Abstract
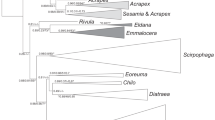
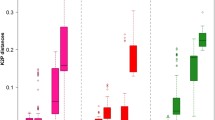
Root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) are important pests of numerous crops worldwide. Some members of this genus have a quarantine status, and accurate species identification is required to prevent further spreading. DNA barcoding is a method for organism identification in non-complex DNA backgrounds based on informative motifs in short DNA stretches (≈600 bp). As part of the EU 7th Framework project QBOL, 15 Meloidogyne species were chosen to compare the resolutions offered by two typical DNA barcoding loci, COI and COII, with the distinguishing signals produced by two ribosomal DNA genes (small and large subunit rDNA; SSU ≈ 1,700 and LSU ≈ 3,400 bp). None of the four markers distinguished between the tropical species Meloidogyne incognita, M. javanica and M. arenaria. Taking P ID (Liberal) values ≥0.93 as a measure for species delimitation, the four mtDNA and rDNA markers performed well for the tropical Meloidogyne species complex, M. enterolobii, M. hapla, and M. maritima. Within cluster III A (Holterman et al. Phytopathology, 99, 227–235, 2009), SSU rDNA did not offer resolution at species level. Both mtDNA loci COI and COII did, whereas for LSU rDNA a longer fragment (≥700 bp) is required. The high level of mitochondrial heteroplasmy recently reported for M. chitwoodi (Humphreys-Pereira and Elling Nematology, 15, 315–327, 2013) was not found in the populations under investigation, suggesting this could be a regional phenomenon. For identification of RKNs, we suggest the combined use of SSU rDNA with one of three other markers presented here.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blaxter, M. L. (2004). The promise of DNA taxonomy. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 359, 669–679.
Blaxter, M. L., De Ley, P., Garey, J. R., Liu, L. X., Scheldeman, P., Vierstraete, A., et al. (1998). A molecular evolutionary framework for the phylum Nematoda. Nature, 392, 71–75.
Blok, V. C., & Powers, T. O. (2009). Biochemical and molecular identification. In R. N. Perry, M. Moens, & J. L. Starr (Eds.), Root-knot nematodes (pp. 98–118). Wallingford: CABI Publishing.
Blok, V. C., Phillips, M. S., & Fargette, M. (1997). Comparison of sequences from the ribosomal DNA intergenic region of Meloidogyne mayaguensis and other major tropical root-knot nematodes. Journal of Nematology, 29, 16–22.
Bonants, P., Groenewald, E., Rasplus, J. Y., Maes, M., De Vos, P., Frey, J. E., et al. (2010). QBOL: a new EU project focusing on DNA barcoding of quarantine organisms. OEPP/EPPO Bulletin, 40, 30–33.
Calvignac, S., Konecny, L., Malard, F., & Douady, C. J. (2011). Preventing the pollution of mitochondrial datasets with nuclear mitochondrial paralogs (numts). Mitochondrion, 11, 246–254.
Derycke, S., Remerie, T., Vierstraete, A., Backeljau, T., van Fleteren, J., Vincx, M., et al. (2005). Mitochondrial DNA variation and cryptic speciation within the free-living marine nematode Pellioditis marina. Marine Ecology-Progress Series, 300, 91–103.
Derycke, S., Backeljau, T., Vlaeminck, C., Vierstraete, A., van Fleteren, J., Vincx, M., et al. (2006). Seasonal dynamics of population genetic structure in cryptic taxa of the Pellioditis marina complex (Nematoda : Rhabditida). Genetica, 128, 307–321.
Derycke, S., Backeljau, T., Vlaeminck, C., Vierstraete, A., van Fleteren, J., Vincx, M., et al. (2007). Spatiotemporal analysis of population genetic structure in Geomonhystera disjuncta (Nematoda, Monhysteridae) reveals high levels of molecular diversity. Marine Biology, 151, 1799–1812.
Derycke, S., De Ley, P., Tandigan De Ley, I., Holovachov, O., Rigaux, A., & Moens, T. (2010a). Linking DNA sequences to morphology: cryptic diversity and population genetic structure in the marine nematode Thoracostoma trachygaster (Nematoda, Leptosomatidae). Zoologica Scripta, 39, 276–289.
Derycke, S., Vanaverbeke, J., Rigaux, A., Backeljau, T., & Moens, T. (2010b). Exploring the use of cytochrome oxidase c subunit 1 (COI) for DNA barcoding of free-living marine nematodes. PLoS ONE, 5, e13716.
Floyd, R., Lima, J., DeWaard, J., Humble, L., & Hanner, R. (2010). Common goals: policy implications of DNA barcoding as a protocol for identification of arthropod pests. Biological Invasions, 12, 2947–2954.
Frey, J. E., & Frey, B. (2004). Origin of intra-individual variation in MR-amplified mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I of Thrips tabaci (Thysanoptera : Thripidae): mitochondrial heteroplasmy or nuclear integration? Hereditas, 140, 92–98.
Giblin-Davis, R. M., Hazir, S., Center, B. J., Ye, W., Keskin, N., Thorp, R. W., et al. (2005). Bursaphelenchus anatolius n. sp (Nematoda : Parasitaphelenchidae), an associate of bees in the genus Halictus. Journal of Nematology, 37, 336–342.
Gibson, T., Blok, V. C., Phillips, M. S., Hong, G., Kumarasinghe, D., Riley, I. T., et al. (2007). The mitochondrial subgenomes of the nematode Globodera pallida are mosaics: evidence of recombination in an animal mitochondrial genome. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 64, 463–471.
Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, C., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Decraemer, W., Vovlas, N., Prior, T., Rius, J. E. P., et al. (2012). Phylogeny, diversity, and species delimitation in some species of the Xiphinema americanum-group complex (Nematoda: Longidoridae), as inferred from nuclear and mitochondrial DNA sequences and morphology. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 134, 561–597.
Hall, T. A. (1999). BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series, 41, 95–98.
Hamilton, C. A., Hendrixson, B. E., Brewer, M. S., & Bond, J. E. (2014). An evaluation of sampling effects on multiple DNA barcoding methods leads to an integrative approach for delimiting species: a case study of the North American tarantula genus Aphonopelma (Araneae, Mygalomorphae, Theraphosidae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 71, 79–93.
Hebert, P. D. N., Cywinska, A., Ball, S. L., & DeWaard, J. R. (2003). Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 270, 313–321.
Holterman, M., van der Wurff, A., van den Elsen, S., van Megen, H., Bongers, T., Holovachov, O., et al. (2006). Phylum-wide analysis of SSU rDNA reveals deep phylogenetic relationships among nematodes and accelerated evolution toward crown clades. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 23, 1792–1800.
Holterman, M., Rybarczyk, K., Van den Elsen, S., Van Megen, H., Mooyman, P., Santiago, R. P., et al. (2008). A ribosomal DNA-based framework for the detection and quantification of stress-sensitive nematode families in terrestrial habitats. Molecular Ecology Resources, 8, 23–34.
Holterman, M., Karssen, G., van den Elsen, S., van Megen, H., Bakker, J., & Helder, J. (2009). Small subunit rDNA-based phylogeny of the Tylenchida sheds light on relationships among some high-impact plant-parasitic nematodes and the evolution of plant feeding. Phytopathology, 99, 227–235.
Holterman, M., Oggenfuss, M., Frey, J. E., & Kiewnick, S. (2012). Evaluation of high-resolution melting curve analysis as a new tool for root-knot nematode diagnostics. Journal of Phytopathology, 160, 59–66.
Hoolahan, A. H., Blok, V. C., Gibson, T., & Dowton, M. (2012). A comparison of three molecular markers for the identification of populations of Globodera pallida. Journal of Nematology, 44, 7–17.
Hu, M., Hoglund, J., Chilton, N. B., Zhu, X. Q., & Gasser, R. B. (2002). Mutation scanning analysis of mitochondria cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 reveals limited gene flow among bovine lungworm subpopulations in Sweden. Electrophoresis, 23, 3357–3363.
Humphreys-Pereira, D., & Elling, A. (2013). Intraspecific variability and genetic structure in Meloidogyne chitwoodi from the USA. Nematology, 15, 315327.
Kiewnick, S., Holterman, M., Helder, H., & Frey, J. E. (2011). QBOL—barcoding as a new tool for identification of quarantine nematodes and their close relatives. Phytopathology, 101, S90.
Kiewnick, S., Braun-Kiewnick, A., & Frey, J. E. (2013a). Development and validation of a real-time PCR assay for the detection and identification of the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne enterolobii, a new EPPO A2 list quarantine organism. Journal of Plant Diseases and Protection, 3, 142.
Kiewnick, S., Wolf, S., Willareth, M., & Frey, J. E. (2013b). Identification of the tropical root-knot nematode species Meloidogyne incognita, M. javanica and M. arenaria using a multiplex PCR assay. Nematology, 15, 891–894.
Kumari, S., Decraemer, W., De Luca, F., & Tiefenbrunner, W. (2010). Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 analysis of Xiphinema diversicaudatum, X. pachtaicum, X. simile and X. vuittenezi (Nematoda, Dorylaimida). European Journal of Plant Pathology, 127, 493–499.
Landa, B. B., Rius, J. E. P., Vovlas, N., Carneiro, R. M. D. G., Maleita, C. M. N., Abrantes, I. M., et al. (2008). Molecular characterization of Meloidogyne hispanica (Nematoda, Meloidogynidae) by phylogenetic analysis of genes within the rDNA in Meloidogyne spp. Plant Disease, 92, 1104–1110.
Liao, D. Q., Pavelitz, T., Kidd, J. R., Kidd, K. K., & Weiner, A. M. (1997). Concerted evolution of the tandemly repeated genes encoding human U2 snRNA (the RNU2 locus) involves vapid intrachromosomal homogenization and rare interchromosomal gene conversion. EMBO Journal, 16, 588–598.
Luca, F., Vovlas, N., Lucarelli, G., Troccoli, A., Radicci, V., Fanelli, E., et al. (2013). Heterodera elachista the Japanese cyst nematode parasitizing corn in Northern Italy: integrative diagnosis and bionomics. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 136, 857–872.
Madani, M., Subbotin, S. A., Ward, L. J., Li, X., & De Boer, S. H. (2010). Molecular characterization of Canadian populations of potato cyst nematodes, Globodera rostochiensis and G. pallida using ribosomal nuclear RNA and cytochrome b genes. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology, 32, 252–263.
Masters, B. C., Fan, V., & Ross, H. A. (2011). Species delimitation—a geneious plugin for the exploration of species boundaries. Molecular Ecology Resources, 11, 154–157.
Meldal, B. H. M., Debenham, N. J., De Ley, P., Tandigan De Ley, I., Van Fleteren, J. R., Vierstraete, A. R., et al. (2007). An improved molecular phylogeny of the Nematoda with special emphasis on marine taxa. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 42, 622–636.
Messing, J. (1983). New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods in Enzymology, 101, 20–78.
Nadler, S. A., & Hudspeth, D. S. S. (2000). Phylogeny of the ascaridoidea (Nematoda : Ascaridida) based on three genes and morphology: hypotheses of structural and sequence evolution. Journal of Parasitology, 86, 380–393.
Otranto, D., Testini, G., De Luca, F., Hu, M., Shamsi, S., & Gasser, R. B. (2005). Analysis of genetic variability within Thelazia callipaeda (Nematoda : Thelazioidea) from Europe and Asia by sequencing and mutation scanning of the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 gene. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 19, 306–313.
Ratnasingham, S., & Hebert, P. D. N. (2007). BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System (www.barcodinglife.org). Molecular Ecology Notes, 7, 355–364.
Rosenberg, N. A. (2007). Statistical tests for taxonomic distinctiveness from observations of monophyly. Evolution, 61, 317–323.
Ross, H. A., Murugan, S., & Li, W. L. S. (2008). Testing the reliability of genetic methods of species identification via simulation. Systematic Biology, 57, 216–230.
Rybarczyk-Mydłowska, K., Mooyman, P., van Megen, H., van den Elsen, S., Vervoort, M., Veenhuizen, P., et al. (2012). Small subunit ribosomal DNA-based phylogenetic analysis of foliar nematodes (Aphelenchoides spp.) and their quantitative detection in complex DNA backgrounds. Phytopathology, 102, 1153–1160.
Subbotin, S. A., Halford, P. D., Warry, A., & Perry, R. N. (2000). Variations in ribosomal DNA sequences and phylogeny of Globodera parasitising solanaceous plants. Nematology, 2, 591–604.
Subbotin, S. A., Vovlas, N., Crozzoli, R., Sturhan, D., Lamberti, F., Moens, M., et al. (2005). Phylogeny of Criconematina Siddiqi, 1980 (Nematoda : Tylenchida) based on morphology and D2-D3 expansion segments of the 28S-rRNA gene sequences with application of a secondary structure model. Nematology, 7, 927–944.
Tandigan De Ley, I., De Ley, P., Vierstraete, A., Karssen, G., Moens, M., & Van Fleteren, J. (2002). Phylogenetic analyses of Meloidogyne small subunit rDNA. Journal of Nematology, 34, 319–327.
Toumi, F., Waeyenberge, L., Viaene, N., Dababat, A., Nicol, J. M., Ogbonnaya, F., et al. (2013). Development of two species-specific primer sets to detect the cereal cyst nematodes Heterodera avenae and Heterodera filipjevi. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 136, 613–624.
Van Megen, H., Van den Elsen, S., Holterman, M., Karssen, G., Mooyman, P., Bongers, T., et al. (2009). A phylogenetic tree of nematodes based on about 1200 full-length small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Nematology, 11, 927–950.
Vervoort, M. T. W., Vonk, J. A., Mooijman, P. J. W., Van den Elsen, S. J. J., Van Megen, H. H. B., Veenhuizen, P., et al. (2012). SSU ribosomal DNA-based monitoring of nematode assemblages reveals distinct seasonal fluctuations within evolutionary heterogeneous feeding guilds. PLoS ONE, 7(10), e47555. doi:10.1371/journal.-pone.0047555.
Vovlas, N., Trisciuzzi, N., Troccoli, A., Luca, F., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., & Castillo, P. (2013). Integrative diagnosis and parasitic habits of Cryphodera brinkmani a non-cyst forming heteroderid nematode intercepted on Japanese white pine bonsai trees imported into Italy. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 135, 717–726.
Wesemael, W. M. L., Viaene, N., & Moens, M. (2011). Root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) in Europe. Nematology, 13, 3–16.
Wuyts, J., De Rijk, P., Van de Peer, Y., Pison, G., Rousseeuw, P., & De Wachter, R. (2000). Comparative analysis of more than 3000 sequences reveals the existence of two pseudoknots in area V4 of eukaryotic small subunit ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Research, 28, 4698–4708.
Ye, W., Giblin-Davis, R. M., Davies, K. A., Purcell, M. F., Scheffer, S. J., Taylor, G. S., et al. (2007). Molecular phylogenetics and the evolution of host plant associations in the nematode genus Fergusobia (Tylenchida: Fergusobiinae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 45, 123–141.
Zhao, Z. Q., Ye, W. M., Giblin-Davis, R. M., Li, D., & Thomas, W. K. (2008). Morphological and molecular analysis of six aphelenchoidoids from Australian conifers and their relationship to Bursaphelenchus (Fuchs, 1937). Nematology, 10, 663–678.
Zijlstra, C., Lever, A. E. M., Uenk, B. J., & van Silfout, C. H. (1995). Differences between ITS regions of isolates of root-knot nematodes Meloidogyne hapla and M. chitwoodi. Phytopathology, 85, 1231–1237.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our thanks to all colleagues who provided nematode material for this study. Funding was supplied by EU 7th Framework project QBOL (KBBE-2008-1-4-01). Initial work on the COI gene was funded by the Swiss State Secretariat for Education and Research (SER) as part of COST Action 872 (project nr. C07.0072). We also would like to acknowledge all colleagues from the QBOL project and our partner institutes for proving the reference material used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiewnick, S., Holterman, M., van den Elsen, S. et al. Comparison of two short DNA barcoding loci (COI and COII) and two longer ribosomal DNA genes (SSU & LSU rRNA) for specimen identification among quarantine root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) and their close relatives. Eur J Plant Pathol 140, 97–110 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0446-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0446-1