Abstract
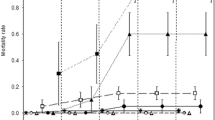
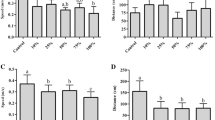
Chemical prroducts used in farming and wastes from livestock can contaminate pond water in agroecosystems due to runoff. Amphibians using these ponds for breeding are probably exposed to pollutants, and serious consequences might be observed afterward at the population level. Assessment biological endpoints of anuran to water quality give a realistic estimate of the probability of occurrence of adverse effects and provide an early warning signal. In this study, the ecotoxicity of agroecosystem ponds from the south of Córdoba province, Argentina, was investigated. Ponds in four sites with different degrees of human disturbance were selected: three agroecosystems (A1, A2, A3) and a site without crops or livestock (SM). The effect of pond water quality on the biological endpoint of Rhinella arenarum tadpoles was examined using microcosms with pond water from sites. Biological endpoints assessed were as follows: mortality, growth, development, morphological abnormalities (in body shape, gut, and labial tooth row formula), behavior, and blood cell parameters (micronucleus and nuclear abnormalities). Results indicated that water from agroecosystems has adverse effect on early life stage of R. arenarum. High mortality and fewer metamorphs were recorded in the A1 and A3 treatments. Tadpoles and metamorphs from A1 and A2 treatments had lower body condition. Tadpoles from A1 and A3 showed the highest prevalence of morphological abnormalities. The lowest amount of tadpoles feeding and the highest percentage of tadpoles swimming on the surface were observed in treatments with agroecosystem pond water. The higher frequencies of micronuclei and nuclear abnormalities were recorded in tadpoles from A1, A2, and A3 treatments. We check the sensitivity of the biological endpoints of R. arenarum tadpoles like early warning indicators of water quality. We found that the poor water quality of agroecosystem ponds has impact on the health of the tadpoles, and this could affect the persistence of populations. We recommend implementation of management actions before the harmful effects of agroecosystem pond water on early life stage of anuran become evident in higher ecological levels.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA-AWWA-WEF (1998). Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater. 20th. Ed. Washington, DC, USA. http://www.standardmethods.org/Accessed 15 Nov 2015
Babini, M. S., Bionda, C. L., Salas, N. E., & Martino, A. L. (2015a). Health status of tadpoles and metamorphs of Rhinella arenarum (Anura, Bufonidae) that inhabit agroecosystems and its implications for land use. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 118, 118–125.
Babini, M. S., Salas, N. E., Bionda, C. L., & Martino, A. L. (2015b). Implicaciones de la urbanización en la presencia, distribución y ecología reproductiva de la fauna de anuros de una ciudad del área central de Argentina. Revista Mexicana de Biodiversidad, 86(1), 188–195.
Balzarini, M. G., Gonzalez, L., Tablada, M., Casanoves, F., Di Rienzo, J. A., & Robledo, C. W. (2008). Infostat. Manual del Usuario. Córdoba, Argentina: Editorial Brujas.
Barni, S., Fraschini, A., Prosperi, E., Vaccarone, V., & Bernini, F. (1995). Possible occurrence of amitotic cell division during haemopoiesis in the Urodele. Comparative Hematology International, 45, 183–188.
Barni, S., Vaccarone, R., Bertone, V., Fraschini, A., Bernini, F., & Fenoglio, C. (2002). Mechanisms of changes to the liver pigmentary component during the annual cycle (activity and hibernation) of Rana esculenta L. Journal of Anatomy, 200, 185–194.
Barni, S., Boncompagni, E., Grosso, A., Bertone, V., Freitas, I., Fasola, M., & Fenoglio, C. (2007). Evaluation of Rana snk esculenta blood cell response to chemical stressors in the environment during the larval and adult phases. Aquatic Toxicology, 81(1), 45–54.
Betanzos Vega, A., Capetillo Piñar, N., Lopeztegui Castillo, A., & Martínez Daranas, B. (2013). Variación espacio-temporal de la turbidez y calidad en cuerpos de agua marina de uso pesquero, región norcentral de Cuba, 2008-2010. Serie Oceanológica, 12, 24–35.
Bionda, C. L., di Tada, I. E., & Lajmanovich, R. C. (2011). Composition of amphibian assemblages in agroecosystems from the central region of Argentina. Russian Journal of Herpetology, 18(2), 93–98.
Bionda, C. L., Salas, N. E., Caraffa, E., Baraquet, M., & Martino, A. L. (2012). On abnormalities recorded in an urban population of Rhinella arenarum from Central Argentina. Herpetology Notes, 5, 237–241.
Bionda, C., Lajmanovich, R., Salas, N., Martino, A., & di Tada, I. E. (2013). Demografía poblacional de Rhinella arenarum (Anura: Bufonidae) y Physalaemus biligonigerus (Anura: Leiuperidae) en agroecosistemas de la provincia de Córdoba, Argentina. Revista Biología Tropical, 61, 1389–1400.
Bosch, B., Mañas, F., Gorla, N., & Aiassa, D. (2011). Micronucleus test in post metamorphic Odontophrynus cordobae and Rhinella arenarum (Amphibia: Anura) for environmental monitoring. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health Sciences, 3(6), 154–163.
Burton, E. C., Gray, M. J., Schmutzer, A. C., & Miller, D. L. (2009). Differential responses of postmetamorphic amphibians to cattle grazing in wetlands. The Journal of Wildlife Management, 73(2), 269–277.
Cabagna, M., Lajmanovich, R. C., Peltzer, P. M., Attademo, M., & Ale, E. (2006). Induction of micronucleus in tadpoles of Odontophrynus americanus (Amphibia: Leptodactylidae) by the pyrethroid insecticide cypermethrin. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 88, 729–737.
Camargo, J. A. (2003). Fluoride toxicity to aquatic organisms: a review. Chemosphere, 50(3), 251–264.
Camargo, J. A., & Alonso, A. (2007). Contaminación por nitrógeno inorgánico en los ecosistemas acuáticos: problemas medioambientales, criterios de calidad del agua, e implicaciones del cambio climático. Revista Ecosistemas, 16(2).
Campana, M. A., Panzeri, A. M., Moreno, V. J., & Dulout, F. N. (2003). Micronuclei induction in Rana catesbeiana tadpoles by the pyrethroid insecticide lambda-cyhalothrin. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 26, 99–103.
Caraffa, E., Bionda, C., Pollo, F., Salas, N., & Martino, A. (2014). Determinación de la frecuencia de micronúcleos en eritrocitos de Bufo arenarum que habitan ambientes urbanizados. Acta Toxicológica Argentina, 21, 2.
CASAFE, Cámara de Sanidad Agropecuaria y Fertilizantes (1999). Guía de Productos Fitosanitarios para la República Argentina. 6ta Ed. Argentina. pp. 1600.
CCME, Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (2003). Canadian water quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life: guidance on the site-specific application of water quality guidelines in Canada: procedures for deriving numerical water quality objectives. In: Canadian environmental quality guidelines. 1999. Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, Winnipeg.
Clotfelter, E. D., Bell, A. M., & Levering, K. R. (2004). The role of animal behaviour in the study of endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Animal Behaviour, 68(4), 665–676.
Cooke, A. S. (1981). Tadpoles as indicators of harmful levels of pollution in the field. Environmental Pollution Series A, Ecological and Biological, 25(2), 123–133.
Da Rocha, C. A. M. (2011). The micronucleus test in erythrocytes of amphibian larvae as tool for xenobiotic exposure risk assessment: a brief review and an example using Lithobates catesbeianus exposed to copper sulphate middle. Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research, 8, 23–29.
Dacie, J. V., & Lewis, S. M. (1995). Practical haematology (8 ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
Dell’Omo, G. (2002). Behavioral ecotoxicology. New York: J. Wiley.
Di Rienzo, J. A., Guzmán, A. W., & Casanoves, F. (2002). A multiple comparisons method based on the distribution of the root node distance of a binary tree. Journal of Agricultural, Biological, and Environmental Statistics, 7(2), 1–14.
Di Rienzo, J.A., Casanoves, F., Balzarini, M.G., Gonzalez, L., Tablada, M. & Robledo, C.W. (2012) InfoStat versión 2012. Grupo InfoStat, FCA, Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Argentina. URL http://www.infostat.com.ar
Donald, P. F. (2004). Biodiversity impacts of some agricultural commodity production systems. Conservation Biology, 18, 17–37.
Duellman, W. E., & Trueb, L. (1986). Biology of amphibians (p. 670). San Francisco, New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company.
Dunson, W. A., Wyman, R. L., & Corbett, E. S. (1992). A symposium on amphibian declines and habitat acidification. Journal of Herpetology, 26, 349–352.
Fenech, M. (2000). The in vitro micronucleus technique. Mutation Research, 455, 81–95.
Feng, S., Kong, Z., Wang, X., Zhao, L., & Peng, P. (2004). Acute toxicity of two novel pesticides on amphibian. Rana N. Hallowel. Chemosphere, 56, 475–463.
Ferrier, V., Gauthier, L., Zoll-Moreux, C.L., & Haridon, J. (1998). Genotoxicity tests in amphibians: a review. Microscale testing in aquatic toxicology: advances, techniques and practice. CRC Press LLC. pp 507–519.
Ficken, K. G., & Byrne, P. G. (2012). Heavy metal pollution negatively correlates with anuran species richness and distribution in South-Eastern Australia. Austral Ecology, 38, 523–533.
Fijan, N. (2002). Morphogenesis of blood cell lineages in channel catfish. Journal of Fish Biology, 60, 999–1014.
Foley, J. A., DeFries, R., Asner, G. P., Barford, C., Bonan, G., Carpenter, S. R., Chapin, F. S., Coe, M. T., Daily, G. C., Gibbs, H. K., Helkowski, J. H., Holloway, T., Howard, E. A., Kucharik, C. J., Monfreda, C., Patz, J. A., Prentice, I. C., Ramankutty, N., & Snyder, P. K. (2005). Global consequences of land use. Science, 309, 570–574.
Foley, J. A., Ramankutty, N., Brauman, K. A., Cassidy, E. S., Gerber, J. S., Johnston, M., Mueller, N. D., O’Connell, C., Ray, D. K., West, P. C., Balzer, C., Bennett, E. M., Carpenter, S. R., Hill, J., Monfreda, C., Polasky, S., Rockstrom, J., Sheehan, J., Siebert, S., Tilman, D., & Zaks, D. P. M. (2011). Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature, 478, 337–342.
Frost, D.R. (2014). Amphibian species of the world: an online reference. Version 6.0 (Date of access). Electronic Database accessible at http://research.amnh.org/herpetology/amphibia/index.html. American Museum of Natural History, New York, USA. Accessed 15 Nov 2015.
GAA, Global Amphibian Assessment. (2004). Summary of key findings. On line: http://www.globalamphibians.org. Accessed 15 Nov 2015.
Gauthier, L., Van der Gaag, M. A., L’haridon, J., Ferrier, V., & Fernandez, M. (1993). In vivo detection of waste water and industrial effluent genotoxicity: use of the newt micronucleus test (Jaylet test). Science of the Total Environment, 138(1), 249–269.
Giuliano Albo, M.J., & Blarasin, M.T. (2013). Hidrogeoquímica y estimación del fondo natural de nitratos del agua subterranea en un agroecosistema del pedemonte de la sierra de Comechingones. Córdoba (Argentina). Revista de la Asociación Geológica Argentina, 71(3).
Gosner, K. L. (1960). A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on identification. Herpetologica, 16, 183–190.
Gray, M. J., Smith, L. M., & Leyva, R. I. (2004). Influence of agricultural landscape structure on a Southern High Plains, USA, amphibian assemblage. Landscape Ecology, 19, 719–729.
Guilherme, S., Válega, M., Pereira, M. E., Santos, M. A., & Pacheco, M. (2008). Erythrocytic nuclear abnormalities in wild and caged fish (Liza aurata) along an environ-mental mercury contamination gradient. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 70, 411–421.
Hamer, A. J., Makings, J. A., Lane, S. J., & Mahony, M. J. (2004). Amphibian decline and fertilizers used on agricultural land in South-Eastern Australia. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 102, 299–305.
Hawkins, A. (2007). Biomonitoring: guide for the use of biological endpoints in monitoring species, habitats, and projects (No. TR-2284-ENV). Commanding Officer-Naval Facilities Engineering Command. Port Hueneme, CA. 147 p.
Hecnar, S. J., & M’Closkey, R. T. (1998). Species richness patterns of amphibians in South-Western Ontario ponds. Journal of Biogeography, 25, 763–772.
Hensel, R. (1867). Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Wirbelthiere Südbrasilens. Archiv für Naturgeschichte, 33, 120–162.
Hopkins, W. A. (2007). Amphibians as models for studying environmental change. ILAR Journal, 48(3), 270–277.
Howe, G. E., Gillis, R., & Mowbray, R. C. (1998). Effect of chemical synergy and larval stage on the toxicity of atrazine and alachlor to amphibian larvae. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 17(3), 519–525.
Ilizaliturri-Hernandez, C. A., González-Mille, D. J., Mejía-Saavedra, J., Espinosa-Reyes, G., Torres-Dosal, A., & Pérez-Maldonado, I. (2013). Blood lead levels, δ-ALAD inhibition, and hemoglobin content in blood of giant toad (Rhinella marina) to asses lead exposure in three areas surrounding an industrial complex in Coatzacoalcos, Veracruz, Mexico. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 85, 1685–1698.
INTA. EEA MANFREDI (2003). Proyecto Regional de Agricultura Sustentable. On line: http://www.inta.gov.ar/manfredi/info/boletines. Accessed 15 Nov 2015
Jofré, G., Reading, C., & di Tada, I. (2007). Habitat selection in the Pampa de Achala toad, Bufo achalensis. Amphibia-Reptilia, 28(1), 129–138.
Kareiva, P., Watts, S., McDonald, R., & Boucher, T. (2007). Domesticated nature: shaping landscapes and ecosystems for human welfare. Science, 316, 1866–1869.
Knutson, M. G., Richardson, W. B., Reineke, D. M., Gray, B. R., Parmelee, J. R., & Weick, S. E. (2004). Agricultural ponds support amphibian populations. Ecological Applications, 14, 669–684.
Krishnamurthy, S. V., & Smith, G. R. (2011). Combined effects of malathion and nitrate on early growth, abnormalities, and mortality of wood frog (Rana sylvatica) tadpoles. Ecotoxicology, 20(6), 1361–1367.
Kwet, A., Reichle, S., Silvano, D., Úbeda, C., Baldo, D., & Di Tada, I. (2004). Rhinella arenarum. The IUCN red list of threatened species. Version 2014.3. <www.iucnredlist.org>. Downloaded on 14 April 2015.
Lajmanovich, R., de La Sierra, P., Marino, F., Peltzer, P., Lenardón, A., & Lorenzatti, E. (2005a). Determinación de residuos de organoclorados en vertebrados silvestres del Litoral fluvial de Argentina. INSUGEO, Miscelánea, 14, 255–262.
Lajmanovich, R. C., Cabagna, M., Peltzer, P. M., Stringhini, G. A., & Attademo, A. M. (2005b). Micronucleus induction in erythrocytes of the Hyla pulchella tadpoles (Amphibia: Hylidae) exposed to insecticide endosulfan. Mutation Research, 587, 67–72.
Lajmanovich, R. C., Peltzer, P. M., Junges, C. M., Attademo, A. M., Sanchez, L. C., & Basso, A. (2010). Activity levels of B-esterases in the tadpoles of 11 species of frogs in the middle Paraná River floodplain: implication for ecological risk assessment of soybean crops. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73, 1517–1524.
Lajmanovich, R. C., Cabagna-Zenklusen, M. C., Attademo, A. M., Junges, C. M., Peltzer, P. M., Bassó, A., & Lorenzatti, E. (2014). Induction of micronuclei and nuclear abnormalities in tadpoles of the common toad (Rhinella arenarum) treated with the herbicides liberty (®) and glufosinate-ammonium. Mutation Research-Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 769, 7–12.
Law 24051 (1993). Residuos peligrosos. InfoLEG, Centro de Documentación e Información, Ministerio de Economía y Finanzas Públicas. On line: http://www.infoleg.gov.ar/. Accessed 15 Nov 2015.
Marco, A. (2002). Contaminación global por nitrógeno y declive de anfibios. Revista Española de Herpetología, 16, 5–17.
Marco, A., & Blaustein, A. R. (1999). The effects of nitrite on behavior and metamorphosis in cascades frogs (Rana cascadae). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 18, 946–949.
McDaniel, T. V., Harris, M. L., Bishop, C. A., & Struger, J. (2004). Development and survivorship of northern leopard frogs (Rana pipiens) and green frogs (Rana clamitans) exposed to contaminants in the water and sediments of the St. Lawrence River near Cornwall. Ontario Water Quality Research Journal of Canada, 39, 160–174.
Meintières, S., Biola, A., Pallardy, M., & Marzin, D. (2001). Apoptosis can be a confusing factor in vitro clastogenic assays. Mutagenesis, 16(3), 243–250.
Metts, B. S., Kurt, A., Scott, D. E., Tuberville, T. D., & Hopkins, W. A. (2012). Interactive effects of maternal and environmental exposure to coal combustion wastes decrease survival of larval southern toads (Bufo terrestris). Environmental Pollution, 164, 211–218.
Mitsch, W. J., & Gosselink, J. G. (2000). Wetlands (3rd ed.p. 920). New York: Wiley.
Newcombe, C. P., & MacDonald, D. D. (1991). Effects of suspended sediments on aquatic ecosystems. North American Journal of Fisheries Management, 11(1), 72–82.
Nori, J., Lescano, J. N., Illoldi-Rangel, P., Frutos, N., Cabrera, M. R., & Leynaud, G. C. (2013). The conflict between agricultural expansion and priority conservation areas: making the right decisions before it is too late. Biological Conservation, 159, 507–513.
Peltzer, P. M., Lajmanovich, R. C., Sánchez Hernández, J. C., Cabagna, M., Attademo, A. M., & Bassó, A. (2008). Effects of agricultural pond eutrophication on survival and health status of Scinax nasicus tadpoles. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 70, 185–197.
Peltzer, P. M., Lajmanovich, R. C., Sanchez, L. C., Attademo, A. M., Junges, C. M., Bionda, C. L., Martino, A. L., & Bassó, A. (2011). Morphological abnormalities in amphibian populations from the mid-eastern region of Argentina. Herpetological Conservation and Biology, 6(3), 432–442.
Peltzer, P. M., Lajmanovich, R. C., Attademo, A. M., Junges, C. M., Cabagna-Zenklusen, M. C., Repetti, M. R., Sigrist, M. E., & Beldoménico, H. (2013). Effect of exposure to contaminated pond sediments on survival, development, and enzyme and blood biomarkers in veined treefrog (Trachycephalus typhonius) tadpoles. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 98, 142–151.
Pollo, F. E., Salas, N. E., Mancini, M. A., & Martino, A. L. (2012). Estudio comparativo de la frecuencia de micronúcleos y anormalidades nucleares en eritrocitos de tres especies ícticas. Acta Toxicológica Argentina, 20(2), 62–67.
Ramankutty, N., Evan, A. T., Monfreda, C., & Foley, J. A. (2008). Farming the planet: 1, geographic distribution of global agricultural lands in the year 2000. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 22, 1–19.
Rossi, R. L. (2006). Impactos recientes de la soja en la Argentina. Panorama productivo del cultivo. Agromercado. Cuadernillo Clásico, 129, 4–7.
Rowe, C. L., Kinney, O. M., Fiori, A. P., & Congdon, J. D. (1996). Oral deformities in tadpoles (Rana catesbeiana) associated with coal ash deposition: effects on grazing ability and growth. Freshwater Biology, 37, 723–730.
Rowe, C. L., Hopkins, W. A., & Congdon, J. D. (2002). Ecotoxicological implications of aquatic disposal of coal combustion residues in the United States: a review. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 80, 207–276.
Rowe, C. L., Hopkins, W. A., & Bridges, C. (2003). Physiological ecology of amphibians in relation to susceptibility to natural and anthropogenic factors. In G. Linder, S. Krest, & D. Sparling (Eds.), Amphibian decline: an integrated analysis of multiple stressor effects (pp. 9–58). Pensacola: Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry Press.
Russo, R. C. (1985). Ammonia, nitrite and nitrate. In G. M. Rand & S. R. Petrocelli (Eds.), Fundamentals of aquatic toxicology (pp. 455–471). Washington DC: Hemisphere Publishing Corporation.
Schmid, W. (1975). The micronucleus test. Mutation Research, 31, 9–15.
Schmutzer, A. C., Gray, M. J., Burton, E. C., & Miller, D. L. (2008). Impacts of cattle on amphibian larvae and the aquatic environment. Freshwater Biology, 53, 2613–2625.
StatSoft. (2001). Statistica for Windows, Release 6.0, Computer Program Manual, StatSoft, Inc. Tulsa, OK, USA.
ter Braak, C. J. K., & Smilauer, P. (2002). CANOCO Reference Manual and CanoDraw for Windows User's guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination (version 4.5). Microcomputer Power. Ithaca, New York. 500 p.
Unrine, J. M., Hopkins, W. A., Romanek, C. S., & Jackson, B. P. (2007). Bioaccumulation of trace elements in omnivorous amphibian larvae: implications for amphibian health and contaminant transport. Environmental Pollution, 149(2), 182–192.
Venturino, A., Rosenbaum, E., Caballero De Castro, A., Anguiano, O. L., Gauna, L., Fonovich De Schroeder, T., & Pechen De D’Angelo, A. M. (2003). Biomarkers of effect in toads and frogs. Biomarkers, 8(3–4), 167–186.
Vera Candioti, J. V., Natale, G. S., Soloneski, S., Ronco, A. E., & Larramendy, M. L. (2010). Sublethal and lethal effects on Rhinella arenarum (Anura, Bufonidae) tadpoles exerted by the pirimicarb-containing technical formulation insecticide Aficida®. Chemosphere, 78, 249–255.
Vonesh, J. R., & de la Cruz, O. (2002). Complex life cycles and density dependence: assessing the contribution of egg mortality to amphibian declines. Oecologia, 133, 325–333.
Wake, D.B. (1991). Declining amphibian populations. Science, 253(5022), pp. 860.
Warner, R.E., Peterson, K.K., & Borgman, L. (1966). Behavioural pathology in fish: a quantitative study of sublethal pesticide toxication. Journal of Applied Ecology, 223–247.
Werner, E. E., & Glennemeier, K. (1999). The influence of forest canopy cover on the breeding pond distributions of several amphibian species. Copeia, 1, 1–12.
Wood, S. L., & Richardson, J. S. (2009). Impact of sediment and nutrient inputs on growth and survival of tadpoles of the western toad. Freshwater Biology, 54(5), 1120–1134.
Young, B. E., Stuart, S. N., Chanson, J. S., Cox, N. A., & Boucher, T. M. (2004). Joyas que están desapareciendo: el estado de los anfibios en el nuevo mundo (p. 53). Arlington, Virginia, USA: Nature Serve.
Acknowledgments
Financial support was provided by SECyT-UNRC (PPI 18/C416) and FONCyT (PICT 2012-0932). SB thanks Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Tecnológicas (CONICET), Argentina, for the fellowship granted. The investigation was conducted according to the state law Protection and Conservation of Wild Fauna (Argentina National Law no. 22.421). Our study was authorized by Cordoba Environmental Agency (A.C.A.S.E.), Environmental Secretary of Córdoba Government, and the Ethical Committee of Investigation of the National University of Río Cuarto (file number 38/11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babini, M.S., Bionda, C.d., Salas, N.E. et al. Adverse effect of agroecosystem pond water on biological endpoints of common toad (Rhinella arenarum) tadpoles. Environ Monit Assess 188, 459 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5473-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5473-2