in patients with chronic fluorosis. Biol Trace Elem Res 143(2):619–624
Zhang C et al (2013) The analog of Ginkgo biloba extract 761 is a protective factor of cognitive impairment induced by chronic fluorosis. Biol Trace Elem Res 153(1–3):229–236
Perumal E et al (2013) A brief review on experimental fluorosis. Toxicol Lett 223(2):236–251
Pan L et al (2014) Fluoride promotes osteoblastic differentiation through canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Toxicol Lett 225(1):34–42
Liu XL et al (2012) The influence of fluoride on the expression of inhibitors of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in rat skin fibroblast Cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 148(1):117–121
Li F, Chong ZZ, Maiese K (2005) Vital elements of the Wnt-Frizzled signaling pathway in the nervous system. Curr Neurovasc Res 2(4):331–340
Glinka A et al (1998) Dickkopf-1 is a member of a new family of secreted proteins and functions in head induction. Nature 391(6665):357–362
Menezes ME et al (2012) Dickkopf1: a tumor suppressor or metastasis promoter? Int J Cancer 130(7):1477–1483
Lowry OH et al (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Shusterman K et al (2014) Wnt-RhoA signaling pathways in fluoride-treated ameloblast-lineage cells. Cells Tissues Organs 199(2–3):159–168
Clevers H (2006) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 127(3):469–480
Leung JY et al (2002) Activation of AXIN2 expression by beta-catenin-T cell factor. A feedback repressor pathway regulating Wnt signaling. J Biol Chem 277(24):21657–21665
Logan CY, Nusse R (2004) The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20:781–810
Ando M et al (1998) Health effects of indoor fluoride pollution from coal burning in China. Environ Health Perspect 106(5):239–244
Fu X et al (2016) High-dose fluoride impairs the properties of human embryonic stem cells via JNK signaling. PLoS One 11(2):e0148819
Mariz K et al (2015) The Wnt inhibitor dickkopf-1: a link between breast cancer and bone metastases. Clin Exp Metastasis 32(8):857–866
Zhu Y et al (2009) Human mesenchymal stem cells inhibit cancer cell proliferation by secreting DKK-1. Leukemia 23(5):925–933
Park YJ et al (2016) Ginkgo biloba extract EGb-761 mediated inhibition of aromatase for the treatment of hormone-dependent breast cancer. Food Chem Toxicol 87:157–165
Chen XH et al (2011) Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb761 on human colon adenocarcinoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 27(3–4):227–232
Chao JC, Chu CC (2004) Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on cell proliferation and cytotoxicity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 10(1):37–41
Wang J, Chen W, Wang Y (2013) A ginkgo biloba extract promotes proliferation of endogenous neural stem cells in vascular dementia rats. Neural Regen Res 8(18):1655–1662
Sun HM ZL, Guan T et al (2008) Study of GBE on promoting proliferation of neural stem cells in the subventricular zone in modeled mice of Parkinson’s disease. Shijie Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi 3(9):518–520
Li R YB, Fan QP et al (2011) Effect of ginkgo biloba extract on learning and memory of developing rats with kindled seizure by pentetrazole and proliferation and differentiation of hippocampal neural stem cells. Shiyong Erke Linchuang Zazhi 26(23):1821–1824
Zhu Z et al (2016) CLOCK promotes 3T3-L1 cell proliferation via Wnt signaling. IUBMB Life 68(7):557–568
Wang KP et al (2015) Morphine protects SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells against Dickkopf1-induced apoptosis. Mol Med Rep 11(2):1174–1180
Visweswaran M et al (2015) Multi-lineage differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells - To Wnt, or not Wnt. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 68:139–147
Spinsanti P et al (2008) Differential activation of the calcium/protein kinase C and the canonical beta-catenin pathway by Wnt1 and Wnt7a produces opposite effects on cell proliferation in PC12 cells. J Neurochem 104(6):1588–1598
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by BK20151159 from the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China, Project 81501185 of National Natural Science Foundation of China, Xuzhou Medical Talents Project and Xuzhou technological and scientific project No. KC14SH50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Cai-Yi Zhang and Rui Chen have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, CY., Chen, R., Wang, F. et al. EGb-761 Attenuates the Anti-proliferative Activity of Fluoride via DDK1 in PC-12 Cells. Neurochem Res 42, 606–614 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2115-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2115-6