Abstract
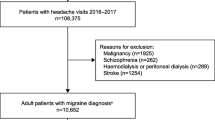
Treatment of chronic migraine with medication overuse requires withdrawal from acute medications. However, guidelines and clear indications for different intensity regimens, i.e., day hospital (DH) vs. inpatient treatment, are not available. Patients completed disability, quality of life (QoL) and depression questionnaires; headaches frequency and overused medications category were collected. Mann–Whitney U test and Chi square were used to assess differences between inpatients and DH patients; Bonferroni correction was applied. 194 patients aged 43.9 ± 12 (160 females) were enrolled (100 from DH, 94 inpatients). Inpatients were older, less educated and with lower employment rates. Inpatients had higher MIDAS scores (P = 0.003) and headache frequency (P = 0.002). They had lower QoL for restrictive (P = 0.002) and preventive components; no difference was found for disability, mood state and QoL emotional component. Patients treated during hospitalization had higher disease severity and lower quality of life, but similar disability and mood state than those treated in DH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Silberstein SD, Lipton RB, Sliwinski M (1996) Classification of daily and near-daily headaches: field trial of revised IHS criteria. Neurology 47:871–875
Castillo J, Munoz P, Guitera V et al (1993) Kaplan Award 1998. Epidemiology of chronic daily headache in the general population. Headache 39:190–196
Natoli JL, Manack A, Dean B et al (2010) Global prevalence of chronic migraine: a systematic review. Cephalalgia 30:599–609
Lipton RB (2009) Tracing transformation: chronic migraine classification, progression, and epidemiology. Neurology 72(Suppl 5):S3–S7
D’Andrea G, D’Amico D, Bussone G et al (2013) The role of tyrosine metabolism in the pathogenesis of chronic migraine. Cephalalgia 33:932–937
Ferraro S, Grazzi L, Muffatti R et al (2012) In medication-overuse headache, fMRI shows long-lasting dysfunction in midbrain areas. Headache 52:1520–1534
Coppola G, Currà A, Di Lorenzo C et al (2010) Abnormal cortical responses to somatosensory stimulation in medication-overuse headache. BMC Neurol 10:126
Bigal ME, Lipton RB (2011) Migraine chronification. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 11:139–148
Bigal ME, Serrano D, Buse D et al (2008) Acute migraine medications and evolution from episodic to chronic migraine: a longitudinal population-based study. Headache 48:1157–1168
Bigal ME, Lipton RB (2009) Overuse of acute migraine medications and migraine chronification. Curr Pain Headache Rep 13:301–307
Starling AJ, Hoffman-Snyder C, Halker RB et al (2011) Risk of development of medication overuse headache with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug therapy for migraine: a critically appraised topic. Neurologist 17:297–299
Limmroth V, Katsarava Z, Fritsche G et al (2002) Features of medication overuse headache following overuse of different acute headache drugs. Neurology 59:1011–1014
Zwart JA, Dyb G, Hagen K et al (2004) Analgesic overuse among subjects with headache, neck, and low-back pain. Neurology 62:1540–1544
Cevoli S, Sancisi E, Grimaldi D et al (2009) Family history for chronic headache and drug overuse as a risk factor for headache chronification. Headache 49:412–418
Rains JC (2008) Chronic headache and potentially modifiable risk factors: screening and behavioral management of sleep disorders. Headache 48:32–39
Buse DC, Silberstein SD, Manack AN et al (2013) Psychiatric comorbidities of episodic and chronic migraine. J Neurol 260:1960–1969
Evers S, Jensen R (2011) Treatment of medication overuse headache—guideline of the EFNS headache panel. Eur J Neurol 18:1115–1121
Paemelaire K, Crevitis L, Goadsby PH et al (2006) Practical management of medication overuse headache. Acta Neurol Belg 106:43–51
Obermann M, Katsarava Z (2007) Management of medication overuse headache. Expert Rev Neurother 7:1145–1155
Grazzi L, Andrasik F, Usai S et al (2008) In-patient vs. day-hospital withdrawal treatment for chronic migraine with medication overuse and disability assessment: results at one-year follow-up. Neurol Sci 29(Suppl 1):S161–S163
Stewart WF, Lipton RB, Whyte J et al (1999) An international study to assess reliability of the Migraine Disability Assessment (MIDAS) score. Neurology 53:988–994
D’Amico D, Mosconi P, Genco S et al (2001) The Migraine Disability Assessment (MIDAS) questionnaire: translation and reliability of the Italian version. Cephalalgia 21:947–952
Ustun TB, Chatterji S, Kostanjsek N et al (2010) Developing the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule 2.0. Bull World Health Organ 88:815–823
Martin BC, Pathak DS, Sharfman MI et al (2000) Validity and reliability of the Migraine-Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire (MSQ Version 2.1). Headache 40:204–215
Raggi A, Giovannetti AM, Schiavolin S et al (2014) Validating the Migraine-Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire v2.1 (MSQ) in Italian inpatients with chronic migraine with a history of medication overuse. Qual Life Res 23:1273–1277
Beck AT, Steer RA, Brown GK (1996) Manual for the Beck Depression Inventory-II. Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Raggi A, Schiavolin S, Leonardi M et al (2015) Chronic migraine with medication overuse: association between disability and quality of life measures, and impact of disease on patients’ lives. J Neurol Sci 348:60–66
Blumenfeld A, Varon S, Wilcox TK et al (2011) Disability, HRQoL and resource use among chronic and episodic migraineurs: results from the International Burden of Migraine Study (IBMS). Cephalalgia 31:301–315
Buse DC, Manack A, Serrano D et al (2010) Sociodemographic and comorbidity profiles of chronic migraine and episodic migraine sufferers. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81:428–432
Raggi A, Giovannetti AM, Leonardi M et al (2012) Disability and mood state in patients with episodic and chronic migraine associated to medication overuse. Neurol Sci 33(Suppl 1):S169–S171
Acknowledgments
This paper is based on the results of DIS.CHRONIC project, sponsored by the Neurological Institute C. Besta IRCCS Foundation.
Conflict of interest
The authors certify that there is no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raggi, A., Schiavolin, S., Leonardi, M. et al. Approaches to treatments of chronic migraine associated with medication overuse: a comparison between different intensity regimens. Neurol Sci 36 (Suppl 1), 5–8 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2134-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2134-0