Abstract
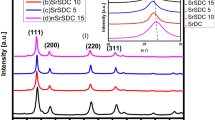
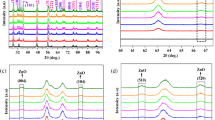
Research on fuel cell components has received great attention owing to the growing need for sustainable energy sources. Bismuth (Bi3+) codoped samarium-doped cerium oxide [Ce1−xSmx−yBiyO2−δ (x = 0.2 and y = 0, 0.05 and 0.1)] nanosystems were prepared by solid-state reaction method. Rietveld structure refinement of X-ray diffraction pattern confirms the cubic fluorite structure along the (111) plane with the decrease in lattice distortion. At the same sintering temperature, pellets exhibit good morphology with better mechanical strength. The conductivity measurements carried out using the Nyquist plot, as well as the modulus spectra, indicate the effect of grain and grain boundary conduction at high temperatures. With the increase in the incorporation of Bi dopant, there is a gradual decrease in ionic conductivity and activation energy. The composition of Ce0.8Sm0.1Bi0.1O2−δ exhibits less ionic conductivity compared to other samples due to the oxygen vacancies attracted by dopant cations. The effect of Bi3+ dopants on samarium-doped ceria lattice structures and the electrical properties of the systems have been discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.C.H. Steel, A. Henizel, Nature 414, 345 (2001)
E.D. Wachsman, K.T. Lee, Science 334, 935 (2011)
S. Omar, E.D. Wachsman, J.L. Jones, J.C. Nino, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 2674 (2009)
L. Blum, Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2, 1 (2005)
J.Y. Park, H. Yoon, E.D. Wachsman, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 88, 2402 (2005)
L.D. Jadhav, S.H. Pawar, M.G. Chourashiya, Bull. Mater. Sci. 30, 97 (2007)
N.M. Sammes, G.A. Tompsett, H. NaÈfea, F. Aldingera, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 19, 1801 (1999)
T. Takahashi, Y. IwaharaHagia, J. ppl. Electrochem. 2, 97 (1972)
H. Kruidhof, Solid State Ionics 50, 181 (1992)
H. Shuk, Solid State Ionics 89, 179 (1996)
N. Jiang, E.D. Wachsman, S. Jung, Solid State Ionics 150, 347 (2002)
M. Biesuz, L. Spiridigliozzi, M. Frasnelli, G. Dell’Agli, M. Vincenzo, Mater. Lett. 190, 17 (2017)
T. Karaca, T. Gürkaynak, M. Altınçekiç, F. Öksüzömer, Ceram. Int. 36, 1101 (2010)
M. Prekajski, M. Stojmenvic, A. Radojkovic, G. Brankovic, H. Oraon, R. Subasri, B. Matovic, J. Alloys Compd. 617, 563 (2014)
G. Accardo, D. Frattini, H.C. Ham, J.H. Han, S.P. Yoon, Ceram. Int. 11, 165 (2017)
W. Zhao, S. An, L. Ma, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 1496 (2011)
R. Punn, A.M. Feteira, D.C. Sinclair, C. Greaves, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 128, 15386 (2006)
T.S. Zhang, J. Ma, H. Cheng, S.H. Chan, Mater. Res. Bullet. 41, 563 (2006)
S. Boskovic, S. Zec, J. Dukic, D. Bucevac, B. Matovic, NANO 33, 43 (2011)
D. Ivanova, A. Kovalevsk, V.V. Kharton, F.M.B. Marques, Bol. Soc. esp. Ceram. V. 47, 201 (2008)
L.C. Yan, J. Hassan, World Appl. Sci. J. 14, 1091 (2011)
A.I.Y. Tok, F.Y.C. Boey, Z. Dong, X.L. Sun, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 190, 217 (2007)
P. Muralitharan, S.H. Jo, D.K. Kim, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 3267 (2008)
V. Thampi, P.R. Padalaand, A.N. Radhakrishnan, New J. Chem. 39, 1469 (2015)
L.B. McCusker, R.B. Von Dreele, D.E. Cox, D. Louer, P. Scardi, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 32, 36 (1999)
J. Kimpton, T.H. Randle, J. Drennan, Solid State Ionics. 149, 89 (2002)
M.J.D. Rushton, A. Chroneos, Sci Rep. 4, 6068 (2014)
J.A. Kilner, Solid State Ionics 129, 13 (2000)
S. Ramesh, V.P. Kumar, P. Kistaiah, C.V. Reddy, Solid State Ionics 181, 86 (2010)
C. Kjølseth, H. Fjeld, Ø. Prytz, P. Inge, C. Estournès, R. Haugsrud, T. Norby, Solid State Ionics 181, 268 (2010)
K.T. Lee, A.A. Lidie, S.Y. Jeon, G.T. Hitz, S.J. Song, E.D. Wachsman, J. Mater. Chem. A. 1, 6199 (2013)
N.M. Sammes, G.A. Tompsett, H. Näfe, F. Aldinger, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 19, 1801 (1999)
E.D. Wachsman, S. Boyapati, M.J. Kaufman, N. Jiang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 83, 1964 (2004)
Acknowledgements
Sandhya K and Chitra Priya N S would like to express sincere thanks to the University of Kerala for their financial support in the form of fellowships. Revathy J S wishes to thank the Department of Science and Technology (DST), INSPIRE fellowship, Govt. of India, for financial assistance [Grant No. IF160231]. The authors thank NIIST Trivandrum, STIC Cochin, and Dept. of Chemistry, Govt. College for Women, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, for the provision of characterization facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sandhya, K., Chitra Priya, N.S., Revathy, J.S. et al. Tailoring the activation energy and the ionic properties of bismuth codoped SDC powder prepared by solid-state reaction method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 12182–12190 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05846-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05846-1