Abstract
Background
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is one of the most common emergencies and severe diseases in the clinic. We sought to verify whether remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPC) has a protective effect on the kidney of child with congenital heart disease undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) surgery. We hypothesized it may be related to the up-regulation of microRNA-21 (miR-21).
Methods
We performed a prospective randomized clinical study among children with congenital heart disease undergoing CPB surgery between January and December 2016. Children were randomized to an RIPC or control group. Patients in each group were divided into an AKI and a non-AKI group according to the occurrence of AKI at 48 h after surgery. Remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPC) conducted by blood-pressure cuff was performed 12 h before surgery. Serum creatinine (SCr), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and miR-21 expression in blood and urine were measured at different time points.
Results
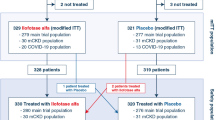
A total of 449 cases (200 RIPC; 249 controls) were enrolled. The male/female ratio was 1.18, with a mean age of 37.50 ± 25.31 months. The incidence of AKI in the RIPC group was significantly lower than that in the control group (19.0% vs. 46.2%, P<0.01). In further analysis, at 6 h, 24 h, and 48 h after CPB operation, blood TNF-α levels were significantly lower in the RIPC group than in the control group (P<0.01); at 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h, urine TNF-α levels were significantly lower in the RIPC group than in the control group (P<0.05). Urine and blood miR-21 expression in the RIPC group increased significantly, while there was no obvious change in the control group.
Conclusions
Remote ischemic preconditioning has a protective effect on the kidney in children with congenital heart disease, which may be related with the up-regulation of miR-21 and down-regulating the inflammatory mediator, such as TNF-α.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali T, Khan I, Simpson W, Prescott G, Townend J, Smith W, Macleod A (2007) Incidence and outcomes in acute kidney injury: a comprehensive population-based study. J Am Soc Nephrol 18(4):1292–1298
Murugan R, Kellum JA (2011) Acute kidney injury: what’s the prognosis? Nat Rev Nephrol 7(4):209–217
Shaw A (2012) Update on acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 143(3):676–681
Li S, Krawczeski CD, Zappitelli M, Devarajan P, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Coca SG, Kim RW, Parikh CR (2011) Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery: a prospective multicenter study. Crit Care Med 39(6):1493–1499
Ho J, Reslerova M, Gali B, Nickerson PW, Rush DN, Sood MM, Bueti J, Komenda P, Pascoe E, Arora RC, Rigatto C (2012) Serum creatinine measurement immediately after cardiac surgery and prediction of acute kidney injury. Am J Kidney Dis 59(2):196–201
Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA (1986) Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 74(5):1124–1136
Cheng Y, Zhu P, Yang J, Liu X, Dong S, Wang X, Chun B, Zhuang J, Zhang C (2010) Ischaemic preconditioning-regulated miR-21 protects heart against ischaemia/reperfusion injury via anti-apoptosis through its target PDCD4. Cardiovasc Res 87(3):431–439
Guan J, Li H, Lv T, Chen D, Yuan Y, Qu S (2013) Bone morphogenetic protein-7 (BMP-7) mediates ischemic preconditioning-induced ischemic tolerance via attenuating apoptosis in rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 441(3):560–566
Ren Z, Cui G, Lu H, Chen X, Jiang J, Liu H, He Y, Ding S, Hu Z, Wang W, Zheng S (2013) Liver ischemic preconditioning (IPC) improves intestinal microbiota following liver transplantation in rats through 16s rDNA-based analysis of microbial structure shift. PLoS One 8(10):e75950
Weiss JB, Eisenhardt SU, Stark GB, Bode C, Moser M, Grundmann S (2012) MicroRNAs in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Cardiovasc Dis 2(3):237–247
Lorenzen JM, Batkai S, Thum T (2013) Regulation of cardiac and renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by microRNAs. Free Radic Biol Med 64:78–84
Godwin JG, Ge X, Stephan K, Jurisch A, Tullius SG, Iacomini J (2010) Identification of a microRNA signature of renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(32):14339–14344
Kaushal GP (2012) Autophagy protects proximal tubular cells from injury and apoptosis. Kidney Int 82(12):1250–1253
Liu F, Lou YL, Wu J, Ruan QF, Xie A, Guo F, Cui SP, Deng ZF, Wang Y (2012) Upregulation of microRNA-210 regulates renal angiogenesis mediated by activation of VEGF signaling pathway under ischemia/perfusion injury in vivo and in vitro. Kidney Blood Press Res 35(3):182–191
Li Z, Deng X, Kang Z, Wang Y, Xia T, Ding N, Yin Y (2015) Elevation of miR-21, through targeting MKK3, may be involved in ischemia pretreatment protection from ischemia-reperfusion induced kidney injury. J Nephrol 29:27–36
The KDIGO Acute Kidney Injury Work Group (2012) KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 2(Suppl):1–138
Cheung MM, Kharbanda RK, Konstantinov IE, Shimizu M, Frndova H, Li J, Holtby HM, Cox PN, Smallhorn JF, Van Arsdell GS, Redington AN (2006) Randomized controlled trial of the effects of remote ischemic preconditioning on children undergoing cardiac surgery: first clinical application in humans. J Am Coll Cardiol 47(11):2277–2282
Mouton R, Pollock J, Soar J, Mitchell DC, Rogers CA (2015) Remote ischaemic preconditioning versus sham procedure for abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: an external feasibility randomized controlled trial. Trials 16(1):377
Jenkins KJ (2004) Risk adjustment for congenital heart surgery: the RACHS-1 method. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg Pediatr Card Surg Ann 7:180–184
Zimmerman RF, Ezeanuna PU, Kane JC, Cleland CD, Kempananjappa TJ, Lucas FL, Kramer RS (2011) Ischemic preconditioning at a remote site prevents acute kidney injury in patients following cardiac surgery. Kidney Int 80(8):861–867
Thielmann M, Kottenberg E, Kleinbongard P, Wendt D, Gedik N, Pasa S, Price V, Tsagakis K, Neuhäuser M, Peters J, Jakob H, Heusch G (2013) Cardioprotective and prognostic effects of remote ischaemic preconditioning in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery: a single-centre randomised, double-blind, controlled trial. Lancet 382(9892):597–604
Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, Molitoris BA, Ronco C, Warnock DG, Levin A (2007) Acute kidney injury network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care 11(2):R31
Xu XH, Chen Q, Chen Y, Lv LX, Zhu CQ, Dai HL, Qian JQ (2010) Effect of ethyl pyruvate on expression of inflammatory factors and mitogen-activated protein kinase proteins in renal ischemic/reperfusion injury in BABL/c mice. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 22(12):750–753
Ma T, Liu XW, Liu Z (2013) Function of the p38MAPK-HSP27 pathway in rat lung injury induced by acute ischemic kidney injury. Biomed Res Int 2013:981235
Ma FY, Tesch GH, Flavell RA, Davis RJ, Nikolic-Paterson DJ (2007) MKK3-p38 signaling promotes apoptosis and the early inflammatory response in the obstructed mouse kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293(5):F1556–F1563
Ramachandran K, Saikumar J, Bijol V, Koyner JL, Qian J, Betensky RA, Waikar SS, Vaidya VS (2013) Human miRNome profiling identifies microRNAs differentially present in the urine after kidney injury. Clin Chem 59(12):1742–1752
Du J, Cao X, Zou L, Chen Y, Guo J, Chen Z, Hu S, Zheng Z (2013) MicroRNA-21 and risk of severe acute kidney injury and poor outcomes after adult cardiac surgery. PLoS One 8(5):e63390
Xu X, Kriegel AJ, Liu Y, Usa K, Mladinov D, Liu H, Fang Y, Ding X, Liang M (2012) Delayed ischemic preconditioning contributes to renal protection by upregulation of miR-21. Kidney Int 82(11):1167–1175
Luca MC, Liuni A, McLaughlin K, Gori T, Parker JD (2013) Daily ischemic preconditioning provides sustained protection from ischemia-reperfusion induced endothelial dysfunction: a human study. J Am Heart Assoc 2(1):e75
Dong S, Cheng Y, Yang J, Li J, Liu X, Wang X, Wang D, Krall TJ, Delphin ES, Zhang C (2009) MicroRNA expression signature and the role of microRNA-21 in the early phase of acute myocardial infarction. J Biol Chem 284(43):29514–29525
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A, Lindow M, Krogh A, Lund AH (2008) Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 283(2):1026–1033
Cheng Y, Zhang C (2010) MicroRNA-21 in cardiovascular disease. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 3(3):251–255
Zhou X, Zhang J, Jia Q, Ren Y, Wang Y, Shi L, Liu N, Wang G, Pu P, You Y, Kang C (2010) Reduction of miR-21 induces glioma cell apoptosis via activating caspase 9 and 3. Oncol Rep 24(1):195–201
Zhou X, Ren Y, Moore L, Mei M, You Y, Xu P, Wang B, Wang G, Jia Z, Pu P, Zhang W, Kang C (2010) Downregulation of miR-21 inhibits EGFR pathway and suppresses the growth of human glioblastoma cells independent of PTEN status. Lab Investig 90(2):144–155
Papagiannakopoulos T, Shapiro A, Kosik KS (2008) MicroRNA-21 targets a network of key tumor-suppressive pathways in glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 68(19):8164–8172
Zhang G, He LS, Wong YH, Qian PY (2013) MKK3 was involved in larval settlement of the barnacle Amphibalanus amphitrite through activating the kinase activity of p38MAPK. PLoS One 8(7):e69510
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J (2001) Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev 81(2):807–869
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by grants from the Natural Science Fund of Hunan Province (2015JJ4029) and Clinical Center for Acute Renal Injury in Children of Hunan Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical considerations
The study complies with the Helsinki declaration and was approved by the local institutional ethics committee of the Hunan Children’s Hospital (ICF2015004), dated 25 November 2015. Informed consent from potential trial participants was obtained from a parent or guardian before enrollment. The model consent form Version 01 dated 5 September 2015 is available under Additional file. Patients could discontinue participation at any time upon request. The study is registered with the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (registration ID: ChiCTR-IOC-15007513).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, Z., Li, Z., Huang, P. et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning upregulates microRNA-21 to protect the kidney in children with congenital heart disease undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass. Pediatr Nephrol 33, 911–919 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3851-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3851-9