Abstract
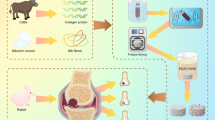
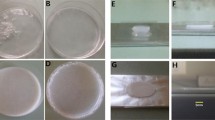
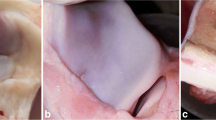
The aim of this study was the development of collagen and collagen/auricular cartilage scaffolds for application in dermal regeneration. Collagen was obtained from bovine tendon by a 72 h-long treatment, while bovine auricular cartilage was treated for 24 h and divided into two parts, external (perichondrium, E) and internal (elastic cartilage, I). The scaffolds were prepared by mixing collagen (C) with the internal part (CI) or the external part (CE) in a 3:1 ratio. Differential scanning calorimetry, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis, microcomputed tomography imaging (micro-CT) and swelling degree were used to characterize the scaffolds. Cytotoxicity, cell adhesion, and cell proliferation assays were performed using the cell line NIH/3T3. All samples presented a similar denaturation temperature (Td) around 48 °C, while CE presented a second Td at 51.2 °C. SEM micrographs showed superficial pores in all scaffolds and micro-CT exhibited interconnected pore spaces with porosity above 60% (sizes between 47 and 149 µm). The order of swelling was CE < CI < C and the scaffolds did not present cytotoxicity, showing attachment rates above 75%—all samples showed a similar pattern of proliferation until 168 h, whereas CI tended to decrease after this time. The scaffolds were easily obtained, biocompatible and had adequate morphology for cell growth. All samples showed high adhesion, whereas collagen-only and collagen/external part scaffolds presented a better cell proliferation rate and would be indicated for possible use in dermal regeneration.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annabi N, Fathi A, Mithieux SM, Martens P, Weiss AS, Dehghani F (2011) The effect of elastin on chondrocyte adhesion and proliferation on poly (ɛ-caprolactone)/elastin composite. Biomaterials 32:1517–1525
Ashworth JC, Best SM, Cameron RE (2014) Quantitative architectural description of tissue engineering scaffolds. Mater Technol 29(5):281–295. https://doi.org/10.1179/1753555714Y.0000000159
Batista TM, Martins VCA, Plepis AMG (2009) Thermal behavior of in vitro mineralized anionic collagen matrices. J Therm Anal Calorim 95(3):945–949
Bet MR, Goissis G, Lacerda CA (2001) Characterization of polyanionic collagen prepared by selective hydrolysis of asparagine and glutamine carboxyamide side chains. Biomacromol 2:1074–1079
Boekema BKHL, Vlig M, Damink LO, Middelkoop E, Eummelen L, Bühren AV, Ulrich MMW (2014) Effect of pore size and cross-linking of a novel collagen–elastin dermal substitute on wound healing. J Mater Sci Mater Med 25:423–433
Bružauskaitė I, Bironaitė D, Bagdonas E, Bernotienė E (2016) Scaffolds and cells for tissue regeneration: different scaffold pore sizes-different cell effects. Cytotechnology 68(3):355–369
Campbell JJ, Husmann A, Hume RD, Watson CJ, Cameron RE (2017) Development of three-dimensional collagen scaffolds with controlled architecture for cell migration studies using breast cancer cell lines. Biomaterials 114:34–43
Chan EC, Kuo S-M, Kong AM, Morrison WA, Dusting GJ, Mitchell GM et al (2016) Three dimensional collagen scaffold promotes intrinsic vascularisation for tissue engineering applications. PLoS ONE 11(2):e0149799. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0149799
Chattopadhyay S, Raines RT (2014) Review collagen-based biomaterials for wound healing. Biopolymers 101(8):821–833
Chaudhari AA, Vig K, Baganizi DR, Sahu R, Dixit S, Dennis V, Singh SR, Pillai SR (2016) Future prospects for scaffolding methods and biomaterials in skin tissue engineering: a review. Int J Mol Sci 17:1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17121974
Daskalova A, Nathala CSR, Bliznakova I, Stoyanova E, Zhelyazkova A, Ganz T, Lueftenegger S, Husinsky W (2014) Controlling the porosity of collagen, gelatin and elastin biomaterials by ultrashort laser pulses. Appl Surf Sci 292:367–377
Dietz HC, Mecham RP (2000) Mouse models of genetic diseases resulting from mutations in elastic fiber proteins. Matrix Biol 19(6):481–488
Dunphy SE, Bratt JA, Akram KM, Forsyth NR, El Han AJ (2014) Hydrogels for lung tissue engineering: biomechanical properties of thin collagen–elastin constructs. J Mech Behav Biomed Mat 38:251–259
Gabbai-Armelin PR, Caliari HM, Silva DF, Cruz MA, Magri AMP, Fernandes KR, Renno ACM (2018) Association of bioglass/collagen/magnesium composites and low level irradiation: effects on bone healing in a model of tibial defect in rats. Laser Ther 27(4):271–282. https://doi.org/10.5978/islsm.27_18-or-25
Grover CN, Cameron RE, Best SM (2012) Investigating the morphological, mechanical and degradation properties of scaffolds comprising collagen, gelatin and elastin for use in soft tissue engineering. J Mech Behav Biomed Mat 10:62–74
Haagdorens M, Cėpla V, Melsbach E, Koivusalo L, Skottman H, Griffith M, Valiokas R, Zakaria N, Pintelon I, Tassignon M-J (2019) In vitro cultivation of limbal epithelial stem cells on surface-modified crosslinked collagen scaffolds. Stem Cells Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7867613
Hadisi Z, Nourmohammadi J, Mohammadi J (2015) Composite of porous starch-silk fibroin nanofiber-calcium phosphate for bone regeneration. Ceram Int 41:10745–10754
Horn MM, Martins VCA, Plepis AMG (2015) Influence of collagen addition on the thermal and morphological properties of chitosan/xanthan hydrogels. Int J Biol Macromol 80:225–230
International Organization for Standardization (2009) ISO 10,993-5: biological evaluation of medical devices—part 5: tests for in vitro cytotoxicity. Genebra
International Organization for Standardization (2012) ISO 10,993-12: biological evaluation of medical devices—part 12: sample preparation and reference materials. Genebra
International Organization for Standardization (2017) ISO 11,137-3: Sterilization of health care products—radiation—part 3: guidance on dosimetric aspects of development, validation and routine control. Genebra
Kaul H, Ventikos Y (2015) On the genealogy of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Tissue Eng Part B 21(2):203–217
Keck M, Haluza D, Burjak S, Eisenbock B, Kamolz L-P, Frey M (2009) Cultivation of keratinocytes and preadipocytes on a collagen–elastin scaffold (Matriderm®): first results of an in vitro study. Eur Surg 41(4):189–193
Kinikoglu B, Rodríguez-Cabello JC, Damour O, Hasirci V (2011) A smart bilayer scaffold of elastin-like recombinamer and collagen for soft tissue engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med 22:1541–1554. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-011-4315-6
Lee P, Yeo GC, Weiss AS (2017) A cell adhesive peptide from tropoelastin promotes sequential cell attachment and spreading via distinct receptors. FEBS J 284:2216–2230. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14114
Lönroth EC, Dahl SE (2003) Citotoxicity of liquidas and powers of chemically different dental materials evaluated using dimethylthiazoldiphenyl tetrazoliun and neutral red tests. Acta Scand 61(1):52–56
Low SP, Williams KA, Canham LT, Voelcker NH (2006) Evaluation of mammalian cell adhesion on surface-modified porous silicon. Biomaterials 27:4538–4546
Milewicz DM, Urbán Z, Boyd C (2000) Genetic disorders of the elastic fiber system. Matrix Biol 19(6):471–480
Minardi S, Taraballi F, Wang X, Cabrera FJ, Van Eps JL, Robbins AB, Sandri M, Moreno MR, Weiner BK, Tasciotti E (2017) Biomimetic collagen/elastin meshes for ventral hernia repair in a rat model. Acta Biomater 50:165–177
Mizutani N, Kageyama S, Yamada M, Hasegawa M, Miyamoto K, Horiuchi T (2014) The behavior of ligament cells cultured on elastin and collagen scaffolds. J Artif Organs 17:50–59
Nam S, Cho W, Cho H, Lee J, Lee E, Son Y (2014) Xiphoid process-derived chondrocytes: a novel cell source for elastic cartilage regeneration. Stem Cell Transl Med 3:1381–1391. https://doi.org/10.5966/sctm.2014-0070
Nguyen T-U, Shojaee M, Bashur CA, Kishore V (2019) Electrochemical fabrication of a biomimetic elastin-containing bi-layered scaffold for vascular tissue engineering. Biofabrication 11:015007. https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5090/aaeab0
Nimeskern L, Utomo L, Lehtoviita I, Fessel G, Snedeker JG, Van Osch GJVM, Müller R, Stok KS (2016) Tissue composition regulates distinct viscoelastic responses in auricular and articular cartilage. J Biomech 49:344–352
Nocera AD, Comín R, Salvatierra NA, Cid MP (2018) Development of 3D printed fibrillar collagen scaffold for tissue engineering. Biomed Microdevices 20:26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-018-0270-z
Okuneva EG, Kozina AA, Baryshnikova NV, Yu Krasnenko A, Yu Tsukanov K, Klimchuk OI, Surkova EI, Ilinsky VV (2019) A novel elastin gene frameshift mutation in a Russian family with cutis laxa: a case report. BMC Dermatol 19:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12895-019-0084-6
Patel M, Fisher JP (2008) Biomaterial scaffolds in pediatric tissue engineering. Pediatr Res 63(5):497–501
Pina S, Ribeiro VP, Marques CF, Maia FR, Silva TH, Reis RL, Oliveira JM (2019) Scaffolding strategies for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications. Materials 12:1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111824
Plessis A, Broeckhoven C, Guelpa A, Le Roux SG (2017) Laboratory x-ray micro-computed tomography: a user guideline for biological samples. GigaScience 6:1–11
Sakata R, Iwakura T, Reddi AH (2015) Regeneration of articular cartilage surface: morphogens, cells, and extracelular matrix scaffolds. Tissue Eng Part B 21(5):461–473
Sletten GB, Dahl JE (1999) Cytotoxicity effects of extracts of compomers. Acta Odont Scand 57(6):316–322
Song P, Zhou C, Fan H, Zhang B, Pei X, Fan Y, Jiang Q, Bao R, Yang Q, Dong Z (2018) Novel 3D porous biocomposite scaffolds fabricated by fused deposition modeling and gas foaming combined technology. Compos Part B Eng 152:151–159
Starcher B, Aycock RL, Hill CH (2005) Multiple roles for elastic fibers in the skin. J Histochem Cytochem 53(4):431–443
Stoppel WL, Ghezzi CE, Mcnamara SL, Black Iii LD, Kaplan DL (2015) Clinical applications of naturally derived biopolymers-based scaffolds for regenerative medicine. Ann Biomed Eng 43(3):657–680
Tejeda-Montes E, Klymov A, Nejadnik MR, Alonso M, Rodriguez-Cabello JC, Walboomers XF, Mata A (2014) Mineralization and bone regeneration using a biactive elastin-like recombinamer membrane. Biomaterials 35:8339–8347
Wang Y, Xu R, He W, Yao Z, Li H, Zhou J, Tan J, Yang S, Zhan R, Luo G, Wu J (2015) Three-dimensional histological structures of the humans dermis. Tissue Eng Part C 21(9):932–944
Zidek J, Vojtova L, Abdel-Mohsen AM, Chmelik J, Zikmund T, Brtnikova J, Jakubicek R, Zubal L, Jan J, Kaiser J (2016) Accurate micro-computed tomography imaging of pore spaces in collagen-based scaffold. J Mater Sci Mater Med 27:110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-016-5717-2
Acknowledgements
This study was financed in part by the following Brazilian institutions: Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001; National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) (308076/2018-4 and 140215/2015-8); Centro de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento Leopoldo Américo Miguez de Mello (Cenpes/Petrobras) (ANP 2014/00389-8); and International Atomic Energy Agency through the IAEA Research Contract No. 18283 (2014-2019). The authors thank the CETER multi-purpose irradiator group for sterilizing the samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Massimino, L.C., da Conceição Amaro Martins, V., Vulcani, V.A.S. et al. Use of collagen and auricular cartilage in bioengineering: scaffolds for tissue regeneration. Cell Tissue Bank 25, 111–122 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-020-09861-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-020-09861-0