Abstract
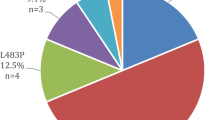
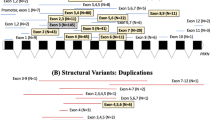
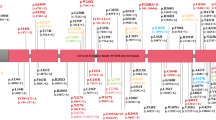
GBA variants are associated with increased risk and earlier onset of Parkinson’s disease (PD), and more rapid disease progression especially with “severe” variants typified by p.L483P. GBA mutation screening studies from South-East Asia, with > 650 million inhabitants of diverse ancestries, are very limited. We investigated the spectrum of GBA variants, and associated clinico-demographic features, in a multi-ethnic PD cohort in Malaysia. Patients (n = 496) were recruited from seven centres, primarily of Chinese (45%), Malay (37%), and Indian (13%) ethnicities. All GBA coding exons were screened using a next-generation sequencing-based PD gene panel and verified with Sanger sequencing. We identified 14 heterozygous GBA alleles consisting of altogether 17 missense variants (8 classified as pathogenic or likely pathogenic for PD) in 25 (5.0%) patients, with a substantially higher yield among early (< 50 years) vs. late-onset patients across all three ethnicities (9.1–13.2% vs. 1.0–3.2%). The most common variant was p.L483P (including RecNciI, n = 11, 2.2%), detected in all three ethnicities. Three novel variants/recombinant alleles of uncertain significance were found; p.P71L, p.L411P, and p.L15S(;)S16G(;)I20V. The common European risk variants, p.E365K, p.T408M, and p.N409S, were not detected. A severe disease course was noted in the majority of GBA-variant carriers, across a range of detected variants. We report a potentially novel observation of spine posture abnormalities in GBA-variant carriers. This represents the largest study on GBA variation from South-East Asia, and highlights that these populations, especially those with EOPD, would be relevant for studies including clinical trials targeting GBA pathways.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and additional files. Further anonymised data from this published article are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Alcalay RN, Caccappolo E, Mejia-Santana H, Tang M, Rosado L, Orbe Reilly M, Ruiz D, Ross B, Verbitsky M, Kisselev S, Louis E, Comella C, Colcher A, Jennings D, Nance M, Bressman S, Scott WK, Tanner C, Mickel S, Andrews H, Waters C, Fahn S, Cote L, Frucht S, Ford B, Rezak M, Novak K, Friedman JH, Pfeiffer R, Marsh L, Hiner B, Siderowf A, Payami H, Molho E, Factor S, Ottman R, Clark LN, Marder K (2012) Cognitive performance of GBA mutation carriers with early-onset PD: the CORE-PD study. Neurology 78(18):1434–1440. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e318253d54b
Alfonso P, Aznarez S, Giralt M, Pocovi M, Giraldo P, Spanish Gaucher’s Disease R (2007) Mutation analysis and genotype/phenotype relationships of Gaucher disease patients in Spain. J Hum Genet 52(5):391–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10038-007-0135-4
Biswas A, Sadhukhan D, Biswas A, Das SK, Banerjee TK, Bal PS, Pal S, Ghosh A, Ray K, Ray J (2021) Identification of GBA mutations among neurodegenerative disease patients from eastern India. Neurosci Lett 751:135816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2021.135816
Blauwendraat C, Nalls MA, Singleton AB (2020a) The genetic architecture of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 19(2):170–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30287-X
Blauwendraat C, Reed X, Krohn L, Heilbron K, Bandres-Ciga S, Tan M, Gibbs JR, Hernandez DG, Kumaran R, Langston RJB (2020b) Genetic modifiers of risk and age at onset in GBA associated Parkinson’s disease and Lewy body dementia. Brain 143(1):234–248. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awz350
Bloem BR, Okun MS, Klein C (2021) Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 397(10291):2284–2303. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00218-X
Brockmann K, Srulijes K, Pflederer S, Hauser AK, Schulte C, Maetzler W, Gasser T, Berg D (2015) GBA-associated Parkinson’s disease: reduced survival and more rapid progression in a prospective longitudinal study. Mov Disord 30(3):407–411. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26071
Choi Y, Chan AP (2015) PROVEAN web server: a tool to predict the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. Bioinformatics 31(16):2745–2747. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv195
Choi JM, Kim WC, Lyoo CH, Kang SY, Lee PH, Baik JS, Koh SB, Ma HI, Sohn YH, Lee MS, Kim YJ (2012) Association of mutations in the glucocerebrosidase gene with Parkinson disease in a Korean population. Neurosci Lett 514(1):12–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2012.02.035
Cilia R, Tunesi S, Marotta G, Cereda E, Siri C, Tesei S, Zecchinelli AL, Canesi M, Mariani CB, Meucci N, Sacilotto G, Zini M, Barichella M, Magnani C, Duga S, Asselta R, Solda G, Seresini A, Seia M, Pezzoli G, Goldwurm S (2016) Survival and dementia in GBA-associated Parkinson’s disease: the mutation matters. Ann Neurol 80(5):662–673. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24777
Creese B, Bell E, Johar I, Francis P, Ballard C, Aarsland D (2018) Glucocerebrosidase mutations and neuropsychiatric phenotypes in Parkinson’s disease and Lewy body dementias: review and meta-analyses. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 177(2):232–241. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.32549
Davis MY, Johnson CO, Leverenz JB, Weintraub D, Trojanowski JQ, Chen-Plotkin A, Van Deerlin VM, Quinn JF, Chung KA, Peterson-Hiller AL, Rosenthal LS, Dawson TM, Albert MS, Goldman JG, Stebbins GT, Bernard B, Wszolek ZK, Ross OA, Dickson DW, Eidelberg D, Mattis PJ, Niethammer M, Yearout D, Hu SC, Cholerton BA, Smith M, Mata IF, Montine TJ, Edwards KL, Zabetian CP (2016) Association of GBA mutations and the E326K polymorphism with motor and cognitive progression in Parkinson disease. JAMA Neurol 73(10):1217–1224. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.2245
den Heijer JM, Cullen VC, Quadri M, Schmitz A, Hilt DC, Lansbury P, Berendse HW, van de Berg WDJ, de Bie RMA, Boertien JM, Boon AJW, Contarino MF, van Hilten JJ, Hoff JI, van Mierlo T, Munts AG, van der Plas AA, Ponsen MM, Baas F, Majoor-Krakauer D, Bonifati V, van Laar T, Groeneveld GJ (2020) A large-scale full GBA1 gene screening in Parkinson’s disease in the Netherlands. Mov Disord 35(9):1667–1674. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.28112
Diez-Fairen M, Benitez BA, Ortega-Cubero S, Lorenzo-Betancor O, Cruchaga C, Lorenzo E, Samaranch L, Carcel M, Obeso JA, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Aguilar M, Coria F, Pastor MA, Pastor P (2018) Pooled-DNA target sequencing of Parkinson genes reveals novel phenotypic associations in Spanish population. Neurobiol Aging 70:325 e321-325 e325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.05.008
Dimitriou E, Moraitou M, Cozar M, Serra-Vinardell J, Vilageliu L, Grinberg D, Mavridou I, Michelakakis H (2020) Gaucher disease: biochemical and molecular findings in 141 patients diagnosed in Greece. Mol Genet Metab Rep 24:100614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgmr.2020.100614
Do J, McKinney C, Sharma P, Sidransky E (2019) Glucocerebrosidase and its relevance to Parkinson disease. Mol Neurodegener 14(1):36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-019-0336-2
Foo JN, Chew EGY, Chung SJ, Peng R, Blauwendraat C, Nalls MA, Mok KY, Satake W, Toda T, Chao Y, Tan LCS, Tandiono M, Lian MM, Ng EY, Prakash KM, Au WL, Meah WY, Mok SQ, Annuar AA, Chan AYY, Chen L, Chen Y, Jeon BS, Jiang L, Lim JL, Lin JJ, Liu C, Mao C, Mok V, Pei Z, Shang HF, Shi CH, Song K, Tan AH, Wu YR, Xu YM, Xu R, Yan Y, Yang J, Zhang B, Koh WP, Lim SY, Khor CC, Liu J, Tan EK (2020) Identification of risk loci for Parkinson disease in Asians and comparison of risk between Asians and Europeans: a genome-wide association study. JAMA Neurol 77(6):746–754. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.0428
Gan-Or Z, Amshalom I, Kilarski LL, Bar-Shira A, Gana-Weisz M, Mirelman A, Marder K, Bressman S, Giladi N, Orr-Urtreger A (2015) Differential effects of severe vs mild GBA mutations on Parkinson disease. Neurology 84(9):880–887. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000001315
Gu X, Li C, Chen Y, Ou R, Cao B, Wei Q, Hou Y, Zhang L, Song W, Zhao B, Wu Y, Shang H (2020) Mutation screening and burden analysis of VPS13C in Chinese patients with early-onset Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 94:311 e311-311 e314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2020.05.005
Hatin WI, Nur-Shafawati AR, Etemad A, Jin W, Qin P, Xu S, Jin L, Tan SG, Limprasert P, Feisal MA, Rizman-Idid M, Zilfalil BA, Consortium HP-AS (2014) A genome wide pattern of population structure and admixture in peninsular Malaysia Malays. Hugo J 8(1):5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11568-014-0005-z
Hertz E, Thornqvist M, Holmberg B, Machaczka M, Sidransky E, Svenningsson P (2019) First clinicogenetic description of Parkinson’s disease related to GBA mutation S107L. Mov Disord Clin Pract 6(3):254–258. https://doi.org/10.1002/mdc3.12743
Inzelberg R, Hattori N, Nisipeanu P, Abo Mouch S, Blumen SC, Carasso RL, Mizuno Y (2003) Camptocormia, axial dystonia, and parkinsonism: phenotypic heterogeneity of a parkin mutation. Neurology 60(8):1393–1394. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000055809.71968.87
Ji S, Wang C, Qiao H, Gu Z, Gan-Or Z, Fon EA, Chan P (2020) Decreased penetrance of Parkinson’s disease in elderly carriers of glucocerebrosidase gene L444P/R mutations: a community-based 10-year longitudinal study. Mov Disord 35(4):672–678. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27971
Kircher M, Witten DM, Jain P, O’Roak BJ, Cooper GM, Shendure J (2014) A general framework for estimating the relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nat Genet 46(3):310–315. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2892
Klein C, Lohmann-Hedrich K, Rogaeva E, Schlossmacher MG, Lang AE (2007) Deciphering the role of heterozygous mutations in genes associated with parkinsonism. Lancet Neurol 6(7):652–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70174-6
Klein C, Hattori N, Marras C (2018) MDSGene: closing data gaps in genotype-phenotype correlations of monogenic Parkinson’s disease. J Parkinsons Dis 8(s1):S25–S30. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-181505
Kopanos C, Tsiolkas V, Kouris A, Chapple CE, Albarca Aguilera M, Meyer R, Massouras A (2019) VarSome: the human genomic variant search engine. Bioinformatics 35(11):1978–1980. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty897
Kumar S, Yadav N, Pandey S, Muthane UB, Govindappa ST, Abbas MM, Behari M, Thelma BK (2020) Novel and reported variants in Parkinson’s disease genes confer high disease burden among Indians. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 78:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.07.014
Lees AJ, Hardy J, Revesz T (2009) Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 373(9680):2055–2066. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60492-X
Lesage S, Anheim M, Condroyer C, Pollak P, Durif F, Dupuits C, Viallet F, Lohmann E, Corvol JC, Honore A, Rivaud S, Vidailhet M, Durr A, Brice A, French Parkinson’s Disease Genetics Study G (2011) Large-scale screening of the Gaucher’s disease-related glucocerebrosidase gene in Europeans with Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 20(1):202–210. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddq454
Li N, Wang L, Zhang J, Tan EK, Li J, Peng J, Duan L, Chen C, Zhou D, He L, Peng R (2020) Whole-exome sequencing in early-onset Parkinson’s disease among ethnic Chinese. Neurobiol Aging 90:150 e155-150 e111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2019.12.023
Lim SY, Tan AH, Ahmad-Annuar A, Klein C, Tan LCS, Rosales RL, Bhidayasiri R, Wu YR, Shang HF, Evans AH, Pal PK, Hattori N, Tan CT, Jeon B, Tan EK, Lang AE (2019) Parkinson’s disease in the Western Pacific region. Lancet Neurol 18(9):865–879. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30195-4
Lim S-Y, Lim JL, Ahmad-Annuar A, Lohmann K, Tan AH, Lim KB, Tay YW, Shing YL, Muthusamy KA, Bauer P, Rolfs A, Klein C (2020a) Clinical phenotype of LRRK2 R1441C in 2 Chinese sisters. Neurodegener Dis 20(1):39–45. https://doi.org/10.1159/000508131
Lim SY, Lim KB, Hor JW, Tan AH (2020b) Brief clinical rating scales should not be overlooked. Mov Disord 35(10):1884–1885. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.28274
Liu G, Boot B, Locascio JJ, Jansen IE, Winder-Rhodes S, Eberly S, Elbaz A, Brice A, Ravina B, van Hilten JJ, Cormier-Dequaire F, Corvol JC, Barker RA, Heutink P, Marinus J, Williams-Gray CH, Scherzer CR, International Genetics of Parkinson Disease Progression C (2016) Specifically neuropathic Gaucher’s mutations accelerate cognitive decline in Parkinson’s. Ann Neurol 80(5):674–685. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24781
Lubbe SJ, Bustos BI, Hu J, Krainc D, Joseph T, Hehir J, Tan M, Zhang W, Escott-Price V, Williams NM, Blauwendraat C, Singleton AB, Morris HR, for International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics C (2021) Assessing the relationship between monoallelic PRKN mutations and Parkinson’s risk. Hum Mol Genet 30(1):78–86. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddaa273
Lucking CB, Durr A, Bonifati V, Vaughan J, De Michele G, Gasser T, Harhangi BS, Meco G, Denefle P, Wood NW, Agid Y, Brice A, French Parkinson’s Disease Genetics Study G, European Consortium on Genetic Susceptibility in Parkinson’s D (2000) Association between early-onset Parkinson’s disease and mutations in the parkin gene. N Engl J Med 342(21):1560–1567. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200005253422103
Mangone G, Bekadar S, Cormier-Dequaire F, Tahiri K, Welaratne A, Czernecki V, Pineau F, Karachi C, Castrioto A, Durif F, Tranchant C, Devos D, Thobois S, Meissner WG, Navarro MS, Cornu P, Lesage S, Brice A, Welter ML, Corvol JC, contributors/investigators (2020) Early cognitive decline after bilateral subthalamic deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease patients with GBA mutations. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 76:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.04.002
Martinez-Martin P, Rojo-Abuin JM, Rodriguez-Violante M, Serrano-Duenas M, Garretto N, Martinez-Castrillo JC, Arillo VC, Fernandez W, Chana-Cuevas P, Arakaki T, Alvarez M, Ibanez IP, Rodriguez-Blazquez C, Chaudhuri KR, Merello M (2016) Analysis of four scales for global severity evaluation in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2:16007. https://doi.org/10.1038/npjparkd.2016.7
Mitsui J, Mizuta I, Toyoda A, Ashida R, Takahashi Y, Goto J, Fukuda Y, Date H, Iwata A, Yamamoto M, Hattori N, Murata M, Toda T, Tsuji S (2009) Mutations for Gaucher disease confer high susceptibility to Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 66(5):571–576. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2009.72
Mohamad Pakarulrazy NF, Syafruddin SE, Ab Mutalib NS, Ahmad-Annuar A, Lim S-Y, Jamal R, Abdul Murad NA, Mohamed Ibrahim N (2020) Glucocerebrosidase genetic variants in Malays with early and late-onset Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Asia 25(1):39–46
Mullin S, Smith L, Lee K, D’Souza G, Woodgate P, Elflein J, Hallqvist J, Toffoli M, Streeter A, Hosking J, Heywood WE, Khengar R, Campbell P, Hehir J, Cable S, Mills K, Zetterberg H, Limousin P, Libri V, Foltynie T, Schapira AHV (2020) Ambroxol for the treatment of patients with Parkinson disease with and without glucocerebrosidase gene mutations: a nonrandomized. Noncontrolled Trial JAMA Neurol 77(4):427–434. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4611
Nalls MA, Pankratz N, Lill CM, Do CB, Hernandez DG, Saad M, DeStefano AL, Kara E, Bras J, Sharma M, Schulte C, Keller MF, Arepalli S, Letson C, Edsall C, Stefansson H, Liu X, Pliner H, Lee JH, Cheng R, International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics C, Parkinson’s Study Group Parkinson’s Research: The Organized GI, andMe, GenePd, NeuroGenetics Research C, Hussman Institute of Human G, Ashkenazi Jewish Dataset I, Cohorts for H, Aging Research in Genetic E, North American Brain Expression C, United Kingdom Brain Expression C, Greek Parkinson’s Disease C, Alzheimer Genetic Analysis G, Ikram MA, Ioannidis JP, Hadjigeorgiou GM, Bis JC, Martinez M, Perlmutter JS, Goate A, Marder K, Fiske B, Sutherland M, Xiromerisiou G, Myers RH, Clark LN, Stefansson K, Hardy JA, Heutink P, Chen H, Wood NW, Houlden H, Payami H, Brice A, Scott WK, Gasser T, Bertram L, Eriksson N, Foroud T, Singleton AB (2014) Large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies six new risk loci for Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 46(9):989–993. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3043
Nalls MA, Blauwendraat C, Vallerga CL, Heilbron K, Bandres-Ciga S, Chang D, Tan M, Kia DA, Noyce AJ, Xue A, Bras J, Young E, von Coelln R, Simon-Sanchez J, Schulte C, Sharma M, Krohn L, Pihlstrom L, Siitonen A, Iwaki H, Leonard H, Faghri F, Gibbs JR, Hernandez DG, Scholz SW, Botia JA, Martinez M, Corvol JC, Lesage S, Jankovic J, Shulman LM, Sutherland M, Tienari P, Majamaa K, Toft M, Andreassen OA, Bangale T, Brice A, Yang J, Gan-Or Z, Gasser T, Heutink P, Shulman JM, Wood NW, Hinds DA, Hardy JA, Morris HR, Gratten J, Visscher PM, Graham RR, Singleton AB, andMe Research T, System Genomics of Parkinson’s Disease C, International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics C (2019) Identification of novel risk loci, causal insights, and heritable risk for Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet Neurol 18(12):1091–1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30320-5
Neumann J, Bras J, Deas E, O’Sullivan SS, Parkkinen L, Lachmann RH, Li A, Holton J, Guerreiro R, Paudel R, Segarane B, Singleton A, Lees A, Hardy J, Houlden H, Revesz T, Wood NW (2009) Glucocerebrosidase mutations in clinical and pathologically proven Parkinson’s disease. Brain 132(Pt 7):1783–1794. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awp044
Nuytemans K, Rajabli F, Bussies PL, Celis K, Scott WK, Singer C, Luca CC, Vinuela A, Pericak-Vance MA, Vance JM (2020) Novel variants in LRRK2 and GBA identified in latino Parkinson disease cohort enriched for caribbean origin. Front Neurol 11:573733. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.573733
Oeda T, Umemura A, Mori Y, Tomita S, Kohsaka M, Park K, Inoue K, Fujimura H, Hasegawa H, Sugiyama H, Sawada H (2015) Impact of glucocerebrosidase mutations on motor and nonmotor complications in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 36(12):3306–3313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.08.027
Olanow CW, Stocchi F (2018) Levodopa: A new look at an old friend. Mov Disord 33(6):859–866. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27216
Pulkes T, Choubtum L, Chitphuk S, Thakkinstian A, Pongpakdee S, Kulkantrakorn K, Hanchaiphiboolkul S, Tiamkao S, Boonkongchuen P (2014) Glucocerebrosidase mutations in Thai patients with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20(9):986–991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.06.007
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, Voelkerding K, Rehm HL, Committee ALQA (2015) Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American college of medical genetics and genomics and the association for molecular pathology. Genet Med 17(5):405–424. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2015.30
Rozenberg R, Fox DC, Sobreira E, Pereira LV (2006) Detection of 12 new mutations in Gaucher disease Brazilian patients. Blood Cells Mol Dis 37(3):204–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcmd.2006.09.004
Ruskey JA, Greenbaum L, Ronciere L, Alam A, Spiegelman D, Liong C, Levy OA, Waters C, Fahn S, Marder KS, Chung W, Yahalom G, Israeli-Korn S, Livneh V, Fay-Karmon T, Alcalay RN, Hassin-Baer S, Gan-Or Z (2019) Increased yield of full GBA sequencing in Ashkenazi Jews with Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Med Genet 62(1):65–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmg.2018.05.005
Sancho Saldana A, Lazaro Romero A, Capablo Liesa JL, Alarcia Alejos R (2021) Camptocormia as the main manifestation of a mutation in the POLG gene. Neurologia 36(5):390–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nrl.2020.07.008
Saunders-Pullman R, Hagenah J, Dhawan V, Stanley K, Pastores G, Sathe S, Tagliati M, Condefer K, Palmese C, Bruggemann N, Klein C, Roe A, Kornreich R, Ozelius L, Bressman S (2010) Gaucher disease ascertained through a Parkinson’s center: imaging and clinical characterization. Mov Disord 25(10):1364–1372. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23046
Sidransky E, Nalls MA, Aasly JO, Aharon-Peretz J, Annesi G, Barbosa ER, Bar-Shira A, Berg D, Bras J, Brice A, Chen CM, Clark LN, Condroyer C, De Marco EV, Durr A, Eblan MJ, Fahn S, Farrer MJ, Fung HC, Gan-Or Z, Gasser T, Gershoni-Baruch R, Giladi N, Griffith A, Gurevich T, Januario C, Kropp P, Lang AE, Lee-Chen GJ, Lesage S, Marder K, Mata IF, Mirelman A, Mitsui J, Mizuta I, Nicoletti G, Oliveira C, Ottman R, Orr-Urtreger A, Pereira LV, Quattrone A, Rogaeva E, Rolfs A, Rosenbaum H, Rozenberg R, Samii A, Samaddar T, Schulte C, Sharma M, Singleton A, Spitz M, Tan EK, Tayebi N, Toda T, Troiano AR, Tsuji S, Wittstock M, Wolfsberg TG, Wu YR, Zabetian CP, Zhao Y, Ziegler SG (2009) Multicenter analysis of glucocerebrosidase mutations in Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 361(17):1651–1661. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0901281
Siebert M, Bock H, Michelin-Tirelli K, Coelho JC, Giugliani R, Saraiva-Pereira M (2012) Novel mutations in the glucocerebrosidase gene of Brazilian Patients with Gaucher disease. JIMD reports-case and research reports, 2012/6, vol 9. Springer, Berlin, pp 7–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/8904_2012_174
Skrahina V, Gaber H, Vollstedt EJ, Forster TM, Usnich T, Curado F, Bruggemann N, Paul J, Bogdanovic X, Zulbahar S, Olmedillas M, Skobalj S, Ameziane N, Bauer P, Csoti I, Koleva-Alazeh N, Grittner U, Westenberger A, Kasten M, Beetz C, Klein C, Rolfs A, Group RS (2021) The rostock international Parkinson’s disease (ROPAD) study: protocol and initial findings. Mov Disord 36(4):1005–1010. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.28416
Straniero L, Asselta R, Bonvegna S, Rimoldi V, Melistaccio G, Solda G, Aureli M, Della Porta M, Lucca U, Di Fonzo A, Zecchinelli A, Pezzoli G, Cilia R, Duga S (2020) The SPID-GBA study: sex distribution, penetrance, incidence, and dementia in GBA-PD. Neurol Genet 6(6):e523. https://doi.org/10.1212/NXG.0000000000000523
Tan EK, Tong J, Fook-Chong S, Yih Y, Wong MC, Pavanni R, Zhao Y (2007) Glucocerebrosidase mutations and risk of Parkinson disease in Chinese patients. Arch Neurol 64(7):1056–1058. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.64.7.1056
Tan AH, Lohmann K, Tay YW, Lim JL, Ahmad-Annuar A, Ramli N, Chin YT, Mawardi AS, Azmi K, Aziz ZA, Puvanarajah SD, Bauer P, Klein C, Rolfs A, Lim SY (2020) PINK1 p.Leu347Pro mutations in Malays: prevalence and illustrative cases. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 79:34–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.08.015
Tay YW, Lim JL, Tan AH, Annuar AA, Lim SY (2021) Rare homozygous PRKN exon 8 and 9 deletion in Malay familial early-onset Parkinson’s disease. Ann Acad Med Singap 50(4):353–355. https://doi.org/10.47102/annals-acadmedsg.2020508
Thaler A, Bregman N, Gurevich T, Shiner T, Dror Y, Zmira O, Gan-Or Z, Bar-Shira A, Gana-Weisz M, Orr-Urtreger A, Giladi N, Mirelman A (2018) Parkinson’s disease phenotype is influenced by the severity of the mutations in the GBA gene. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 55:45–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.05.009
Vollstedt E-J, Kasten M, Klein C, Group MGGPsDS (2019) Using global team science to identify genetic Parkinson’s disease worldwide. Ann Neurol 86(2):153–157. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25514
Winder-Rhodes SE, Evans JR, Ban M, Mason SL, Williams-Gray CH, Foltynie T, Duran R, Mencacci NE, Sawcer SJ, Barker RA (2013) Glucocerebrosidase mutations influence the natural history of Parkinson’s disease in a community-based incident cohort. Brain 136(Pt 2):392–399. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws318
Wu Y-R, Chen C-M, Chao C-Y, Ro L-S, Lyu R-K, Chang K-H, Lee-Chen G-J (2007) Glucocerebrosidase gene mutation is a risk factor for early onset of Parkinson disease among Taiwanese. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78(9):977–979. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2006.105940
Yu E, Rudakou U, Krohn L, Mufti K, Ruskey JA, Asayesh F, Estiar MA, Spiegelman D, Surface M, Fahn S, Waters CH, Greenbaum L, Espay AJ, Dauvilliers Y, Dupre N, Rouleau GA, Hassin-Baer S, Fon EA, Alcalay RN, Gan-Or Z (2021) Analysis of heterozygous PRKN variants and copy-number variations in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 36(1):178–187. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.28299
Zampieri S, Cattarossi S, Bembi B, Dardis A (2017) GBA analysis in next-generation era: pitfalls, challenges, and possible solutions. J Mol Diagn 19(5):733–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmoldx.2017.05.005
Zhao Y, Qin L, Pan H, Liu Z, Jiang L, He Y, Zeng Q, Zhou X, Zhou X, Zhou Y, Fang Z, Wang Z, Xiang Y, Yang H, Wang Y, Zhang K, Zhang R, He R, Zhou X, Zhou Z, Yang N, Liang D, Chen J, Zhang X, Zhou Y, Liu H, Deng P, Xu K, Xu K, Zhou C, Zhong J, Xu Q, Sun Q, Li B, Zhao G, Wang T, Chen L, Shang H, Liu W, Chan P, Xue Z, Wang Q, Guo L, Wang X, Xu C, Zhang Z, Chen T, Lei L, Zhang H, Wang C, Tan J, Yan X, Shen L, Jiang H, Zhang Z, Hu Z, Xia K, Yue Z, Li J, Guo J, Tang B (2020) The role of genetics in Parkinson’s disease: a large cohort study in Chinese mainland population. Brain 143(7):2220–2234. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awaa167
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant awarded to AAA from the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (FRGS/1/2018/SKK08/UM/02/3). SYL and AHT are supported by the University of Malaya Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorder Research Program (PV035-2017). CK and KL are supported by the DFG (FOR2488). The authors gratefully acknowledge the patients for their consent and participation in this report, including publication of the videos. Gene panel testing was provided as an in-kind contribution from CENTOGENE, Rostock, Germany.
Funding
The Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS/1/2018/SKK08/UM/02/3) and University of Malaya Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Research Program (PV035-2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: S-YL, AA-A, CK; Design: S-YL, AA-A; funding acquisition: AHT, AA-A, S-YL, CK; sample acquisition: S-YL, AHT, JLL, KAI, ZAA, ASM, SDP, TTL, IL, JCEO, YKC, KAM; laboratory investigations: JLL, YWT, AA-A, KL, PB; statistical analysis: JLL; manuscript preparation—writing of first draft: JLL, AAA, S-YL; manuscript preparation—review, critique and approval: all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the University of Malaya Medical Research and Ethics Committee (MREC) and the Malaysian Ministry of Health National Medical Research Register (NMRR).
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants included in this study.
Consent for publication
The participants have consented to the submission of video recordings to the journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
MOESM1 (2 March 2010; aged 45 years, 9 years after PD diagnosis). 2.5 h post-levodopa. Moderate-to-severe generalized choreiform (although at times jerky) dyskinesias. The patient is able to walk well. Speech is moderately hypophonic (MP4 54,974 KB)
MOESM2 (3 September 2013). 2 h post-levodopa (ON-medication state). Disabling truncal extension dyskinesias requiring close supervision to stand and to walk; speech moderate-to-severely hypophonic (MP4 54,974 KB)
MOESM3 (5 May 2015). 1 h post-levodopa. Dyskinesias somewhat improved on low-dose clozapine treatment 25 mg bid (MP4 72,618 KB)
MOESM4 10 January 2014 (aged 50 years, 11 years after PD diagnosis). 2 h post-levodopa (ONmedication condition). Generalized dyskinesias including frequent truncal flexion movements, which contibute to him falling (MP4 82,650)
MOESM5 6 October 2020 (aged 71 years, 19 years after PD diagnosis). Speech is moderately slurred. There is a mild-to-moderate lean of the body to the right whilst seated. She has intermittent tremor in the upper limbs, more on the right (also an obvious dependent tremor when standing). She has difficulty obeying even simple verbal and gestural commands to hold both arms outstretched or to perform finger-to-nose testing (not shown). She requires two-person assistance to stand and to take a few small steps (MP4 90,598 KB)
MOESM6 4 September 2009 (aged 54 years, 18 years after PD diagnosis). ON-medication and ONDBS condition, during the course of a post-DBS Core Assessment Program for Surgical Interventional Therapies (CAPSIT) evaluation showing severe dysarthria and hypophonia, postural instability, and significant gait difficulty. Limb bradykinesia was however well-controlled (MP4 54,974 KB)
MOESM7 18 September 2020 (aged 61 years, 20 years or more after PD diagnosis). 3.5 h postlevodopa (OFF-medication state), with severe axial and appendicular parkinsonism. There is severe facial masking, speech is moderately hypophonic and slurred, and there is a moderate-to-severe stoop and body lean to the left. Movements are severely bradykinetic. Two-person assistance is needed to stand and to take a few very small steps (MP4 109,746 KB)
MOESM8 (21 October 2016; aged 59 years, 16 years after PD diagnosis). Patient complaining of stooped posture and lateral flexion of the trunk, which progressively worsens the longer she sits or stands, but mostly resolves upon lying down. This first developed two years prior (MP4 76,687 KB)
MOESM9 (18 Jan 2019). The abnormal posture has become more marked with camptocormia Pisa syndrome (with moderate lean of the trunk to the right). Her speech is still quite clear (MP4 51,315 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, J.L., Lohmann, K., Tan, A.H. et al. Glucocerebrosidase (GBA) gene variants in a multi-ethnic Asian cohort with Parkinson’s disease: mutational spectrum and clinical features. J Neural Transm 129, 37–48 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-021-02421-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-021-02421-0