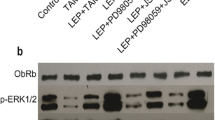
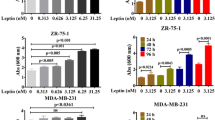
Abstract
Esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) is one of the most common malignancies in the world which is associated the increased prevalence of obesity. In the context of obesity, leptin can directly contribute to progression of EAC. Adiponectin inhibits leptin-induced oncogenic signaling in EAC cells. However, the exact molecular mechanisms linking obesity, adipokines, and EAC remain far from completely understood. In the present study, we tested the role of ubiquitin-like with PHD and ring finger domains 1 (UHRF1) in adiponectin-induced protective effects against leptin-induced EAC cell proliferation. We found that globular adiponectin (gAD) significantly inhibited leptin-induced increase of cell proliferation and decrease of apoptosis in OE 19 cells. Moreover, leptin-induced increase of UHRF1 expression was suppressed by gAD. Compared with normal controls, UHRF1 expression was markedly increased in EAC tissues and cell lines. Silence of UHRF1 increased the expression of cleaved caspase 3 and 9 and Bax, reduced the expression of Bcl-2, promoted apoptosis, and inhibited cell proliferation in OE 19 cells. Overexpression of UHRF1 significantly blocked gAD-induced decrease of cell proliferation and increase of apoptosis in leptin-treated cells. Silence of adiponectin receptor 1/2 (AdipoR1/2) could inhibit gAD-induced decrease of cell proliferation and increase of apoptosis in leptin-treated cells. Silence of AdipoR2, but not AdipoR1, suppressed gAD-induced decrease of UHRF1 expression in leptin-treated cells. The results indicated that gAD inhibited the prooncogenic effects of leptin via AdipoR2-mediated suppression of UHRF1. Our study provides novel insights into the role of UHRF1 in the development of EAC and the mechanism of antitumor effect of gAD.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA, Luketich JD (2013) Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet 381:400–412. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(12)60643-6
Pohl H, Welch HG (2005) The role of overdiagnosis and reclassification in the marked increase of esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:142–146. doi:10.1093/jnci/dji024
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Smigal C, Thun MJ (2006) Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin 56:106–130
Anaparthy R, Sharma P (2014) Progression of Barrett oesophagus: role of endoscopic and histological predictors. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 11:525–534. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2014.69
Eloubeidi MA, Mason AC, Desmond RA, El-Serag HB (2003) Temporal trends (1973–1997) in survival of patients with esophageal adenocarcinoma in the United States: a glimmer of hope? Am J Gastroenterol 98:1627–1633. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07454.x
Li X, Galipeau PC, Paulson TG, Sanchez CA, Arnaudo J, Liu K, Sather CL, Kostadinov RL, Odze RD, Kuhner MK, Maley CC, Self SG, Vaughan TL, Blount PL and Reid BJ (2014) Temporal and spatial evolution of somatic chromosomal alterations: a case-cohort study of Barrett’s esophagus. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 7: 114–127. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.capr-13-0289
Lagergren J, Bergstrom R, Nyren O (1999) Association between body mass and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and gastric cardia. Ann Intern Med 130:883–890
Buttar NS, Wang KK (2004) Mechanisms of disease: Carcinogenesis in Barrett’s esophagus. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 1:106–112. doi:10.1038/ncpgasthep0057
Carr JS, Zafar SF, Saba N, Khuri FR, El-Rayes BF (2013) Risk factors for rising incidence of esophageal and gastric cardia adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Cancer 44:143–151. doi:10.1007/s12029-013-9480-z
Nie S, Chen T, Yang X, Huai P, Lu M (2014) Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with esophageal adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Dis Esophagus 27:645–653. doi:10.1111/dote.12194
Beales IL, Garcia-Morales C, Ogunwobi OO and Mutungi G (2014) Adiponectin inhibits leptin-induced oncogenic signalling in oesophageal cancer cells by activation of PTP1B. Mol Cell Endocrinol 382:150–158. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2013.08.013
Mokrowiecka A, Sokolowska M, Luczak E, Dudojc M, Wieczfinska J, Kacprzak D, Wierzchniewska-Lawska A, Pawliczak R, Malecka-Panas E (2013) Adiponectin and leptin receptors expression in Barrett’s esophagus and normal squamous epithelium in relation to central obesity status. J Physiol Pharmacol 64:193–199
Thompson OM, Beresford SA, Kirk EA, Bronner MP, Vaughan TL (2010) Serum leptin and adiponectin levels and risk of Barrett’s esophagus and intestinal metaplasia of the gastroesophageal junction. Obesity (Silver Spring) 18:2204–2211. doi:10.1038/oby.2009.508
Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, Ohannesian JP, Marco CC, McKee LJ, Bauer TL et al (1996) Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med 334:292–295. doi:10.1056/nejm199602013340503
Lord GM, Matarese G, Howard JK, Baker RJ, Bloom SR, Lechler RI (1998) Leptin modulates the T-cell immune response and reverses starvation-induced immunosuppression. Nature 394:897–901. doi:10.1038/29795
Tsuchiya T, Shimizu H, Horie T, Mori M (1999) Expression of leptin receptor in lung: leptin as a growth factor. Eur J Pharmacol 365:273–279
Hardwick JC, Van Den Brink GR, Offerhaus GJ, Van Deventer SJ, Peppelenbosch MP (2001) Leptin is a growth factor for colonic epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 121:79–90
Somasundar P, Frankenberry KA, Skinner H, Vedula G, McFadden DW, Riggs D, Jackson B, Vangilder R, Hileman SM, Vona-Davis LC (2004) Prostate cancer cell proliferation is influenced by leptin. J Surg Res 118:71–82. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2004.01.017
Howard JM, Cathcart MC, Healy L, Beddy P, Muldoon C, Pidgeon GP, Reynolds JV (2014) Leptin and adiponectin receptor expression in oesophageal cancer. Br J Surg 101:643–652. doi:10.1002/bjs.9469
Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Miyagawa J, Hotta K, Shimomura I, Nakamura T, Miyaoka K, Kuriyama H, Nishida M, Yamashita S, Okubo K, Matsubara K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (1999) Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 257:79–83
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Ito Y, Tsuchida A, Yokomizo T, Kita S, Sugiyama T, Miyagishi M, Hara K, Tsunoda M, Murakami K, Ohteki T, Uchida S, Takekawa S, Waki H, Tsuno NH, Shibata Y, Terauchi Y, Froguel P, Tobe K, Koyasu S, Taira K, Kitamura T, Shimizu T, Nagai R, Kadowaki T (2003) Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 423:762–769. doi:10.1038/nature01705
Ishikawa M, Kitayama J, Kazama S, Hiramatsu T, Hatano K, Nagawa H (2005) Plasma adiponectin and gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:466–472
Dalamaga M, Diakopoulos KN, Mantzoros CS (2012) The role of adiponectin in cancer: a review of current evidence. Endocr Rev 33:547–594. doi:10.1210/er.2011-1015
Petridou E, Mantzoros C, Dessypris N, Koukoulomatis P, Addy C, Voulgaris Z, Chrousos G, Trichopoulos D (2003) Plasma adiponectin concentrations in relation to endometrial cancer: a case-control study in Greece. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:993–997. doi:10.1210/jc.2002-021209
Li H, Stampfer MJ, Mucci L, Rifai N, Qiu W, Kurth T, Ma J (2010) A 25-year prospective study of plasma adiponectin and leptin concentrations and prostate cancer risk and survival. Clin Chem 56:34–43. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2009.133272
Ogunwobi OO, Beales IL (2008) Globular adiponectin, acting via adiponectin receptor-1, inhibits leptin-stimulated oesophageal adenocarcinoma cell proliferation. Mol Cell Endocrinol 285:43–50. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2008.01.023
Vucenik I, Stains JP (2012) Obesity and cancer risk: evidence, mechanisms, and recommendations. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1271:37–43. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06750.x
Lagergren J (2011) Influence of obesity on the risk of esophageal disorders. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8:340–347. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2011.73
Hopfner R, Mousli M, Jeltsch JM, Voulgaris A, Lutz Y, Marin C, Bellocq JP, Oudet P, Bronner C (2000) ICBP90, a novel human CCAAT binding protein, involved in the regulation of topoisomerase IIalpha expression. Cancer Res 60:121–128
Sharif J, Muto M, Takebayashi S, Suetake I, Iwamatsu A, Endo TA, Shinga J, Mizutani-Koseki Y, Toyoda T, Okamura K, Tajima S, Mitsuya K, Okano M, Koseki H (2007) The SRA protein Np95 mediates epigenetic inheritance by recruiting Dnmt1 to methylated DNA. Nature 450:908–912. doi:10.1038/nature06397
Bostick M, Kim JK, Esteve PO, Clark A, Pradhan S, Jacobsen SE (2007) UHRF1 plays a role in maintaining DNA methylation in mammalian cells. Science 317:1760–1764. doi:10.1126/science.1147939
Unoki M, Daigo Y, Koinuma J, Tsuchiya E, Hamamoto R, Nakamura Y (2010) UHRF1 is a novel diagnostic marker of lung cancer. Br J Cancer 103:217–222. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605717
Sabatino L, Fucci A, Pancione M, Carafa V, Nebbioso A, Pistore C, Babbio F, Votino C, Laudanna C, Ceccarelli M, Altucci L, Bonapace IM, Colantuoni V (2012) UHRF1 coordinates peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma (PPARG) epigenetic silencing and mediates colorectal cancer progression. Oncogene 31:5061–5072. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.3
Mudbhary R, Hoshida Y, Chernyavskaya Y, Jacob V, Villanueva A, Fiel MI, Chen X, Kojima K, Thung S, Bronson RT, Lachenmayer A, Revill K, Alsinet C, Sachidanandam R, Desai A, SenBanerjee S, Ukomadu C, Llovet JM, Sadler KC (2014) UHRF1 overexpression drives DNA hypomethylation and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 25:196–209. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2014.01.003
Arima Y, Hirota T, Bronner C, Mousli M, Fujiwara T, Niwa S, Ishikawa H, Saya H (2004) Down-regulation of nuclear protein ICBP90 by p53/p21Cip1/WAF1-dependent DNA-damage checkpoint signals contributes to cell cycle arrest at G1/S transition. Genes Cells 9:131–142
Tien AL, Senbanerjee S, Kulkarni A, Mudbhary R, Goudreau B, Ganesan S, Sadler KC, Ukomadu C (2011) UHRF1 depletion causes a G2/M arrest, activation of DNA damage response and apoptosis. Biochem J 435:175–185. doi:10.1042/bj20100840
Muto M, Kanari Y, Kubo E, Takabe T, Kurihara T, Fujimori A, Tatsumi K (2002) Targeted disruption of Np95 gene renders murine embryonic stem cells hypersensitive to DNA damaging agents and DNA replication blocks. J Biol Chem 277:34549–34555. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205189200
Ge TT, Yang M, Chen Z, Lou G, Gu T (2016) UHRF1 gene silencing inhibits cell proliferation and promotes cell apoptosis in human cervical squamous cell carcinoma CaSki cells. J Ovarian Res 9:42. doi:10.1186/s13048-016-0253-8
Wang BC, Lin GH, Wang B, Yan M, He B, Zhang W, Yang AK, Long ZJ, Liu Q (2016) UHRF1 suppression promotes cell differentiation and reduces inflammatory reaction in anaplastic thyroid cancer. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.10674
Nakamura K, Baba Y, Kosumi K, Harada K, Shigaki H, Miyake K, Kiyozumi Y, Ohuchi M, Kurashige J, Ishimoto T, Iwatsuki M, Sakamoto Y, Yoshida N, Watanabe M, Nakao M, Baba H (2016) UHRF1 regulates global DNA hypomethylation and is associated with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.11067
Yang C, Wang Y, Zhang F, Sun G, Li C, Jing S, Liu Q, Cheng Y (2013) Inhibiting UHRF1 expression enhances radiosensitivity in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep 40:5225–5235. doi:10.1007/s11033-013-2559-6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare none conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Cheng, Y., Yin, X. et al. Globular adiponectin inhibits leptin-stimulated esophageal adenocarcinoma cell proliferation via adiponectin receptor 2-mediated suppression of UHRF1. Mol Cell Biochem 431, 103–112 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-2980-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-2980-6