Abstract
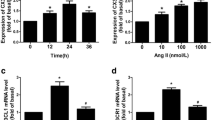
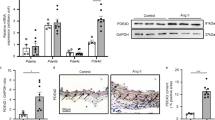
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 (ERK5), a recently discovered mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), plays a key role in the development and pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease. In order to clarify the pathophysiological significance of ERK5 in vascular remodeling, we investigated ERK5 phosphorylation in hypertrophy of human aortic smooth muscle cells (HASMCs) induced by angiotensin II (Ang II). The AT1 receptor was involved in Ang II-induced ERK5 activity. Hypertrophy was detected by the measurement of protein synthesis with [3H]-Leu incorporation in cultured HASMCs. Ang II rapidly induced phosphorylation of ERK5 at Thr218/Tyr220 residues in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Activation of myocyte enhancer factor-2C (MEF2C) by ERK5 was inhibited by PD98059. Transfecting HASMCs with small interfering RNA (siRNA) to silence ERK5 inhibited Ang II-induced cell hypertrophy. Thus, ERK5 phosphorylation contributes to MEF2C activation and subsequent HASMC hypertrophy induced by Ang II, for a novel molecular mechanism in cardiovascular diseases induced by Ang II.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe J, Kusuhara M, Ulevitch RJ et al (1996) Big mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (BMK1) is a redox-sensitive kinase. J Biol Chem 271:16586–16590. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.28.16586
Zhou G, Bao ZQ, Dixon JE (1995) Components of a new human protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem 270:12665–12669
Yan C, Luo H, Lee JD et al (2001) Molecular cloning of mouse ERK5/BMK1 splice variants and characterization of ERK5 functional domains. J Biol Chem 276:10870–10878. doi:10.1074/jbc.M009286200
Wang X, Merritt AJ, Seyfried J et al (2005) Targeted deletion of mek5 causes early embryonic death and defects in the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5/myocyte enhancer factor 2 cell survival pathway. Mol Cell Biol 25:336–345. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.1.336-345.2005
Regan CP, Li W, Boucher DM et al (2002) Erk5 null mice display multiple extraembryonic vascular and embryonic cardiovascular defects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:9248–9253. doi:10.1073/pnas.142293999
Sohn SJ, Sarvis BK, Cado D et al (2002) ERK5 MAPK regulates embryonic angiogenesis and acts as a hypoxia-sensitive repressor of vascular endothelial growth factor expression. J Biol Chem 277:43344–43351. doi:10.1074/jbc.M207573200
Yan L, Carr J, Ashby PR, Murry-Tait V et al (2003) Knockout of ERK5 causes multiple defects in placental and embryonic development. BMC Dev Biol 3:11. doi:10.1186/1471-213X-3-11
Wang X, Tournier C (2006) Regulation of cellular functions by the ERK5 signalling pathway. Cell Signal 18:753–760. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.11.003
Rovida E, Navari N, Caligiuri A et al (2008) ERK5 differentially regulates PDGF-induced proliferation and migration of hepatic stellate cells. J Hepatol 48:107–115. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2007.08.010
Sharma G, Goalstone ML (2007) Regulation of ERK5 by insulin and angiotensin-II in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 354:1078–1083. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.01.102
Mulloy R, Salinas S, Philips A et al (2003) Activation of cyclin D1 expression by the ERK5 cascade. Oncogene 22:5387–5398. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206839
Dong F, Gutkind JS, Larner AC (2001) Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor induces ERK5 activation, which is differentially regulated by protein-tyrosine kinases and protein kinase C. Regulation of cell proliferation and survival. J Biol Chem 276:10811–10816. doi:10.1074/jbc.M008748200
Kato Y, Tapping RI, Huang S et al (1998) Bmk1/Erk5 is required for cell proliferation induced by epidermal growth factor. Nature 395:713–716. doi:10.1038/27234
Dinev D, Jordan BW, Neufeld B et al (2001) Extracellular signal regulated kinase 5 (ERK5) is required for the differentiation of muscle cells. EMBO Rep 2:829–834. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kve177
Zhao M, Liu Y, Bao M et al (2002) Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation requires both p38 and BMK1 MAP kinases. Arch Biochem Biophys 400:199–207. doi:10.1016/S0003-9861(02)00028-0
Kato Y, Kravchenko VV, Tapping RI et al (1997) BMK1/ERK5 regulates serum-induced early gene expression through transcription factor MEF2C. EMBO J 16:7054–7066. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.23.7054
Diaz-Meco MT, Moscat J (2001) MEK5, a new target of the atypical protein kinase C isoforms in mitogenic signaling. Mol Cell Biol 21:1218–1227. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.4.1218-1227.2001
Dzau VJ, Lopez-Ilasaca M (2005) Searching for transcriptional regulators of Ang II-induced vascular pathology. J Clin Invest 115:2319–2322. doi:10.1172/JCI26384
Brasier AR, Jamaluddin M, Han Y et al (2000) Angiotensin II induces gene transcription through cell-type-dependent effects on the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) transcription factor. Mol Cell Biochem 212:155–169. doi:10.1023/A:1007133710837
Yoshida T, Hoofnagle MH, Owens GK (2004) Myocardin and Prx1 contribute to angiotensin II-induced expression of smooth muscle alpha-actin. Circ Res 94:1075–1082. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000125622.46280.95
Zhan Y, Brown C, Maynard E et al (2005) Ets-1 is a critical regulator of Ang II-mediated vascular inflammation and remodeling. J Clin Invest 115:2508–2516. doi:10.1172/JCI24403
Takahashi Y, Watanabe H, Murakami M et al (2007) Involvement of transient receptor potential canonical 1 (TRPC1) in angiotensin II-induced vascular smooth muscle cell hypertrophy. Atherosclerosis 195:287–296. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.12.033
Hou Y, Okamoto C, Okada K et al (2007) c-Myc is essential for urokinase plasminogen activator expression on hypoxia-induced vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res 75:186–194. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2007.02.033
Wong C, Jin ZG (2005) Protein kinase C-dependent protein kinase D activation modulates ERK signal pathway and endothelial cell proliferation by vascular endothelial growth factor. J Biol Chem 280:33262–33269. doi:10.1074/jbc.M503198200
Touyz RM, Berry C (2002) Recent advances in angiotensin II signaling. Braz J Med Biol Res 35:1001–1015. doi:10.1590/S0100-879X2002000900001
Yoon SC, Ahn YM, Jun SJ et al (2005) Region-specific phosphorylation of ERK5-MEF2C in the rat frontal cortex and hippocampus after electroconvulsive shock. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 29:749–753. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2005.04.006
Shishido T, Woo CH, Ding B et al (2008) Effects of MEK5/ERK5 association on small ubiquitin-related modification of ERK5: implications for diabetic ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. Circ Res 102:1416–1425. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.168138
Chang L, Karin M (2001) Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 410:37–40. doi:10.1038/35065000
Hayashi M, Kim SW, Imanaka-Yoshida K et al (2004) Targeted deletion of BMK1/ERK5 in adult mice perturbs vascular integrity and leads to endothelial failure. J Clin Invest 113:1138–1148
Cavanaugh JE, Ham J, Hetman M et al (2001) Differential regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK1/2 and ERK5 by neurotrophins, neuronal activity, and cAMP in neurons. J Neurosci 21:434–443
Fujii Y, Matsuda S, Takayama G et al (2008) ERK5 is involved in TCR-induced apoptosis through the modification of Nur77. Genes Cells 13:411–419. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2443.2008.01177.x
Sharma G, Goalstone ML (2005) Dominant negative FTase (DNFTalpha) inhibits ERK5, MEF2C and CREB activation in adipogenesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 245:93–104. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2005.10.027
Ushio-Fukai M, Zuo L, Ikeda S et al (2005) CAbl tyrosine kinase mediates reactive oxygen species- and caveolin-dependent AT1 receptor signaling in vascular smooth muscle: role in vascular hypertrophy. Circ Res 97:829–836. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000185322.46009.F5
Han J, Jiang Y, Li Z et al (1997) Activation of the transcription factor MEF2C by the MAP kinase p38 in inflammation. Nature 386:296–299. doi:10.1038/386296a0
Morimoto H, Kondoh K, Nishimoto S et al (2007) Activation of a C-terminal transcriptional activation domain of ERK5 by autophosphorylation. J Biol Chem 282:35449–35456. doi:10.1074/jbc.M704079200
Mody N, Leitch J, Armstrong C et al (2001) Effects of MAP kinase cascade inhibitors on the MKK5/ERK5 pathway. FEBS Lett 502:21–24. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02651-5
Nishimoto S, Nishida E (2006) MAPK signalling: ERK5 versus ERK1/2. EMBO Rep 7:782–786. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400755
Benedetto BD, Hitz C, Hölter SM et al (2007) Differential mRNA distribution of components of the ERK/MAPK signalling cascade in the adult mouse brain. J Comp Neurol 500:542–556. doi:10.1002/cne.21186
Chen HI, Hsieh NK, Chang HR et al (2008) Arterial haemodynamics on ventricular hypertrophy in rats with simulated aortic stiffness. Pflugers Arch 455:595–606. doi:10.1007/s00424-007-0320-5
Daugherty A, Cassis L (2004) Angiotensin II-mediated development of vascular diseases. Trends Cardiovasc Med 14:117–120. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2004.01.002
Takahashi N, Saito Y, Kuwahara K et al (2005) Hypertrophic responses to cardiotrophin-1 are not mediated by STAT3, but via a MEK5-ERK5 pathway in cultured cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 38:185–192. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2004.10.016
Shin SY, Yang JM, Choo SM et al (2008) System-level investigation into the regulatory mechanism of the calcineurin/NFAT signaling pathway. Cell Signal 20:1117–1124. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.01.023
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the technical assistance from Dr. Jinbo Feng, and Dr. Guanghui Liu in histopathological and molecular biological analysis. This study was supported by the National 973 Basic Research Program of China (No.2007CB512003) and Natural Fund of Shandong Province (Y2007C012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhuo Zhao and Jing Geng contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Z., Geng, J., Ge, Z. et al. Activation of ERK5 in angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy of human aortic smooth muscle cells. Mol Cell Biochem 322, 171–178 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-9954-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-9954-7