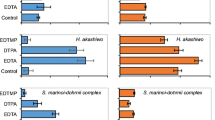
Abstract
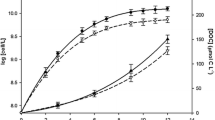
The major fractions of dissolved iron in seawater exist as a complex with organic ligands. A high bioavailability of iron bound to humic acid (HA) compared to the other model ligands, such as desferrioxamine B or ferrichrome, has been reported, which implies the importance of HA to control the geochemical behavior and the transfer of Fe to marine phytoplankton, particularly in estuarine and coastal waters. In the current work, the effect of different HA fractions (>100, 100–30, 30–10, 10–5, and 5–3 kDa), which were extracted from lignite, on the comparative solubility of iron in seawater and the corresponding influence on iron uptake and growth rate of the phytoplankton Prymnesium parvum (Haptophyta) was studied using laboratory cultures. The lower-molecular-weight (MW) HA fractions, such as 30–10, 10–5, and 5–3 kDa, remained soluble in the simulated seawater medium for a longer time span compared to the higher MW fractions. The lower MW fractions facilitated higher iron solubility and assisted in achieving a better phytoplankton growth rate. However, a reciprocal impact on phytoplankton growth rates was observed when the HA concentration increased to a higher range (0.18 to 18 mg-C L−1). The highest intracellular Fe uptake in phytoplankton occurred with 30–10 kDa HA in seawater, and the extracellular dissolved Fe concentrations were higher for smaller-sized HA fractions. In summary, our study showed that the controlled addition of lower MW fractions of HA (up to 30–10 kDa) in estuarine waters could ensure the accelerated uptake of Fe in phytoplankton as well as a better growth rate.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abualhaija MM, Whitby H, van den Berg CMG (2015) Competition between copper and iron for humic ligands in estuarine waters. Mar Chem 172:46–56
Adani F, Genevini P, Zaccheo P, Zocchi G (1998) The effect of commercial humic acid on tomato plant growth and mineral nutrition. J Plant Nutr 21:561–575
Aiken GR (1985) Isolation and concentration techniques for aquatic humic substances. In: Aiken GR, McKnight DM, Wershaw RL, MacCarthy P (eds) Humic substances in soil, sediment and water: geochemistry and isolation. Wiley-Interscience, NY, pp. 363–385
Allen AE, LaRoche J, Maheswari U, Lommer M, Schauer N, Lopez PJ, Finazzi G, Fernie AR, Bowler C (2008) Whole-cell response of the pennate diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum to iron starvation. P Natl Acad Sci USA 105:10438–10443
Anderson MA, Morel FM (1982) The influence of aqueous iron chemistry on the uptake of iron by the coastal diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii. Limnol Oceanogr 27:789–813
Avena MJ, Wilkinson KJ (2002) Disaggregation kinetics of a peat humic acid: mechanism and pH effects. Environ Sci Technol 36:5100–5105
Batchelli S, Muller FLL, Chang K-C, Lee C-L (2010) Evidence for strong but dynamic iron–humic colloidal associations in humic-rich coastal waters. Environ Sci Technol 44:8485–8490
Begum ZA, Rahman IMM, Sawai H, Tate Y, Maki T, Hasegawa H (2012) Stability constants of Fe(III) and Cr(III) complexes with dl-2-(2-carboxymethyl)nitrilotriacetic acid (GLDA) and 3-hydroxy-2,2'-iminodisuccinic acid (HIDS) in aqueous solution. J Chem Eng Data 57:2723–2732
Begum ZA, Rahman IMM, Hasegawa H (2013) Management of EDTA-containing aqueous effluent: environmental concerns and remedies. In: Molnar A (ed) EDTA: synthesis, uses and environmental concerns. Nova Science Publishers, Hauppauge, NY, pp. 163–177
Boyd PW, Arrigo KR, Strzepek R, van Dijken GL (2012) Mapping phytoplankton iron utilization: insights into Southern Ocean supply mechanisms. J Geophys Res-Oceans 117:C06009
Boye M, van den Berg CMG (2000) Iron availability and the release of iron-complexing ligands by Emiliania huxleyi. Mar Chem 70:277–287
Boye M, van den Berg CMG, de Jong JTM, Leach H, Croot P, de Baar HJW (2001) Organic complexation of iron in the Southern Ocean. Deep-Sea Res I 48:1477–1497
Brand LE (1991) Minimum iron requirements of marine-phytoplankton and the implications for the biogeochemical control of new production. Limnol Oceanogr 36:1756–1771
Brand LE, Sunda WG, Guillard RRL (1983) Limitation of marine phytoplankton reproductive rates by zinc, manganese, and iron. Limnol Oceanogr 28:1182–1198
Brigante M, Zanini G, Avena M (2009) Effect of pH, anions and cations on the dissolution kinetics of humic acid particles. Colloid Surface A 347:180–186
Bruland KW, Rue EL (2001) Analytical methods for the determination of concentrations and speciation of iron. In: Turner DR, Hunter KA (eds) The biogeochemistry of iron in seawater. IUPAC series on analytical and physical chemistry of environmental systems, vol 7. Wiley, Chichester, England, pp. 255–289
Bundy RM, Abdulla HAN, Hatcher PG, Biller DV, Buck KN, Barbeau KA (2015) Iron-binding ligands and humic substances in the San Francisco Bay estuary and estuarine-influenced shelf regions of coastal California. Mar Chem 173:183–194
Carlsson P, Granéli E (1993) Availability of humic bound nitrogen for coastal phytoplankton. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 36:433–447
Carlsson P, Granéli E, Tester P, Boni L (1995) Influences of riverine humic substances on bacteria, protozoa, phytoplankton, and copepods in a coastal plankton community. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 127:213–221
Carvalho WF, Granéli E (2010) Contribution of phagotrophy versus autotrophy to Prymnesium parvum growth under nitrogen and phosphorus sufficiency and deficiency. Harmful Algae 9:105–115
Chassapis K, Roulia M, Tsirigoti D (2009) Chemistry of metal–humic complexes contained in Megalopolis lignite and potential application in modern organomineral fertilization. Int J Coal Geol 78:288–295
Chen M, Wang WX (2008) Accelerated uptake by phytoplankton of iron bound to humic acids. Aquat Biol 3:155–166
Chen J, Gu B, LeBoeuf EJ, Pan H, Dai S (2002) Spectroscopic characterization of the structural and functional properties of natural organic matter fractions. Chemosphere 48:59–68
Chen J, LeBoeuf EJ, Dai S, Gu B (2003) Fluorescence spectroscopic studies of natural organic matter fractions. Chemosphere 50:639–647
Christl I, Metzger A, Heidmann I, Kretzschmar R (2005) Effect of humic and fulvic acid concentrations and ionic strength on copper and lead binding. Environ Sci Technol 39:5319–5326
Conte P, Spaccini R, Piccolo A (2006) Advanced CPMAS-13C NMR techniques for molecular characterization of size-separated fractions from a soil humic acid. Anal Bioanal Chem 386:382–390
Conte P, Spaccini R, Smejkalova D, Nebbioso A, Piccolo A (2007) Spectroscopic and conformational properties of size-fractions acid separated from a lignite humic acid. Chemosphere 69:1032–1039
Croot PL, Heller MI (2012) The importance of kinetics and redox in the biogeochemical cycling of iron in the surface ocean. Front Microbiol 3:219
Edvardsen B, Imai I (2006) The ecology of harmful flagellates within Prymnesiophyceae and Raphidophyceae. In: Granéli E, Turner JT (eds) Ecology of harmful algae. Springer, Berlin, pp. 67–79
Engebretson RR, Von Wandruszka R (1997) The effect of molecular size on humic acid associations. Org Geochem 26:759–767
Engebretson RR, von Wandruszka R (1998) Kinetic aspects of cation-enhanced aggregation in aqueous humic acids. Environ Sci Technol 32:488–493
Fang K, Yuan D, Zhang L, Feng L, Chen Y, Wang Y (2015) Effect of environmental factors on the complexation of iron and humic acid. J Environ Sci 27:188–196
Fistarol GO, Legrand C, Granéli E (2003) Allelopathic effect of Prymnesium parvum on a natural plankton community. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 255:115–125
Flegal AR, Smith GJ, Gill GA, Sanudowilhelmy S, Anderson LCD (1991) Dissolved trace-element cycles in the San-Francisco Bay estuary. Mar Chem 36:329–363
Fujii M, Rose AL, Waite TD, Omura T (2010) Oxygen and superoxide-mediated redox kinetics of iron complexed by humic substances in coastal seawater. Environ Sci Technol 44:9337–9342
Ghosh K, Schnitzer M (1980) Macromolecular structures of humic substances. Soil Sci 129:266–276
Gledhill M, Buck KN (2012) The organic complexation of iron in the marine environment: a review. Front Microbiol 3:69
Glover HE (1978) Iron in Maine coastal waters; seasonal variation and its apparent correlation with a dinoflagellate bloom. Limnol Oceanogr 23:534–537
Goldberg MC, Weiner ER (1994) Fluorescence measurements of the volume, shape, and fluorophore composition of fulvic acid from the Suwannee River. In: Averett RC, Leenheer JA, Mcknight DM, Thorn KA (eds) Humic substances in the Suwannee River, Georgia: interactions, properties, and proposed structures (United States Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper 2373). U.S. Geological Survey, Denver, CO, pp. 99–113
Granéli E, Olsson P, Sundström B, Edler L (1989) In situ studies of the effects of humic acids on dinoflagellates and diatoms. In: Okaichi T, Anderson DM, Nemoto T (eds) Red tides: biology, environmental science, and toxicology. Elsevier, NY, pp. 209–212
Hassler CS, Schoemann V, Nichols CM, Butler ECV, Boyd PW (2011) Saccharides enhance iron bioavailability to Southern Ocean phytoplankton. P Natl Acad Sci USA 108:1076–1081
Heller MI, Gaiero DM, Croot PL (2013) Basin scale survey of marine humic fluorescence in the Atlantic: relationship to iron solubility and H2O2. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 27:88–100
Hudson RJM, Morel FMM (1989) Distinguishing between extra- and intracellular iron in marine phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 34:1113–1120
Hudson RJM, Morel FMM (1990) Iron transport in marine-phytoplankton - kinetics of cellular and medium coordination reactions. Limnol Oceanogr 35:1002–1020
Hutchins DA, Witter AE, Butler A, Luther GW (1999) Competition among marine phytoplankton for different chelated iron species. Nature 400:858–861
Iwade S, Kuma K, Isoda Y, Yoshida M, Kudo I, Nishioka J, Suzuki K (2006) Effect of high iron concentrations on iron uptake and growth of a coastal diatom Chaetoceros sociale. Aquat Microb Ecol 43:177–191
Jaffé R, Cawley KM, Yamashita Y (2014) Applications of excitation emission matrix fluorescence with parallel factor analysis (EEM-PARAFAC) in assessing environmental dynamics of natural dissolved organic matter (DOM) in aquatic environments: a review. In: Rosario-Ortiz F (ed) Advances in the physicochemical characterization of dissolved organic matter: impact on natural and engineered systems. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp. 27–73
James SV, Valenti TW, Prosser KN, Grover JP, Roelke DL, Brooks BW (2011) Sunlight amelioration of Prymnesium parvum acute toxicity to fish. J Plankton Res 33:265–272
Johnson KS, Gordon RM, Coale KH (1997) What controls dissolved iron concentrations in the world ocean? Mar Chem 57:137–161
Kalinichev AG, Kirkpatrick RJ (2007) Molecular dynamics simulation of cationic complexation with natural organic matter. Eur J Soil Sci 58:909–917
Kipton H, Powell J, Town RM (1992) Solubility and fractionation of humic acid; effect of pH and ionic medium. Anal Chim Acta 267:47–54
Kosakowska A, Nędzi M, Pempkowiak J (2007) Responses of the toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa to iron and humic substances. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:365–370
Krachler R, Krachler RF, von der Kammer F, Süphandag A, Jirsa F, Ayromlou S, Hofmann T, Keppler BK (2010) Relevance of peat-draining rivers for the riverine input of dissolved iron into the ocean. Sci Total Environ 408:2402–2408
Krachler R, Krachler RF, Wallner G, Hann S, Laux M, Cervantes Recalde MF, Jirsa F, Neubauer E, von der Kammer F, Hofmann T, Keppler BK (2015) River-derived humic substances as iron chelators in seawater. Mar Chem 174:85–93
Kuma K, Tanaka J, Matsunaga K (1999) Effect of natural and synthetic organic-Fe(III) complexes in an estuarine mixing model on iron uptake and growth of a coastal marine diatom, Chaetoceros sociale. Mar Biol 134:761–769
Kuma K, Isoda Y, Nakabayashi S (2003) Control on dissolved iron concentrations in deep waters in the western North Pacific: iron(III) hydroxide solubility. J Geophys Res 108:3289
Kustka AB, Allen AE, Morel FMM (2007) Sequence analysis and transcriptional regulation of iron acquisition genes in two marine diatoms. J Phycol 43:715–729
Laglera LM, Battaglia G, van den Berg CMG (2011) Effect of humic substances on the iron speciation in natural waters by CLE/CSV. Mar Chem 127:134–143
Lis H, Shaked Y, Kranzler C, Keren N, Morel FMM (2015) Iron bioavailability to phytoplankton: an empirical approach. ISME J 9:1003–1013
Liu X, Millero FJ (2002) The solubility of iron in seawater. Mar Chem 77:43–54
Lyman J, Fleming R (1940) Composition of sea water. J Mar Res 3:134–146
Mackey DJ, Zirino A (1994) Comments on trace metal speciation in seawater or do “onions” grow in the sea? Anal Chim Acta 284:635–647
Maldonado MT, Price NM (2001) Reduction and transport of organically bound iron by Thalassiosira oceanica (Bacillariophyceae). J Phycol 37:298–309
Marchetti A, Sherry ND, Kiyosawa H, Tsuda A, Harrison PJ (2006) Phytoplankton processes during a mesoscale iron enrichment in the NE subarctic Pacific: part I—biomass and assemblage. Deep-Sea Res II 53:2095–2113
Martin JH, Fitzwater SE (1988) Iron deficiency limits phytoplankton growth in the north-east Pacific subarctic. Nature 331:341–343
Miano TM, Senesi N (1992) Synchronous excitation fluorescence spectroscopy applied to soil humic substances chemistry. Sci Total Environ 117–118:41–51
Milne CJ, Kinniburgh DG, Tipping E (2001) Generic NICA-Donnan model parameters for proton binding by humic substances. Environ Sci Technol 35:2049–2059
Morel FMM, Rueter JG, Anderson DM, Guillard RRL (1979) Aquil: a chemically defined phytoplankton culture medium for trace metal studies. J Phycol 15:135–141
Morel FMM, Kustka AB, Shaked Y (2008) The role of unchelated Fe in the iron nutrition of phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 53:400–404
Naito K, Matsui M, Imai I (2005) Ability of marine eukaryotic red tide microalgae to utilize insoluble iron. Harmful Algae 4:1021–1032
Naito K, Imai I, Nakahara H (2008) Complexation of iron by microbial siderophores and effects of iron chelates on the growth of marine microalgae causing red tides. Phycol Res 56:58–67
Pandey AK, Pandey SD, Misra V (2000) Stability constants of metal-humic acid complexes and its role in environmental detoxification. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 47:195–200
Perminova IV, Frimmel FH, Kudryavtsev AV, Kulikova NA, Abbt-Braun G, Hesse S, Petrosyan VS (2003) Molecular weight characteristics of humic substances from different environments as determined by size exclusion chromatography and their statistical evaluation. Environ Sci Technol 37:2477–2485
Peuravuori J, Žbánková P, Pihlaja K (2006) Aspects of structural features in lignite and lignite humic acids. Fuel Process Technol 87:829–839
Piccolo A (2001) The supramolecular structure of humic substances. Soil Sci 166:810–832
Piccolo A (2002) The supramolecular structure of humic substances: a novel understanding of humus chemistry and implications in soil science. In: Sparks DL (ed) Advances in agronomy, vol 75. Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 57–134
Piccolo A, Pietramellara G, Mbagwu JSC (1997) Use of humic substances as soil conditioners to increase aggregate stability. Geoderma 75:267–277
Pullin MJ, Cabaniss SE (1995) Rank analysis of the pH-dependent synchronous fluorescence spectra of six standard humic substances. Environ Sci Technol 29:1460–1467
Ricca G, Severini F (1993) Structural investigations of humic substances by IR-FT, 13C-NMR spectroscopy and comparison with a maleic oligomer of known structure. Geoderma 58:233–244
Robertson AP, Leckie JO (1999) Acid/base, copper binding, and Cu2+/H+ exchange properties of a soil humic acid, an experimental and modeling study. Environ Sci Technol 33:786–795
Rose AL, Waite TD (2003) Kinetics of iron complexation by dissolved natural organic matter in coastal waters. Mar Chem 84:85–103
Rue EL, Bruland KW (1997) The role of organic complexation on ambient iron chemistry in the equatorial Pacific Ocean and the response of a mesoscale iron addition experiment. Limnol Oceanogr 42:901–910
Salmon TP, Rose AL, Neilan BA, Waite TD (2006) The FeL model of iron acquisition: nondissociative reduction of ferric complexes in the marine environment. Limnol Oceanogr 51:1744–1754
Schlosser C, Croot PL (2008) Application of cross-flow filtration for determining the solubility of iron species in open ocean seawater. Limnol Oceanogr Meth 6:630–642
Schlosser C, Croot PL (2009) Controls on seawater Fe(III) solubility in the Mauritanian upwelling zone. Geophys Res Lett 36:L18606
Schlosser C, De La Rocha CL, Croot PL (2011) Effects of iron surface adsorption and sample handling on iron solubility measurements. Mar Chem 127:48–55
Schlosser C, De La Rocha CL, Streu P, Croot PL (2012) Solubility of iron in the Southern Ocean. Limnol Oceanogr 57:684–697
Senesi N, Miano TM, Provenzano MR, Brunetti G (1989) Spectroscopic and compositional comparative characterization of I.H.S.S. reference and standard fulvic and humic acids of various origin. Sci Total Environ 81–82:143–156
Senesi N, Miano TM, Provenzano MR, Brunetti G (1991) Characterization, differentiation, and classification of humic substances by fluorescence spectroscopy. Soil Sci 152:259–271
Shaked Y, Lis H (2012) Disassembling iron availability to phytoplankton. Front Microbiol 3:123
Shaked Y, Kustka AB, Morel FMM (2005) A general kinetic model for iron acquisition by eukaryotic phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 50:872–882
Sholkovitz ER, Boyle EA, Price NB (1978) The removal of dissolved humic acids and iron during estuarine mixing. Earth Planet Sci Lett 40:130–136
Stevenson FJ (1994) Humus chemistry: genesis, composition, reactions. Wiley, NY
Stevenson FJ, Goh KM (1971) Infrared spectra of humic acids and related substances. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 35:471–483
Strzepek RF, Harrison PJ (2004) Photosynthetic architecture differs in coastal and oceanic diatoms. Nature 431:689–692
Sunda WG, Huntsman SA (1995) Iron uptake and growth limitation in oceanic and coastal phytoplankton. Mar Chem 50:189–206
Sutton R, Sposito G (2005) Molecular structure in soil humic substances: the new view. Environ Sci Technol 39:9009–9015
Suzuki Y, Yamaguchi Y, Suzuki S, Hirata S, Aihara M, Hiraki K (2002) Characteristics of aquatic humic substances in natural waters by synchronous and derivative synchronous fluorescence spectrum. Anal Sci 17(Suppl):i1605–i1608
Tehranifar A, Ameri A (2012) Effect of humic acid on nutrient uptake and physiological characteristic Fragaria ananassa var: Camarosa. J Biol Environ Sci 6:77–79
Terzulli A, Kosman DJ (2010) Analysis of the high-affinity iron uptake system at the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii plasma membrane. Eukaryot Cell 9:815–826
Thurman EM, Malcolm RL (1981) Preparative isolation of aquatic humic substances. Environ Sci Technol 15:463–466
Thurman EM, Wershaw RL, Malcolm RL, Pinckney DJ (1982) Molecular size of aquatic humic substances. Org Geochem 4:27–35
von Wandruszka R, Ragle C, Engebretson R (1997) The role of selected cations in the formation of pseudomicelles in aqueous humic acid. Talanta 44:805–809
Waite TD (2001) Thermodynamics of the iron system in seawater. In: Turner DR, Hunter KA (eds) The biogeochemistry of iron in seawater. Wiley, Chichester, pp. 291–342
Wells ML (1999) Manipulating iron availability in nearshore waters. Limnol Oceanogr 44:1002–1008
Yang RJ, van den Berg CMG (2009) Metal complexation by humic substances in seawater. Environ Sci Technol 43:7192–7197
Yeats PA, Strain PM, Whitehouse BG (1990) Cross-flow filtration of colloids from aquatic environments. Limnol Oceanogr 35:1368–1375
Yoshida M, Kuma K, Iwade S, Isoda Y, Takata H, Yamada M (2006) Effect of aging time on the availability of freshly precipitated ferric hydroxide to coastal marine diatoms. Mar Biol 149:379–392
Yun C-W, Ferea T, Rashford J, Ardon O, Brown PO, Botstein D, Kaplan J, Philpott CC (2000) Desferrioxamine-mediated iron uptake in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: evidence for two pathways of iron uptake. J Biol Chem 275:10709–10715
Acknowledgments
The research has partially been supported by the Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (15H05118) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 26.4 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hasegawa, H., Tate, Y., Ogino, M. et al. Laboratory culture experiments to study the effect of lignite humic acid fractions on iron solubility and iron uptake rates in phytoplankton. J Appl Phycol 29, 903–915 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0982-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0982-5