Abstract
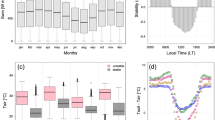
This study focuses on the relationships between wind velocity, temperature, water vapour, CO2, and the stability parameters over an alpine wetland. The turbulence data collected by a suite of instruments in the Maduo wetland, which is located at the source of the Yellow River (from June to August 2014), were used to study the characteristics of turbulence transport, turbulence kinetic energy, humidity variance, temperature variance, CO2 variance, and turbulence intensity. The results show that the normalized standard deviation of the wind velocity components (σ u , σ v , and σ w ) generally satisfies a 1/3 power-law relation. The values of σ u,v,w /u * increase with increasing |(z − d)/L|. Moreover, the normalized standard deviation of the temperature, CO2, and water vapour is scatter under stable stratification at night. However, they increase as the absolute stability parameters decrease under unstable stratification. The results also indicate that the turbulent kinetic energy and turbulence intensity reach their peak values when the stability parameter is close to zero. When the wind velocity is less than 2 m/s, the turbulence intensities in the three directions decrease rapidly with increasing wind velocity. Moreover, the average value of C D (the overall momentum transfer coefficient) is significantly larger than those of C H (the sensible heat transfer coefficient) under different conditions. The bulk transport coefficient decreases as the stability increases. Finally, because of the high temperatures, the leaf stomata are nearly closed, and the pulse of the CO2 flux is very small at noon time. Meanwhile, the latent and sensible heat fluxes reach their maximum values.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo OC, Costa FD, Oliveira PES et al (2014) The influence of submeso processes on stable boundary layer similarity relationships. J Atmos Sci 71(1):207–225
Agarwal P, Yadav AK, Gulati A et al (1995) Surface layer turbulence processes in low wind speeds over land. Atmos Environ 29(16):2089–2098
Al-Jiboori MH, Xu Y, Qian Y (2001) Turbulence characteristics over complex terrain in West China. Bound Layer Meteorol 101(1):109–126
Andreas EL, Hicks BB (2002) Comments on ‘Critical test of the validity of Monin–Obukhov similarity during convective conditions’. J Atmos Sci 59(17):2605–2607
Bastiaanssen WGM, Menenti M, Feddes RA et al (1998) A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL). 1. Formulation. J Hydrol 212–213(1–4):213–229
Bian LG, Lu LH, Cheng YJ (2001) Turbulent measurement over the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Q J Appl Meteorol 12:1–13
Bradley EF, Antonia RA, Chambers AJ (1981) Turbulence Reynolds number and the turbulent kinetic energy balance in the atmospheric surface layer. Bound Layer Meteorology 21(2):183–197
Brutsaert W (1973) Further comments on ‘radiation, evaporation and the maintenance of turbulence under stable conditions in the lower atmosphere’. Bound Layer Meteorol 3:394–396
Chen BL (2014) A study of land surface energy and water in soil freezing and thawing process and impact on regional climate of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau (Doctor). Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing (Chinese)
Chen YG, Zhang Y, Wang SY (2014) Seasonal variation of turbulence characteristics over Alpine meadow ecosystem. Plateau Meteorol 33:585–595 (Chinese)
Dyer AJ, Bradley EF (1982) Flux-gradient relationship in the constant flux layer. Q J R Meteorol Soc 96:495–506
Grachev AA, Bariteau L, Fairall CW et al (2011) Turbulent fluxes and transfer of trace gases from ship-based measurements during TexAQS 2006. J Geophys Res Atmos 116(D13):1016–1022
Grachev AA, Leo LS, Sabatino SD et al (2016) Structure of turbulence in Katabatic flows below and above the wind-speed maximum. Bound Layer Meteorol 159(3):469–494
Hamming RW (2006) Numerical methods for scientists and engineers/R.W. Hamming. Koleksi Buku Upt Perpustakaan Universitas Negeri Malang
Han C, Ma Y, Su Z, Chen X, Zhang L, Li M, Sun F (2015) Estimates of effective aerodynamic roughness length over mountainous areas of the Tibetan Plateau. Q J Roy Meteor Soc 141:1457–1465
Harlow FH, Welch JE (1965) Numerical calculation of Time-dependent viscous incompressible flow of fluid with free surface. Phys Fluids 8(12):2182
Hicks BB (1978) Some limitations of dimensional analysis and power laws. Bound Layer Meteorol 14(4):567–569
Högström U (1996) Review of some basic characteristics of the atmospheric surface layer. Bound Layer Meteor 78:215–246
Johansson C, Smedman A-S, Högström U, Brasseur JG, Khanna S (2001) Critical test of the validity of Monin-Obukhov similarity during convective conditions. J Atmos Sci 58:1549–1566
Katul G, Goltz SM, Hsieh CI, Cheng Y, Mowry F, Sigmon J (1995) Estimation of surface heat and momentum fluxes using the flux-variance method above uniform and non-uniform terrain. Bound Layer Meteorol 74:237–260
Klipp CL, Mahrt L (2004) Flux–gradient relationship, self-correlation and intermittency in the stable boundary layer. Q J R Meteorol Soc 132(617):1375
Lagouarde JP, Mcaneney KJ (1992) Daily sensible heat flux estimation from a single measurement of surface temperature and maximum air temperature. Bound Layer Meteorol 59(4):341–362
Leuning R (2004) Measurements of trace gas fluxes in the atmosphere using eddy covariance: WPL corrections revisited. Handbook of Micrometeorology:119–132
Li GP, Duan TY, Gong YF (2002) A composite study of the surface fluxes on the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Meteorol Sin 60:453–459
Li MS, Ma YM, Ma WQ, Hu Z, Ishikawa H, Su Z, Sun F (2006) Analysis of turbulence characteristics over the Northern Tibetan Plateau area. Adv Atmos Sci 23:579–585
Li Y, Li YQ, Zhao XB (2009) Analysis of turbulent characteristics in the surface layer in Litang region on the east edge of Tibetan Plateau. Plateau Meteorol 4:745–753 (Chinese)
Li SS, Lv SH, Gao YH (2012) Analysis of the statistical characteristics of the turbulent data at Maqu area in the upper Yellow River. Adv Earth Sci 27:901–907
Liu SH, Liu HP, Hong ZX (1996) The turbulence structure in the near-surface atmospheric layer over the Horqin Grassland. Chin J Atmos Sci 3:378–383 (Chinese)
Ma YM, Ma WQ, Hu ZY, Li MS, Wang JM (2002) Similarity analysis of atmospheric turbulent intensity over grassland surface of Qinghai–Xizang Plateau. Plateau Meteorol 21:514–517 (Chinese)
Mahrt L (2009) Characteristics of Submeso winds in the stable boundary layer. Bound Layer Meteorol 130(1):1–14
Mahrt L, Sun J, Blumen W, Delany T, Oncley S (1998) Nocturnal boundary layer regimes. Bound Layer Meteorol 88:255–278
Moraes OLL, Acevedo OC, Degrazia GA, Anfossi D, Silva RD, Anabor V (2005) Surface layer turbulence parameters over a complex terrain. Atmos Environ 39:3103–3112
Nadeau DF, Pardyjak ER, Higgins CW et al (2013) Similarity scaling over a steep Alpine Slope. Bound Layer Meteorol 147(3):401–419
Nordbo A, Järvi L, Haapanala S, Moilanen J, Vesala T (2013) Intra-city variation in urban morphology and turbulence structure in Helsinki, Finland. Bound Layer Meteorol 146:469–496
Panofsky HA, Dutton JA (1984) Atmospheric turbulence: models and methods for engineering applications. Wiley, New York
Panofsky HA, Tennekes H, Lenschow DH, Wyngaard JC (1977) The characteristics of turbulent velocity components in the surface layer under convective conditions. Bound Layer Meteorol 11:355–361
Pawlak W, Fortuniak K, Siedlecki M et al (2016) Urban–Wetland contrast in turbulent exchange of methane. Atmos Environ 145:176–191
Pegahfar N, Bidokhti AA (2013) Similarity relations in a stable and relatively neutral surface layer in an urban area with complex topography (Tehran). Environ Fluid Mech 13(1):1–31
Qi YQ, Wang JM, Li J (1996) A study of turbulent transfer characteristics in Wu Daoliang area of Qinghai–Xizang Plateau. Plateau Meteorol 15:172–177 (Chinese)
Quan L, Hu F (2009) Relationship between turbulent flux and variance in the urban canopy. Meteorol Atmos Phys 104:29–36
Rannik Ü (1998) On the surface layer similarity at a complex forest site. J Geophys Res Atmos 103:8685–8697
Schotanus P, Nieuwstadt FTM, Bruin HARD (1983) Temperature measurement with a sonic anemometer and its application to heat and moisture fluxes. Bound-Layer Meteorol 6(1):81–93
Shang LY, Lv SH, Zhang Y, Luo SQ (2011) Analysis on atmospheric surface layer turbulence characteristic during soil freezing and thawing seasons in Eastern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Plateau Meteorol 30:30–37 (Chinese)
Shao Y, Hacker JM (1990) Local similarity relationships in a horizontally inhomogeneous boundary layer. Bound Layer Meteorol 52(1):17–40
Singha A, Sadr R (2012) Characteristics of surface layer turbulence in coastal area of Qatar. Environ Fluid Mech 12(6):515–531
Stiperski I, Rotach MW (2016) On the measurement of turbulence over complex mountainous terrain. Bound Layer Meteorol 159(1):1–25
Sun J, Hu ZY, Chen XL (2012) Comparative analysis on momentum bulk transfer coefficients and roughness length under the different underlying surfaces in upper and middle reaches of Heihe River Basin. Plateau Meteorol 31:920–926 (Chinese)
Wang JM, Liu XH, Ma YM (1993) Turbulence structure and transfer characteristics in the surface layer of HEIFE Gobi area. Acta Meteorol Sin 3:343–350 (Chinese)
Wang HJ, Jing L, Gao YX (2005) A simulation study on the shrunk wetland around Qinghai Lake and regional climate. Wetland Sci 3:83–97 (Chinese)
Wang S, Yu Z, Lü S et al (2013) Estimation of turbulent fluxes using the flux-variance method over an alpine meadow surface in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Adv Atmos Sci 30:411–424
Weaver HL (1990) Temperature and humidity flux variance relations determined by one dimensional eddy correlation. Bound Layer Meteorol 53:77–91
Wu H, Ye BS, Wu JK (2013) Analysis on turbulent feature of Alpine meadow in the upper reach of Shule River. Plateau Meteorol 32:368–376 (Chinese)
Xu XD, Zhou MY, Chen JY (2001) Comprehensive physical image of the dynamic and thermal structure of the land-atmosphere process on the Qinghai Tibetan Plateau. Sci China 31:428–440
Xu X, Zhou M, Chen J (2002) A comprehensive physical pattern of land-air dynamic and thermal structure on the Qinghai–Xizang Plateau. Sci China 45:577–694
Yang Z, Liu JS, Zhu YW (2010) Analyses of turbulence characteristics in the surface layer at Dali of the western Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau. Trans Atmos Sci 33:117–124
Yue P, Zhang Q, Zhao W (2015) Characteristics of turbulence transfer in surface layer over semi-arid grassland in Loess Plateau in summer. Plateau Meteorol 34:21–29 (Chinese)
Zhu ZK, Ma YM, Li MS (2007) Diurnal and seasonal variations of the carbon dioxide over the Alpine meadow ecosystem on the northern slope of the Qomolangma. Plateau Meteorol 26:1300–1304 (Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41530529, 41505078, and 41405079) and the Key Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZZD-EW-13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: S. T. Castelli.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, D., Wen, J., Ma, Y. et al. The warm season characteristics of the turbulence structure and transfer of turbulent kinetic energy over alpine wetlands at the source of the Yellow River. Meteorol Atmos Phys 130, 529–542 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-017-0534-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-017-0534-9