Abstract
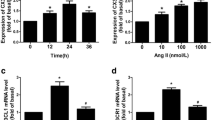
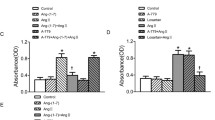
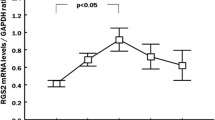
To investigate the effect of the angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) on AT1R expression, ERK1/2 and STAT3 protein phosphorylation in rat vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) was studied. VSMCs were transfected with a lentiviral vector including the ACE2 gene and with siRNA to regulate the level of ACE2 in VSMCs. The levels of mRNA and proteins of ACE2, AT1R, ERK1/2, p-ERK1/2, STAT3, and p-STAT3 in VSMCs were examined using real-time PCR and western blot. The proliferation of VSMCs was observed by CCK-8 assay and BrdU measurement. Upregulation of ACE2 inhibited the growth of cells elicited by angiotensin II (Ang II). ACE2 significantly suppressed the level of the AT1 receptor (AT1R) protein induced by Ang II and phosphorylated the ERK1/2 and STAT3 proteins in the downstream signaling pathway. The transcriptional and translational levels of ACE2 were significantly lower in the si-ACE2 group than in the control group. The level of AT1R mRNA and protein, both with the phosphorylation expression of ERK1/2 and STAT3 protein in the si-ACE2 group and the Ang II group, were significantly enhanced than those in the control group. ACE2 significantly inhibited the growth of VSMCs. ACE2 inhibited the proliferation of VSMCs by suppressing AT1R and the downstream ERK1/2 and STAT3 signaling axes. Also, Ang II enhanced the level of AT1R and phosphorylated ERK1/2 and STAT3 by inhibiting the level of the ACE2 mRNA and protein.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agata J, Ura N, Yoshida H, et al. 2006 Olmesartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker with an inhibitory effect on angiotensin-converting enzyme. Hypertens. Res. 29 865–874
Alie N, Eldib M, Fayad ZA, et al. 2014 Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease: PET/CT for the evaluation of atherosclerosis and inflammation. Clin. Med. Insights Cardiol. 8 13–21
Bodiga S, Zhong JC, Wang W, et al. 2011 Enhanced susceptibility to biomechanical stress in ACE2 null mice is prevented by loss of the p47(phox) NADPH oxidase subunit. Cardiovasc. Res. 91 151–161
Crackower MA, Sarao R, Oudit GY, et al. 2002 Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is an essential regulator of heart function. Nature 417 822–828
Danilczyk U and Penninger JM 2006 Angiotensin-converting enzyme II in the heart and the kidney. Circ. Res. 98 463–471
Donoghue M, Hsieh F, Baronas E, et al. 2000 A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1–9. Circ. Res. 87 E1–E9
Donoghue M, Wakimoto H, Maguire CT, et al. 2003 Heart block, ventricular tachycardia, and sudden death in ACE2 transgenic mice with downregulated connexins. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 35 1043–1053
Fagyas M, Úri K, Siket IM, et al. 2014 New perspectives in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) II: albumin suppresses angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) activity in human. PLoS One 9 e87844
Gallagher PE, Chappell MC, Ferrario CM, et al. 2006 Distinct roles for ANG II and ANG-(1–7) in the regulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in rat astrocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 290 C420–C426
Gallagher PE, Ferrario CM and Tallant EA 2008 MAP kinase/phosphatase pathway mediates the regulation of ACE2 by angiotensin peptides. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 295 C1169–C1174
Gurley SB, Allred A, Le TH, et al. 2006 Altered blood pressure responses and normal cardiac phenotype in ACE2-null mice. J. Clin. Invest. 116 2218–2225
Huentelman MJ, Grobe JL, Vazquez J, et al. 2005 Protection from angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis by systemic lentiviral delivery of ACE2 in rats. Exp. Physiol. 90 783–790
Husarek KE, Zhang X, McCallinhart PE, et al. 2016 Isolation of murine coronary vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Vis. Exp. 111 53983
Imai Y, Kuba K, Rao S, et al. 2005 Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure. Nature 436 112–116
Iwata M, Cowling I, Gurantz D, et al. 2005 Angiotensin-(1-7) binds to specific receptors on cardiac fibroblasts to initiate antifibrotic and antitrophic effects. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 289 H2356–H2363
Jarajapu YPR 2021 Targeting angiotensin-converting enzyme-2/angiotensin-(1–7)/Mas receptor axis in the vascular progenitor cells for cardiovascular diseases. Mol. Pharmacol. 99 29–38
Kostenis E, Milligan G, Christopoulos A, et al. 2005 G-protein-coupled receptor Mas is a physiological antagonist of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Circulation 111 1806–1813
Kuba K, Imai Y, Ohto-Nakanishi T, et al. 2010 Trilogy of ACE2: a peptidase in the renin-angiotensin system, a SARS receptor, and a partner for amino acid transporters. Pharmacol. Ther. 128 119–128
Kuba K, Imai Y, Rao S, et al. 2005 A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury. Nat. Med. 11 875–879
Liu J, Chen Q, Liu S, et al. 2018 Sini decoction alleviates E. coli induced acute lung injury in mice via equilibrating ACE-Ang II-AT1R and ACE2-Ang-(1–7)-Mas axis. Life Sci. 208 139–148
Neyrinck AP and Matthay MA 2009 The role of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in endotoxin-induced lung injury in rats. Crit. Care Med. 37 776–777
Ocaranza MP, Michea L, Chiong M, et al. 2014 Recent insights and therapeutic perspectives of angiotensin-(1–9) in the cardiovascular system. Clin. Sci. 127 549–557
Oz M and Lorke DE 2021 Multifunctional angiotensin converting enzyme 2, the SARS-CoV-2 entry receptor, and critical appraisal of its role in acute lung injury. Biomed. Pharmacother. 136 111193
Patel VB, Zhong JC, Grant MB, et al. 2016 Role of the ACE2/Angiotensin 1–7 axis of the renin-angiotensin system in heart failure. Circ. Res. 118 1313–1326
Sampaio WO, Souza dos Santos RA, Faria-Silva R, et al. 2007 Angiotensin-(1–7) through receptor Mas mediates endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation via Akt-dependent pathways. Hypertension 49 185–192
Santos RAS, Oudit GY, Verano-Braga T, et al. 2019 The renin-angiotensin system: going beyond the classical paradigms. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 316 H958–H970
Su Z, Zimpelmann J and Burns KD 2006 Angiotensin-(1–7) inhibits angiotensin II-stimulated phosphorylation of MAP kinases in proximal tubular cells. Kidney Int. 69 2212–2218
Tesanovic S, Vinh A, Gaspari TA, et al. 2010 Vasoprotective and atheroprotective effects of angiotensin (1–7) in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 30 1606–1613
Tipnis SR, Hooper NM, Hyde R, et al. 2000 A human homolog of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 275 33238–33243
Wösten-van Asperen RM, Lutter R, Specht PA, et al. 2011 Acute respiratory distress syndrome leads to reduced ratio of ACE/ACE2 activities and is prevented by angiotensin-(1–7) or an angiotensin II receptor antagonist. J. Pathol. 225 618–627
Xu P, Sriramula S and Lazartigues E 2011 ACE2/ANG-(1–7)/Mas pathway in the brain: the axis of good. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 300 R804–R817
Zhang C, Zhao YX, Zhang YH, et al. 2010 Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 attenuates atherosclerotic lesions by targeting vascular cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107 15886–15891
Zhou L, Xue H, Wang Z, et al. 2012 Angiotensin-(1–7) attenuates high glucose-induced proximal tubular epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via inhibiting ERK1/2 and p38 phosphorylation. Life Sci. 90 454–462
Zhuang MW, Cheng Y, Zhang J, et al. 2020 Increasing host cellular receptor-angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 expression by coronavirus may facilitate 2019-nCoV (or SARS-CoV-2) infection. J. Med. Virol. 92 2693–2701
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank all hospital staff for participating in and supporting this study.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Scientific Research Project of the Joint Funds for the Innovation of Science and Technology, Fujian Province (no. 2021Y9132), Professor Academic Development Fund of Fujian Medical University in China (no. JS14023), and Startup Fund for Scientific Research of Fujian Medical University (no. 2021QH1057).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Satyajit Rath
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, J., Lu, Z., Li, R. et al. ACE2 inhibits proliferation of smooth muscle cell through AT1R and its downstream signaling pathway. J Biosci 48, 25 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-023-00339-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-023-00339-1