Abstract
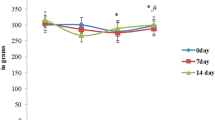
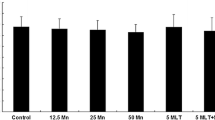
Manganese (Mn) is a potent neurotoxin involved in the initiation and progression of various cognitive disorders. Oxidative stress is reported as one of accepted mechanisms of Mn toxicity. The present study was designed to explore the effects of silymarin, a natural antioxidant, in attenuating the toxicity induced by Mn in rat cerebellum. In this investigation, rats were treated orally with MnCl2 (20 mg/ml) for 30 days, subsets of these animals were treated intraperitoneally daily with silymarin (100 mg/kg) along with respective controls. Mn exposure caused a marked oxidative stress in cerebellum as indicated by a significant decrease in the activities of enzymatic antioxidants like superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase and in the levels of non-enzymatic antioxidants like reduced glutathione (GSH), total thiols and vitamin C. Conversely an increase was obtained in lipid and protein markers such as thiobarbituric reactive acid substances, lipid hydroperoxide and protein carbonyl products contents. A Significant increase in acetylcholinesterase and a decrease in Na+/K+-ATPase activities were also shown, with a substantial rise in the expression of acetylcholinesterase and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and nitric oxide levels. The potential effect of SIL to prevent Mn induced neurotoxicity was also reflected by histopathological observations. Rats exposed to Mn showed a reduced number and morphological alterations of cerebellar Purkinje cells. These phenomenons were completely reversed by SIL co-treatment. We concluded that silymarin may protect against Mn-induced oxidative stress in cerebellum by inhibiting both lipid and protein oxidation and by activating acetylcholinesterase and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) gene expression.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sen S, Flynn MR, Du G, Tröster AI, An H, Huang X (2011) Manganese accumulation in the olfactory bulbs and other brain regions of “asymptomatic” welders. Toxicol Sci 121(1):160–167
Aschner M (1997) Manganese neurotoxicity and oxidative damage. In: Conner JR (ed) Metals and oxidative damage in neurological disorders. Plenum, New York, pp 77–93
Lander F, Kristiansen J, Lauritsen JM (1999) Manganese exposure in foundry furnacemen and scrap recycling workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 72:546–550
Erikson KM, Dorman DC, Lash LH, Aschner M (2007) Manganese inhalation by rhesus monkeys is associated with brain regional changes in biomarkers of neurotoxicity. Toxicol Sci 97(2):459–466
Montes S, Alcaraz-Zubeldia M, Muriel P, Riso C (2001) Striatal manganese accumulation induces changes in dopamine metabolism in the cirrhoticrat. Brain Res 891:123–129
Chen CJ, Liao SL (2002) Oxidative stress involves in astrocytic alterations induced by manganese. Exp Neurol 175:216–225
Chtourou Y, Fetoui H, Sefi M, Trabelsi K, Barkallah M, Boudawara T, Kallel H, Zeghal N (2010) Silymarin, a natural antioxidant, protects cerebral cortex against manganese-induced neurotoxicity in adult rats. Biometals 6:985–996
Myhrer T (2003) Neurotransmitter systems involved in learning and memory in the rat: a meta-analysis based on studies of four behavioral tasks. Brain Res Rev 41:268–287
Filipov NM, Seegal RF, Lawrence DA (2005) Manganese potentiates in vitro production of proinflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide by microglia through a nuclear factor kappa B-dependent mechanism. Toxicol Sci 84:139–148
Moreno JA, Streifel KM, Sullivan KA, Legare ME, Tjalkens RB (2009) Developmental exposure to manganese (Mn) increases adult susceptibility to inflammatory activation of glia and neuronal protein nitration. Toxicol Sci 112(2):405–415
Bae JH, Jang BC, Suh SI, Ha E, Baik HH, Kim SS, Lee MY, Shin DH (2006) Manganese induces inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression via activation of both MAP kinase and PI3 K/Akt pathways in BV2 microglial cells. Neurosci Lett 398:151–154
Moreno JA, Sullivan KA, Carbone DL, Hanneman WH, Tjalkens RB (2008) Manganese potentiates nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent expression of nitric oxide synthase 2 in astrocytes by activating soluble guanylate cyclase and extracellular responsive kinase signaling pathways. J Neurosci Res 86:2028–2038
Lev-Ram V, Makings LR, Keitz PF, Kao JP, Tsien RY (1995) Long-term depression in cerebellar Purkinje neurons results from coincidence of nitric oxide and depolarization-induced Ca2+ transients. Neuron 15:407–415
Simon DK, Standaert DG (1999) Neuroprotective therapies. Med Clin North Am 83(2):509–523
Wagoner J, Negash A, Kane OJ et al (2010) Multiple effects of silymarin on the hepatitis C virus life cycle. Hepatology 51(6):1912–1921
Polyak SJ, Morishima C, Lohmann V, Pal S, Lee DY, Liu Y, Graf TN, Oberlies NH (2010) Identification of hepatoprotective flavonolignans from silymarin. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 107(13):5995–5999
Lu P, Mamiya T, Lu LL, Mouri A, Niwa M, Hiramatsu M, Zou LB, Nagai T, Ikejima T, Nabeshima T (2009) Silibinin attenuates amyloid b 25–35 peptide-induced memory impairments: implication of inducible nitric-oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-a in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 331(1):319–326
Yaghmaei P, Parivar K, Masoudi A, Darab M, Amini E (2009) The effect of silybin on passive avoidance learning and pathological changes in hippocampal CA1 and DG regions in male Wistar rats offspring. J Asian Nat Prod Res 11:514–522
Asghar Z, Masood Z (2008) Evaluation of antioxidant properties of silymarin and its potential to inhibit peroxyl radicals in vitro. Pak J Pharm Sci 21(3):249–254
Koksal E, Gulcin I, Beyza S, Sarikaya O, Bursal E (2008) In vitro antioxidant activity of silymarin. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 24(2):395–405
Fetoui H, Mahjoubi-Samet A, Jammousi K, Ellouze F, Guermazi F, Zeghal N (2006) Energy restriction in pregnant and lactating rats lowers bone mass of their progeny. Nutr Res 26:421–426
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Euro J Biochem 47:469–474
Flohe L, Gunzler WA (1984) Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 105:114–121
Fairbanks VF, Klee GG (1999) Biochemical aspects of hematology. In: Burtis CA, Ashwood ER (eds) Tietz textbook of clinical chemistry, 3rd edn. WB Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 1642–1644
Zahler WL, Cleland WW (1968) A specific and sensitive assay for disulfides. J Biol Chem 243:716–719
Jacques-Silva MC, Nogueira CW, Broch LC, Flores EM, Rocha JBT (2001) Diphenyl diselenide and ascorbic changes deposition of selenium and ascorbic in liver and brain of mice. Pharmacol Toxicol 88:119–125
Archer S (1993) Measurement of nitric oxide in biological models. FASEB J 7:349–359
Draper HH, Hadley M (1990) Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Ezymol 86:421–431
Jiang ZY, Hunt JV, Wolff SP (1992) Ferrous ion oxidation in the presence of xylenol orange for detection of lipid hydroperoxide in low-density lipoprotein. Anal Biochem 202:384–389
Evans P, Lyras L, Halliwell B (1999) Measurement of protein carbonyls in human brain tissue. Methods Enzymol 300:145–156
Wyse AT, Streck EL, Worm P, Wajner A, Ritter F, Netto CA (2000) Preconditioning prevents the inhibition of Na+, K+-ATPase activity after brain ischemia. Neurochem Res 25:971–975
Carfagna MA, Ponsler GD, Muhoberac BB (1996) Inhibition of ATPase activity in rat synaptic plasma membranes by simultaneous exposure to metals. Chem Biol Interact 100(1):53–65
Ellman GE, Courtney KD, Andersen JV, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Tsakiris S, Angelogianni P, Schulpis KH, Stavridis JC (2000) Protective effect of L -phenylalanine on rat brain acetylcholine esterase inhibition induced by free radicals. Clin Biochem 33(2):103–106
Bensoussan H, Grancolas L, Dhieux-Lestaevel B, Delissen O, Vacher CM, Dublineau I, Voisin P, Gourmelon P, Taouis M, Lestaevel P (2009) Heavy metal uranium affects the brain cholinergic system in rat following sub-chronic and chronic exposure. Toxicology 261(1–2):59–67
Kumar A, Singh RL, Babu GN (2010) Cell death mechanisms in the early stages of acute glutamate neurotoxicity. Neurosci Res 66:271–278
Becerra-Verdin EM, Bermúdez-Barba MV, Salazar-Leal ME, Ancer Rodríguez J, Romero-Diaz V, Soto-Domínguez A, Ballesteros-Eliozondo RG, Saucedo-Cardenas O, Piñeyro Lopez A, Sepúlveda-Saavedra J (2009) Karwinskia humboldtiana (buckthorn) fruit causes central nervous system damage during chronic intoxication in the rat. Toxicon 53(6):645–651
Chtourou Y, Trabelsi K, Fetoui H, Mkannez G, Kallel H, Zeghal N (2011) Manganese induces oxidative stress, redox state unbalance and disrupts membrane bound ATPases on murine neuroblastoma cells in vitro: protective role of silymarin. Neurochem Res 36(8):1546–1557
Aschner M, Nass R, Guilarte TR, Schneider JS, Zheng W (2007) Manganese: recent advances in understanding its transport and neurotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 221:131–147
Gunter TE, Gavin CE, Aschner M, Gunter KK (2006) Speciation of manganese in cells and mitochondria: a search for the proximal cause of manganese neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 27:765–776
Gazák R, Purchartová K, Marhol P, Zivná L, Sedmera P, Valentová K, Kato N, Matsumura H, Kaihatsu K, Kren V (2010) Antioxidant and antiviral activities of silybin fatty acid conjugates. Euro J Med Chem 45:1059–1067
Bosisio E, Benelli C, Pirola O (1992) Effect of the flavanolignans of Silybum marianum L. on lipid peroxidation in rat liver microsomes and freshly isolated hepatocytes. Pharmacol Res 25(2):147–154
Basiglio CL, Sánchez Pozzi EJ, Mottino AD, Roma MG (2009) Differential effects of silymarin and its active component silibinin on plasma membrane stability and hepatocellular lysis. Chem Biol Interact 179(2–3):297–303
Murray J, Taylor SW, Zhang B, Ghosh S (2003) Oxidative damage to mitochondrial complex I due to peroxynitrite. J Biol Chem 278:37223–37230
Kang JS, Jeon YJ, Kim HM, Han SH, Yang KH (2002) Inhibition of inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression by silymarin in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:138–144
Lees GJ (1993) Contributory mechanisms in the causation of neurodegenerative disorders. Neuroscience 54:287–322
Wang XQ, Xiao AY, Sheline C, Hyrc K, Yang A, Goldberg MP et al (2003) Apoptotic insults impair Na+, K+-ATPase activity as a mechanism of neuronal death mediated by concurrent ATP deficiency and oxidant stress. J Cell Sci 116:2099–2110
Sato A, Sato Y, Uchida S (2004) Activation of the intracerebral cholinergic nerve fibers originating in the basal forebrain. Neurosci Lett 361:90–93
Liapi C, Zarros A, Galanopoulou P, Theocharis S, Skandali N, Al-Humadi H, Anifantaki F, Gkrouzman E, Mellios Z, Tsakiris S (2008) Effects of Short-Term Exposure to Manganese on the Adult Rat Brain Antioxidant Status and the Activities of Acetylcholinesterase, (Na+, K+)-ATPase and Mg2+-ATPase: Modulation by l-Cysteine. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 103(2):171–175
Wasserman GA, Liu X, Parvez F, Ahsan H, Levy D, Factor-Litvak P, Kline J, van Geen A, Slavkovich V, Lolacono NJ, Cheng Z, Zheng Y, Graziano JH (2006) Water manganese exposure and children’s intellectual function in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ Health Persp 114:124–129
Tota S, Kamat PK, Shukla R, Nath C (2011) Improvement of brain energy metabolism and cholinergic functions contributes to the beneficial effects of silibinin against streptozotocin induced memory impairment. Behav Brain Res 221(1):207–215
Kuhad A, Chopra K (2007) Curcumin attenuates diabetic encephalopathy in rats: behavioral and biochemical evidences. Eur J Pharmacol 576:34–42
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to Miss Dalenda Kchaou for her assistance in histolological techniques. The present work was supported by the grants of DGRST (Appui à la Recherche Universitaire de base, ARUB 99/UR/08-73) Tunisia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chtourou, Y., Fetoui, H., Garoui, E.M. et al. Improvement of Cerebellum Redox States and Cholinergic Functions Contribute to the Beneficial Effects of Silymarin Against Manganese-Induced Neurotoxicity. Neurochem Res 37, 469–479 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0632-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0632-x