Abstract
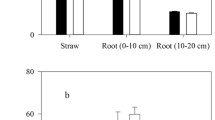
There is concern that transgenic Bt-crops carry genes that could have undesirable effects on natural and agro-ecosystem functions. We investigated the effect of Bt-cotton (expressing the Cry 1Ac protein) on several microbial and biochemical indicators in a sandy loam soil. Bt-cotton (MRC-6301Bt) and its non-transgenic near-isoline (MRC-6301) were grown in a net-house on a sandy clay loam soil. Soil and root samples were collected 60, 90, and 120 days after sowing. Soil from a control (no-crop) treatment was also included. Samples were analysed for microbial biomass C, N and P (MBC, MBN, MBP), total organic carbon (TOC), and several soil enzyme activities. The microbial quotient (MQ) was calculated as the ratio of MBC-to-TOC. The average of the three sampling events revealed a significant increase in MBC, MBN, MBP and MQ in the soil under Bt-cotton over the non-Bt isoline. The TOC was similar in Bt and non-Bt systems. Potential N mineralization, nitrification, nitrate reductase, and acid and alkaline phosphatase activities were all higher in the soil under Bt-cotton. Root dry weights were not different (P > 0.05), but root volume of Bt-cotton was higher on 90 and 120 days than that of non-Bt cotton. The time of sampling strongly affected the above parameters, with most being highest on 90 days after sowing. We concluded from the data that there were some positive or no negative effects of Bt-cotton on the studied indicators, and therefore cultivation of Bt-cotton appears to be no risk to soil ecosystem functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, T. H., & Domsch, K. H. (1989). Ratios of microbial biomass carbon to total organic carbon in arable soils. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 21, 471–479. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(89)90117-X.
Blackwood, C. B., & Buyer, J. S. (2004). Soil microbial communities associated with Bt and non-Bt corn in three soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 33, 832–836.
Bremner, E., & Kesssel, V. C. (1990). Extractability of microbial 14C and 15N following addition of variable rates of labeled glucose and ammonium sulphate to soil. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 22, 707–713. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(90)90019-V.
Brookes, P. C., Landham, A., Pruden, G., & Jenkinson, D. S. (1985). Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: A rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 17, 837–842. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(85)90144-0.
Brookes, P. C., Powlson, D. S., & Jenkinson, D. S. (1982). Measurement of microbial biomass phosphorus in soil. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 14, 319–329. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(82)90001-3.
Bruinsma, M., Kowalchuk, G. A., & van Veen, J. A. (2003). Effects of genetically modified plants on microbial communities and processes in soil. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 37, 329–337.
Donegan, K. K., Palm, C. J., Fieland, V. J., Porteous, L. A., Ganio, L. M., Schaller, D. L., et al. (1995). Changes in levels, species, and DNA fingerprints of soil microorganisms associated with cotton expressing the Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki endotoxin. Applied Soil Ecology, 2, 111–124. doi:10.1016/0929-1393(94)00043-7.
Donegan, K. K., & Seidler, R. J. (1999). Effects of transgenic plants on soil and plant microorganisms. In S. G. Pandalai (Ed.), Recent research development in microbiology (Vol. 3, Part II, pp. 415–424). Trivandrum, India: Research Signpost.
Dunsfield, K. E., & Germida, J. J. (2004). Impact of genetically modified crops on soil- and plant-associated microbial communities. Journal of Environmental Quality, 33, 806–815.
Fang, M., Motavalli, P. P., Kremer, R. J., & Nelson, K. A. (2007). Assessing changes in soil microbial communities and carbon mineralization in Bt and non-Bt corn residue-amended soils. Applied Soil Ecology, 37, 150–160. doi:10.1016/j.apsoil.2007.06.001.
Frankenberger, W. T., & Dick, W. A. (1983). Relationships between enzyme activities and microbial growth and activity indices in soil. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 47, 945–951.
Gomez, E., Ferreras, L., & Toresani, S. (2006). Soil bacterial functional diversity as influenced by organic amendment application. Bioresource Technology, 97, 1484–1489. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2005.06.021.
Griffiths, B. S., Caul, S., Thompson, J., Birch, A. N. E., Scrimgeour, C., Cortet, J., et al. (2006). Soil microbial and faunal community responses to Bt maize and insecticide in two soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 35, 734–741. doi:10.2134/jeq2005.0344.
Höfte, H., & Whiteley, H. R. (1989). Insecticidal crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis. Microbiological Reviews, 53, 242–255.
James, C. (2006). Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops: 2006. ISAAA Brief No. 35 (p. 12). Ithaca, NY: ISAAA.
Jenkinson, D. S., & Ladd, J. N. (1981). Microbial biomass in soil, measurement and turn over. In E. A. Paul, & J. N. Ladd (Eds.), Soil biochemistry (Vol. 5 , pp. 415–471). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Liu, B., Zeng, Q., Yan, F., Xu, H., & Xu, C. (2005). Effects of transgenic plants on soil microorganisms. Plant and Soil, 271, 1–13. doi:10.1007/s11104-004-1610-8.
Lynch, J. M., & Panting, L. M. (1980). Cultivation and the soil biomass. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 12, 29–33. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(80)90099-1.
Mandal, M., Patra, A. K., Singh, D., & Masto, R. E. (2007). Effect of long-term application of manure and fertilizer on biological and biochemical activities in soil during crop development stages. Bioresource Technology, 98, 3585–3592. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2006.11.027.
Motavalli, P. P., Kremer, R. J., Fang, M., & Means, N. E. (2004). Impact of genetically modified crops and their management on soil microbially mediated plant nutrient transformations. Journal of Environmental Quality, 33, 816–824.
Nannipieri, P., Ascher, J., Ceccherini, M. T., Landi, L., Pietramellara, G., & Renella, G. (2003). Microbial diversity and soil functions. European Journal of Soil Science, 54, 655–670. doi:10.1046/j.1351-0754.2003.0556.x.
O’Callaghan, M., Glare, T. R., Burgess, E. P. J., & Malone, L. A. (2005). Effects of plants genetically modified for insect resistance on nontarget organisms. Annual Review of Entomology, 50, 271–292. doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.50.071803.130352.
Patra, A. K., Abbadie, L., Clays-Josserand, A., Degrange, V., Grayston, S. J., Guillaumaud, N., et al. (2006). Effects of management regime and plant species on the enzyme activity and genetic structure of N-fixing, denitrifying and nitrifying bacterial communities in grassland soils. Environmental Microbiology, 8, 1005–1016. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.00992.x.
Pushpadas, M. V. (1979). Utilization of phosphorus from indigenous rock phosphates by legumes, as influenced by soil and plant factors. Ph.D. thesis, Division of Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry, Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi, 110 012, India.
Reddy, M. S., & Chhonkar, P. K. (1990). Dissimilatory nitrate reductase in soil and flood-waters as influenced by regulatory chemicals and oxygen stress. Journal of the Indian Society of Soil Science, 37, 658–662.
Rui, Y. K., Yi, G. X., Zhao, J., Wang, B. M., Li, Z. H., Zhai, Z. X., et al. (2005). Changes of Bt toxin in the rhizosphere of transgenic Bt cotton and its influence on soil functional bacteria. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 21, 1279–1284. doi:10.1007/s11274-005-2303-z.
Schmidt, E. L., & Belser, L. W. (1982). Nitrifying bacteria. In A. L. Page, R. H. Miller, & D. R. Keeney (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis, Part 2 (2nd ed., pp. 1011–1026). Wisconsin: American Society of Agronomy.
Snyder, J. D., & Trofymow, J. A. (1984). Rapid accurate wet oxidation diffusion procedure for determining organic and inorganic carbon in plant and soil samples. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 15, 1587–1597.
Stotzky, G. (2004). Persistence and biological activity in soil of the insecticidal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis, especially from transgenic plants. Plant and Soil, 266, 77–89. doi:10.1007/s11104-005-5945-6.
Sun, C. X., Chen, L. J., Wu, Z. J., Zhou, L. K., & Shimizu, H. (2007). Soil persistence of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) toxin from transgenic Bt cotton tissues and its effect on soil enzyme activities. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 43, 617–620. doi:10.1007/s00374-006-0158-6.
Tabatabai, M. A., & Bremner, J. M. (1969). Use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 1, 301–307. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(69)90012-1.
Tarafdar, J. C., & Claassen, N. (1988). Organic phosphorus compounds as a phosphorus source for higher plants through the activity of phosphatase produced by plant roots and microorganisms. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 5, 308–312. doi:10.1007/BF00262137.
Waring, S. A., & Bremner, J. M. (1964). Ammonium production in soil under waterlogged conditions as an index of nitrogen availability. Nature, 201, 951–952. doi:10.1038/201951a0.
Wei, X. D., Zou, H. L., Chu, L. M., Liao, B., Ye, C. M., & Lan, C. Y. (2006). Field released transgenic papaya affects microbial communities and enzyme activities in soil. Plant and Soil, 285, 347–358. doi:10.1007/s11104-006-9020-8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarkar, B., Patra, A.K., Purakayastha, T.J. et al. Assessment of biological and biochemical indicators in soil under transgenic Bt and non-Bt cotton crop in a sub-tropical environment. Environ Monit Assess 156, 595–604 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0508-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0508-y