Abstract
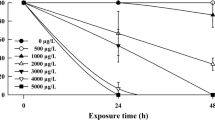
The mining sector has great importance to the economic activity in Brazil. However, it is also responsible for several environmental impacts such as the rupture of the Fundão dam (Mariana, Brazil) that resulted in the spillage of 50 million m3 of mining tailings in the Doce River Basin. This study evaluated the acute and chronic effects of Fundão tailings on growth, development, respiration rates, swimming performance, and avoidance behavior of Lithobates catesbeianus tadpoles. Results showed that 96-h exposure to different dilutions (10, 25, 50, 75, and 100%) of a stock solution containing mining tailings (50 g/L) caused no mortality of tadpoles; however, the most concentrated solution decreased the swimming speed of the animals. After 16 days, tadpoles exposed to 25, 50, and 100% treatments had both swimming speed and distance traveled reduced. Oxygen consumption was also decreased in tadpoles exposed to the 100% solution after 20 days. Avoidance test indicated that tadpoles avoided lower tailing concentrations, but a reduced avoidance response was attested to the higher concentrations, probably due to the toxic effects of the residues that prevented animals’ displacement. Chemical analysis confirmed the occurrence of cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), and aluminum (Al) in Fundão tailings and its presence in the mouth and inside the intestine of treated tadpoles indicated the ingestion of metals by these organisms. This study showed that even presenting low lethal toxicity, long-term exposure to mining tailings from Fundão dam caused morphophysiological and behavioral damage in tadpoles.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data pertaining to this manuscript are deposited in text, tables, and figures.
References
Alford, R. A., & Richards, S. J. (1999). Global amphibian declines: a problem in applied ecology. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 30, 133–165.
Alonso, A., Lange, H. J., & Peeters, E. T. H. M. (2009). Development of a feeding behavioural bioassay using the freshwater amphipod Gammarus pulex and the multispecies freshwater biomonitor. Chemosphere, 75, 341–346.
Araújo, C. V. M., Shinn, C., Moreira-Santos, M., Lopes, I., Espíndola, E. L. G., & Ribeiro, R. (2014a). Copper-driven avoidance and mortality in temperate and tropical tadpoles. Aquatic Toxicology, 146, 70–75.
Araújo, C. V. M., Shinn, C., Vasconcelos, A. M., Ribeiro, R., & Espíndola, E. L. G. (2014b). Preference and avoidance responses by tadpoles: the fungicide pyrimethanil as a habitat disturber. Ecotoxicology, 23, 851–860.
Araújo, C. V. M., Pereira, K. C., & Blasco, J. (2018). Avoidance response by shrimps to a copper gradient: does high population density prevent avoidance of contamination? Environmental Toxicology, 37, 3095–3101.
Barreto M L (2001) Mineração e desenvolvimento sustentável: desafios para o Brasil. CETEM/MCT, Rio de Janeiro pp 215. http://www.ibram.org.br/sites/1300/1382/00000729.pdf. Acessed 30 november 2019.
Batayneh, A. T. (2012). Toxic (aluminum, beryllium, boron, chromium and zinc) in groundwater: health risk assessment. I J Environ Sci Te, 9, 153–162.
Boone, M. D., Bridges, C. M., & Rothermel, B. B. (2001). Growth and development of larval green frogs (Rana clamitans) exposed to multiple doses of an insecticide. Oecologia, 129, 518–524.
Bridges, C., Little, E., Gardiner, D., Petty, J., & Huckins, J. (2004). Assessing the toxicity and teratogenicity of pond water in north-central Minnesota to amphibians. Environemental Science and Pollution Research, 11, 233–239.
Brodeur, J. C., Asorey, C. M., Sztrum, A., & Herkovits, J. (2009). Acute and subchronic toxicity of arsenite and zinc to tadpoles of Rhinella arenarum both alone and in combination. J Toxicol Env Health, 72, 884–890.
Broomhall, S. (2004). Egg temperature modifies predator avoidance and the effects of the insecticide endosulfan on tadpoles of an Australian frog. JApp Ecol, 41, 105–113.
Carvalho, M. S., Ribeiro, K. D., Moreira, R. M., & Almeida, A. M. (2017). Concentração de metais no rio Doce em Mariana, Minas Gerais, Brasil. Acta Brasiliensis, 1, 37–41.
Chen, T. H., Gross, J. A., & Karasov, W. H. (2007). Adverse effects of chronic copper expo-sure in larval northern leopard frogs (Rana pipiens). Env Toxicol Chem, 26, 1470–1475.
CONAMA (2005) Resolução CONAMA n°357 de 17/03/2005. http://www2.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi=459. Accessed 22 August 2019.
Coddington, E., & Moore, F. L. (2003). Neuroendocrinology of context-dependent stress responses: Vasotocin alters the effect of corticosterone on amphibian behaviors. Hormones and Behavior, 43, 222–228.
Denoël, M., D’Hooghe, B., Ficetola, G. F., Brasseur, C., De Pauw, E., Thomé, J. P., & Kestemont, P. (2012). Using sets of behavioral biomarkers to assess short-term effects of pesticide: a study case with endosulfan on frog tadpoles. Ecotoxicology, 21, 1240–1250.
Freda, J., Cavdek, V., & McDonald, D. G. (1990). Role of organic complexation in the toxicity of aluminum to Rana pipiens embryos and Bufo americanus tadpoles. Can J Fish and Aquat Sci, 47, 217–224.
Fernandes FRC, Alamino RCJ, Araújo ER (2014) Recursos minerais e comunidade: impactos humanos, socioambientais e econômicos. CETEM/MCTI, Rio de Janeiro pp 379. http://verbetes.cetem.gov.br/verbetes/Texto.aspx?p=7&s=1. Acessed 30 november 2019.
Freitas, C. M., Silva, M. A., & Menezes, F. C. (2016). O desastre na barragem de mineração da Samarco: fratura exposta dos limites do Brasil na redução de risco de desastres. Ciência e Cultura, 68, 25–30.
Freitas, J. S., Girotto, L., Goulart, B. V., Alho, L. O. G., Gebara, R. C., Montagner, C. C., Schiesari, L., & Espíndola, E. L. G. (2019). Effects of 2,4-D-based herbicide (DMA® 806) on sensitivity, respiration rates, energy reserves and behavior of tadpoles. Ecotox Environ Safe, 82, 109446.
Fryday, S., & Thompson, H. (2012). Toxicity of pesticides to aquatic and terrestrial life stages of amphibians and occurrence, habitat use and exposure of amphibian species in agricultural environments. European Food Safety Authority Supporting Publications, 9, 1–348.
Gardner, T. (2001). Declining amphibian populations: a global phenomenon in conservation biology. Ani Biodiv Conserv, 24, 25–44.
Gerhardt, A., Bisthoven, L. J., & Soares, A. M. V. M. (2005). Effects of acid mine drainage and acidity on the activity of Choroterpes picteti (Ephemeroptera: Leptophlebiidae). Arch Environ Cont Tox, 48, 450–458.
Gerhardt, A., Ingram, M. K., Kang, I. J., & Ulitzur, S. (2006). In situ on-line toxicity biomonitoring in water: recent developments. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 25, 2263–2271.
Grant, E. H., Miller, D. A., Schmidt, B. R., Adams, M. J., Amburgey, S. M., Chambert, T., Cruickshank, S. S., Fisher, R. N., Green, D. M., Hossack, B. R., Johnson, P. T., Joseph, M. B., Rittenhouse, T. A., Ryan, M. E., Waddle, J. H., Walls, S. C., Bailey, L. L., Fellers, G. M., Gorman, T. A., Ray, A. M., Pilliod, D. S., Price, S. J., Saenz, D., Sadinski, W., & Muths, E. (2016). Quantitative evidence for the effects of multiple drivers on continental scale amphibian declines. Scientific Reports, 6, 25625.
Greulich, K., & Pflugmacher, S. (2003). Differences in susceptibility of various life stages of amphibians to pesticide exposure. Aquatic Toxicology, 65, 329–336.
Gosner, K. (1960). A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on 750 identification. Herpetologica, 16, 183–190.
Gross, J. A., Chen, T. H., & Karasov, W. H. (2007). Lethal and sublethal effects of chronic cadmium exposure on northern leopard frog (Rana pipiens) tadpoles. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 26, 1192–1197.
Hayes, T. B., Falso, P., Gallipeau, S., & Stice, M. (2010). The cause of global amphibian declines: A developmental endocrinologist’s perspective. The Journal of Experimental Biology, 213, 921–933.
Hem, J. D. (1972). Chemistry and occurrence of cadmium and zinc in surface water and groundwater. Water Resources Research, 8, 661–679.
Hopkins, W.A., Congdon, J., & Ray, J.K (2000). Incidence and impact of axial malformations in larval bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana) developing in sites polluted by a coal-burning power plant. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 19:862–868.
IBGE (2011). Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. Available at: http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/estatistica/populacao/censo2010/default.shtm. Acessed 22 Mar 2019.
IBAMA (2015). Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis. Laudo Técnico Preliminar - Rompimento da Barragem de Rejeito do Fundão Mariana/MG. Brasília, dezembro de 2015.
James, S. M., & Little, E. E. (2003). The effects of chronic cadmium exposure on American toad (Bufo americanus) tadpoles. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 22, 377–380.
Juncá FA, Pavan D, Jesus TB, Eterovick P (2017) Girinos como bioindicadores da qualidade da água do Rio Doce; GREENPEACE; Universidade Estadual de Feira de Santana. https://www.greenpeace.org.br/hubfs/Campanhas/Agua_Para_Quem/documentos/GP_girinosbioindicadoresRioDoce.pdf. Acessed 30 november 2019.
Jung, R. E., & Jagoe, C. H. (1995). Effects of low pH and aluminum on body size, swimming performance, and susceptibility to predation of green tree frog (Hyla cinerea) tadpoles. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 73, 2171–2183.
Khangarot, B. S., Sehgal, A., & Bhasin, M. K. (1985). “Man and biosphere” – studies on the Sikkim Himalayas. Part 5: Acute toxicity of selected heavy metals on the tadpoles of Rana hexadactyla. Acta Hydroch Hydrobiol, 13, 259–263.
Lanctôt, C., Bennett, W., Wilson, S., Fabbro, L., Leusch, F. D. L., & Melvina, S. D. (2016). Behaviour, development and metal accumulation in striped marsh frog tadpoles (Limnodynastes peronii) exposed to coal mine wastewater. Aquatic Toxicology, 173, 218–227.
Lefcort, H., Meguire, R. A., Wilson, L. H., & Ettinger, W. F. (1998). Heavy metals alter the survival, growth, metamorphosis, and antipredatory behavior of Columbia spotted frog (Rana luteiventris) tadpoles. Arch Environ Con Tox, 35, 447–456.
Lehner, P. N. (1996). Handbook of ethological methods. New York: Garland STPM Press.
Lima, S. L., & Agostinho, C. A. (1989). A Criação de Rãs. São Paulo: Globo.
Little, E. E., Archeski, R. D., Flerov, B. A., & Kozlovskaye, V. I. (1990). Behavioural indicators of sublethal toxicity in rainbow trout. Arch Environ Con Tox, 19, 380–385.
Lopes, L. M. N. (2016). O rompimento da barragem de Mariana e seus impactos socioambientais. Sinapse Múltipla, 5(1), 1–14.
Macedo-Sousa, J. A., Gerhardt, A., Brett, C. M. A., Nogueira, A. J. A., & Soares, A. M. (2008). Behavioural responses of indigenous benthic invertebrates (Echinogammarus meridionalis, Hydropsyche pellucidula and Choroterpes picteti) to a pulse of acid mine drainage: a laboratorial study. Environmental Pollution, 156, 966–973.
Mann, R. M., Hyne, R. V., Choung, C. B., & Wilson, S. P. (2009). Amphibians and agricultural chemicals: review of the risks in a complex environment. Environmental Pollution, 157, 2903–2927.
Marcantonio, A. S., Ranzani-Paiva, M. J. T., França, F. M., Dias, D. C., Teixeira, P. C., & Ferreira, C. M. (2011). Toxicidade do sulfato de zinco para rã-touro (Lithobates catesbeianus): acute toxicity, chronic toxicity and hematomogical parameters. Boletim do Instituto de Pesca, 37, 143–154.
Massarin, S., Alonzo, F., Garcia-Sanchez, L., Gilbin, R., Garnier-Laplace, J., & Poggiale, J. C. (2010). Effects of chronic uranium exposure on life history and physiology of Daphnia magna over three successive generations. Aquatic Toxicology, 99, 309–319.
Mechi, A., & Sanches, D. L. (2010). Impactos ambientais da mineração no Estado de São Paulo. Estudos Avançados, 24, 209–220.
Melvin, S. D., & Houlahan, J. E. (2012). Tadpole mortality varies across experimental venues: do laboratory populations predict responses in nature? Oecologia, 169, 861–868.
Miranda ADO (2017) Potencial de Aprovechamiento de Lodos Generados en el Proceso de Potabilización de água para Consumo Humano. Dissertation, Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala.
Moreira, R. A., Freitas, J. S., Pinto, T. J. S., Schiesari, L., Daam, M. A., Montagner, C. C., Goulart, B. V., & Espindola, E. L. G. (2019). Mortality, spatial avoidance and swimming behavior of bullfrog tadpoles (Lithobates catesbeianus) exposed to the herbicide Diuron. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 230, 125.
Moreira-Santos, M., Donato, C., Lopes, I., & Ribeiro, R. (2008). Avoidance tests with small fish: determination of the median avoidance concentration and of the lowest-observed-effect gradient. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 27, 1575–1582.
Peles, J. D. (2013). Effects of chronic aluminum and copper exposure on growth and development of wood frog (Rana sylvatica) larvae. Aquatic Toxicology, 140(141), 242–248.
Peltzer, P. M., Junges, C. M., Attademo, A. M., Bassó, A., Grenón, P., & Lajmanovich, R. C. (2013). Cholinesterase activities and behavioral changes in Hypsiboas pulchellus (Anura: Hylidae) tadpoles exposed to glufosinate ammonium herbicide. Ecotoxicology, 22, 1165–1173.
Pestana, J. L. T., Ré, A., Nogueira, A. J. A., & Soares, A. M. V. M. (2007). Effects of cadmium and zinc on the feeding behaviour of two freshwater crustaceans: Atyaephyra desmarestii (Decapoda) and Echinogammarus meridionalis (Amphipoda). Chemosphere, 68, 1556–1562.
Pollo, F. E., Grenat, P. R., Salinas, Z. A., Otero, M. A., Salas, N. E., & Martino, A. L. (2017). Evaluation in situ of genotoxicity and stress in South American common toad Rhinella arenarum in environments related to fluorite mine. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(22), 18179–18187.
Pollo, F. E., Grenat, P. R., Otero, M. A., Salas, N. E., & Martino, A. L. (2016). Assessment in situ of genotoxicity in tadpoles and adults of frog Hypsiboas cordobae (barrio 1965) in habiting aquatic ecosystems associated to fluorite mine. Ecotox Environ Safe, 133, 466–474.
Raimondo, S., Rowe, C. L., & Congdon, J. D. (1998). Exposure to coal ash impacts swimming performance and predator avoidance in larval bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana). Journal of Herpetology, 32, 289–292.
Rao, I. J., & Madhyastha, M. N. (1987). Toxicities of some heavy metals to the tadpoles of frog, Microhyla ornata (Dumeril & Bibron). Toxicology Letters, 36, 205–208.
Samarco (2005) EIA - Estudos de Impacto Ambiental Acompanhado de ART. Barragem do Fundão. http://www.siam.mg.gov.br/siam/lc/2013/0001519840952013/7086862005.pdf. Accessed 8 February 2018.
Samarco (2013) Relatório de Avaliação do Desempenho Ambiental Barragem do Fundão. Mariana, MG. http://www.siam.mg.gov.br/siam/lc/2013/0001519840952013/7086862013.pdf. Accessed 8 february 2018.
Santos TCCS, Câmara JBD (2002) Relatório perspectivas do meio ambiente no Brasil - GEO-BRASIL. Edições Ibama, Brasília 409 pp. http://www.terrabrasilis.org.br/ecotecadigital/pdf/geo-brasil-2002-perspectivas-do-meio-ambiente-no-brasil.pdf. Accessed 22 August 2019.
Schiesari, L., & Corrêa, D. T. (2016). Consequences of agroindustrial sugarcane production to freshwater biodiversity. GCB Bioenergy, 8, 644–657.
Shinn, C., Marco, A., & Serrano, L. (2008). Inter- and intra-specific variation on sensitivity of larval amphibians to nitrite. Chemosphere, 71, 507–514.
Shuhaimi-Othman, M., Nadzifah, Y., Umirah, N. S., & Ahmad, A. K. (2012). Toxicity of metals to tadpoles of the common Sunda toad, Duttaphrynus melanostictus. Toxicol Environ Chem, 94, 364–376.
Sokal R, Rohlf FJ (1995) Biometry: the principles and practices of statistics in biological research. International Biometric Society New York.
Souza, L. A., Sobreira, F. G., & Filho, J. F. P. (2005). Cartografia e Diagnóstico Geoambiental Aplicados ao Orçamento Territorial do Município de Mariana – MG. Revista Brasileira de Cartografia, 57, 189–203.
Srivastav, A. K., Srivastav, S., & Suzuki, N. (2016). Acute toxicity of a heavy metal cadmium to an anuran, the Indian skipper frog Rana cyanophlyctis. Iran J Toxicol, 10, 39–43.
Sparling, D. W., Linder, G., Bishop, C., & Krest, S. (2010). Ecotoxicology of amphibians and reptiles. Boca Raton: SETAC/Taylor & Francis.
Storer, T. I., & Usinger, R. L. (1979). Zoologia Geral (757p). Companhia Editora Nacional: São Paulo.
Veronez, A. C. S., Salla, R. V., Baronia, V. D., Barcarolli, I. F., Bianchinic, A., Martinez, C. B. R., & Chippari-Gomesa, A. R. (2016). Genetic and biochemical effects induced by iron ore, Fe and Mn exposure in tadpoles of the bullfrog Lithobates catesbeianus. Aquatic Toxicology, 174, 101–108.
Widder, P. D., & Bidwell, J. R. (2006). Cholinesterase activity and behavior in chlorpyrifos-exposed Rana sphenocephala tadpoles. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 25, 2446–2454.
Wojtaszek, B. F., Staznik, B., Chartrand, D. T., Stephenson, G. R., & Thompson, D. G. (2004). Effects of vision® herbicide on mortality, avoidance response, and growth of amphibian larvae in two forest wetlands. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 23, 832–842.
Yabe, M. J. S. (1998). Metais pesados em águas superficiais como estratégia de caracterização de bacias hidrográficas. Química Nova, 21, 551.
Yan, D., Jiang, X., Xu, S., Wang, L., Bian, Y., & Yu, G. (2008). Quantitative structure-toxicity relationship study of lethal concentration to tadpole (Bufo vulgaris formosus) for organophosphorous pesticides. Chemosphere, 71, 1809–1815.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Agrobusiness RanaMat (Matão, Brazil) for providing the tadpoles. We also thank Diego Correia da Silva and Obede Rodrigues Alves for collecting the tailings samples in Mariana, MG, Brazil and Cristiano V. M. Araújo for supporting us with data analysis from Avoidance test.
Funding
This study was funded by “Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo” (FAPESP, Brazil, grant no. 2017/13377-6 and 2018/06259-0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Consent to Participate
All authors inform consent to participate in this manuscript.
Consent for Publication
Authors inform consent for the publication of any associated data and accompanying images.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(PDF 480 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Girotto, L., Espíndola, E.L.G., Gebara, R.C. et al. Acute and Chronic Effects on Tadpoles (Lithobates catesbeianus) Exposed to Mining Tailings from the Dam Rupture in Mariana, MG (Brazil). Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 325 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04691-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04691-y