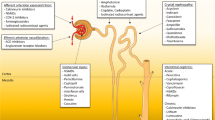
Abstract
Several drugs and other compounds can induce acute and/or chronic nephrotoxicity. The goal of this study was to review clinical features of nephrotoxicity induced by ‘atypical’ or ‘unconventional’ agents, such as environmental agents (metals, minerals, animals), food agents (mushrooms, aristolochic acid, medicinal traditional herbals, dietary supplements, melamine), drugs, and other products (ethylene glycol). Nephrotoxicity varies according to local background, dependent on different food and cultural customs, as well as to differences in local fauna and flora. The incidence of such a phenomenon is not well known. Many different pathophysiological pathways are involved, and the spectrum of renal lesions is rather wide. ‘Epidemic nephrotoxicity’ may occur, as recently illustrated by the melamine epidemics in Chinese infants receiving powdered milk formulas; a rapid reaction to unusual increased frequency of acute kidney injury and nephrolithiasis in young children has led to a rapid analysis from international experts, with subsequent recommendations for diagnosis and care. Nephrotoxicity should be considered when there is any unexplained renal impairment, especially in children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cochat P, Bacchetta J (2008) Néphrotoxicité. EMC Pediatrie. 4-084-B-10
Solhaug MJ, Bolger PM, Jose PA (2004) The developing kidney and environmental toxins. Pediatrics 113:1084–1091
Ferguson MA, Vaidya VS, Bonventre JV (2008) Biomarkers of nephrotoxic acute kidney injury. Toxicology 245:182–193
Van Vleet TR, Schnellmann RG (2003) Toxic nephropathy: environmental chemicals. Semin Nephrol 23:500–508
Patzer L (2008) Nephrotoxicity as a cause of acute kidney injury in children. Pediatr Nephrol 23:2159–2173
Bearman SI, Appelbaum FR, Buckner CD, Petersen FB, Fisher LD, Clift RA, Thomas ED (1988) Regimen-related toxicity in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Oncol 6:1562–1568
van de Water B, de Graauw M, Le Devedec S, Alderliesten M (2006) Cellular stress responses and molecular mechanisms of nephrotoxicity. Toxicol Lett 162:83–93
Servais H, Ortiz A, Devuyst O, Denamur S, Tulkens PM, Mingeot-Leclercq MP (2008) Renal cell apoptosis induced by nephrotoxic drugs: cellular and molecular mechanisms and potential approaches to modulation. Apoptosis 13:11–32
Krenova M, Pelclova D (2007) Does unintentional ingestion of ethylene glycol represent a serious risk? Hum Exp Toxicol 26:59–67
Schwerk N, Desel H, Schulz M, Schwerk C, Kiess W, Siekmeyer W (2007) Successful therapy of paediatric ethylene glycol poisoning: a case report and annual survey by a regional poison centre. Acta Paediatr 96:461–463
Poldelski V, Johnson A, Wright S, Rosa VD, Zager RA (2001) Ethylene glycol-mediated tubular injury: identification of critical metabolites and injury pathways. Am J Kidney Dis 38:339–348
Barceloux DG, Krenzelok EP, Olson K, Watson W (1999) American Academy of Clinical Toxicology Practice Guidelines on the Treatment of Ethylene Glycol Poisoning. Ad Hoc Committee. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 37:537–560
Caravati EM, Heileson HL, Jones M (2004) Treatment of severe pediatric ethylene glycol intoxication without hemodialysis. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 42:255–259
Harry P, Jobard E, Briand M, Caubet A, Turcant A (1998) Ethylene glycol poisoning in a child treated with 4-methylpyrazole. Pediatrics 102:E31
Daniel L, Robert A, Lesavre P, Figarella-Branger D (2004) Severe mesangiolysis in a patient exposed to glycol ether solvents. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19:2679
Sabolic I (2006) Common mechanisms in nephropathy induced by toxic metals. Nephron Physiol 104:p107–114
Marsden PA (2003) Increased body lead burden—cause or consequence of chronic renal insufficiency? N Engl J Med 348:345–347
Fontanellas A, Navarro S, Moran-Jimenez MJ, Sanchez-Fructuoso AI, Vegh I, Barrientos A, de Salamanca RE (2002) Erythrocyte aminolevulinate dehydratase activity as a lead marker in patients with chronic renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis 40:43–50
Sanchez-Fructuoso AI, Blanco J, Cano M, Ortega L, Arroyo M, Fernandez C, Prats D, Barrientos A (2002) Experimental lead nephropathy: treatment with calcium disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate. Am J Kidney Dis 40:59–67
Ekong EB, Jaar BG, Weaver VM (2006) Lead-related nephrotoxicity: a review of the epidemiologic evidence. Kidney Int 70:2074–2084
Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Hsu KH, Yu CC (2003) Environmental lead exposure and progression of chronic renal diseases in patients without diabetes. N Engl J Med 348:277–286
Schoeters G, Den Hond E, Zuurbier M, Naginiene R, van den Hazel P, Stilianakis N, Ronchetti R, Koppe JG (2006) Cadmium and children: exposure and health effects. Acta Paediatr Suppl 95:50–54
Huff J, Lunn RM, Waalkes MP, Tomatis L, Infante PF (2007) Cadmium-induced cancers in animals and in humans. Int J Occup Environ Health 13:202–212
Cengiz N, Uslu Y, Gok F, Anarat A (2005) Acute renal failure after overdose of colloidal bismuth subcitrate. Pediatr Nephrol 20:1355–1358
Islek I, Uysal S, Gok F, Dundaroz R, Kucukoduk S (2001) Reversible nephrotoxicity after overdose of colloidal bismuth subcitrate. Pediatr Nephrol 16:510–514
Aymaz S, Gross O, Krakamp B, Ortmann M, Dienes HP, Weber M (2001) Membranous nephropathy from exposure to mercury in the fluorescent-tube-recycling industry. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16:2253–2255
Mortada WL, Sobh MA, El-Defrawy MM, Farahat SE (2002) Mercury in dental restoration: is there a risk of nephrotoxicity? J Nephrol 15:171–176
Barregard L, Trachtenberg F, McKinlay S (2008) Renal effects of dental amalgam in children: the New England children’s amalgam trial. Environ Health Perspect 116:394–399
Picaud JC, Cochat P, Parchoux B, Berthier JC, Gilly J, Chareyre S, Larbre F (1991) Acute renal failure in a child after chewing of match heads. Nephron 57:225–226
Bhowmik D, Mathur R, Bhargava Y, Dinda AK, Agarwal SK, Tiwari SC, Dash SC (2001) Chronic interstitial nephritis following parenteral copper sulfate poisoning. Ren Fail 23:731–735
Zimmerman KL, Barber DS, Ehrich MF, Tobias L, Hancock S, Hinckley J, Binder EM, Jortner BS (2007) Temporal clinical chemistry and microscopic renal effects following acute uranyl acetate exposure. Toxicol Pathol 35:1000–1009
Magdo HS, Forman J, Graber N, Newman B, Klein K, Satlin L, Amler RW, Winston JA, Landrigan PJ (2007) Grand rounds: nephrotoxicity in a young child exposed to uranium from contaminated well water. Environ Health Perspect 115:1237–1241
Tao SH, Bolger PM (1997) Hazard assessment of germanium supplements. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 25:211–219
Kaneko K, Chiba M, Hashizume M, Kunii O, Sasaki S, Shimoda T, Yamashiro Y, Caypil W, Dauletbaev D (2003) Renal tubular dysfunction in children living in the Aral Sea Region. Arch Dis Child 88:966–968
Hogan SL, Satterly KK, Dooley MA, Nachman PH, Jennette JC, Falk RJ (2001) Silica exposure in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated glomerulonephritis and lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:134–142
Stratta P, Canavese C, Messuerotti A, Fenoglio I, Fubini B (2001) Silica and renal diseases: no longer a problem in the 21st century? J Nephrol 14:228–247
Simon P, Halimi JM, Cordonnier D (2001) Tobacco and kidney. Nephrologie 22:137–140
Gambaro G, Verlato F, Budakovic A, Casara D, Saladini G, Del Prete D, Bertaglia G, Masiero M, Checchetto S, Baggio B (1998) Renal impairment in chronic cigarette smokers. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:562–567
Cooper RG (2006) Effect of tobacco smoking on renal function. Indian J Med Res 124:261–268
Crowe AV, Howse M, Bell GM, Henry JA (2000) Substance abuse and the kidney. QJM 93:147–152
Satarug S, Ujjin P, Vanavanitkun Y, Nishijo M, Baker JR, Moore MR (2004) Effects of cigarette smoking and exposure to cadmium and lead on phenotypic variability of hepatic CYP2A6 and renal function biomarkers in men. Toxicology 204:161–173
Halimi JM, Philippon C, Mimran A (1998) Contrasting renal effects of nicotine in smokers and non-smokers. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:940–944
Kwon C, Zaritsky A, Dharnidharka VR (2003) Transient proximal tubular renal injury following Ecstasy ingestion. Pediatr Nephrol 18:820–822
Woodrow G, Turney JH (1999) Ecstasy-induced renal vasculitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14:798
Ninkovic M, Selakovic V, Dukic M, Milosavljevic P, Vasiljevic I, Jovanovic M, Malicevic Z (2008) Oxidative stress in rat kidneys due to 3, 4-methylenedioxymetamphetamine (ecstasy) toxicity. Nephrology (Carlton) 13:33–37
Hurault de Ligny B, El Haggan W, Comoz F, Lobbedez T, Pujo M, Griveau AM, Bottet P, Bensadoun H, Ryckelynck JP (2005) Early loss of two renal grafts obtained from the same donor: role of ecstasy? Transplantation 80:153–156
Farber SJ, Huertas VE (1976) Intravenously injected marihuana syndrome. Arch Intern Med 136:337–339
Bohatyrewicz M, Urasinska E, Rozanski J, Ciechanowski K (2007) Membranous glomerulonephritis may be associated with heavy marijuana abuse. Transplant Proc 39:3054–3056
Glauser J, Queen JR (2007) An overview of non-cardiac cocaine toxicity. J Emerg Med 32:181–186
Bemanian S, Motallebi M, Nosrati SM (2005) Cocaine-induced renal infarction: report of a case and review of the literature. BMC Nephrol 6:10
Edmondson DA, Towne JB, Foley DW, Abu-Hajir M, Kochar MS (2004) Cocaine-induced renal artery dissection and thrombosis leading to renal infarction. WMJ 103:66–69
Nzerue CM, Hewan-Lowe K, Riley LJ Jr (2000) Cocaine and the kidney: a synthesis of pathophysiologic and clinical perspectives. Am J Kidney Dis 35:783–795
Chippaux JP (1998) Snake-bites: appraisal of the global situation. Bull World Health Organ 76:515–524
Sitprija V (2006) Snakebite nephropathy. Nephrology (Carlton) 11:442–448
Pinho FM, Zanetta DM, Burdmann EA (2005) Acute renal failure after Crotalus durissus snakebite: a prospective survey on 100 patients. Kidney Int 67:659–667
Reisman RE (2005) Unusual reactions to insect stings. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 5:355–358
Hasan S, Hassan K (2005) Proteinuria associated with centipede bite. Pediatr Nephrol 20:550–551
Chao YW, Yang AH, Ng YY, Yang WC (2004) Acute interstitial nephritis and pigmented tubulopathy in a patient after wasp stings. Am J Kidney Dis 43:e15–19
Bhatta N, Singh R, Sharma S, Sinnha A, Raja S (2005) Acute renal failure following multiple wasp stings. Pediatr Nephrol 20:1809–1810
Bahloul M, Ben Hmida M, Belhoul W, Ksibi H, Kallel H, Ben Hamida C, Chaari A, Chelly H, Rekik N, Bouaziz M (2004) Le syndrome hémolytique et urémique secondaire à une envenimation scorpionique: à propos de 2 cas. Néphrologie 25:49–51
Deekajorndech T, Kingwatanakul P, Wananukul S (2004) Acute renal failure in a child with jellyfish contact dermatitis. J Med Assoc Thai 87(Suppl 2):S292–294
Mizuno M, Nozaki M, Morine N, Suzuki N, Nishikawa K, Morgan BP, Matsuo S (2007) A protein toxin from the sea anemone Phyllodiscus semoni targets the kidney and causes a severe renal injury with predominant glomerular endothelial damage. Am J Pathol 171:402–414
Mizuno M, Nishikawa K, Yuzawa Y, Kanie T, Mori H, Araki Y, Hotta N, Matsuo S (2000) Acute renal failure after a sea anemone sting. Am J Kidney Dis 36:E10
Cochat P, Larbre F (1988) Nephrotic syndrome after a medusa sting. Pediatrie 43:419–420
Riella MC, Chula D, de Freitas S, Mazza M, Pachaly M (2008) Acute renal failure and haemorrhagic syndrome secondary to toxin of caterpillars (Lonomia obliqua). NDT Plus 6:445–446
Chan K, Lee A, Onell R, Etches W, Nahirniak S, Bagshaw SM, Larratt LM (2008) Caterpillar-induced bleeding syndrome in a returning traveller. CMAJ 179:158–161
Saviuc P, Garon D, Danel V, Richard JM (2001) Cortinarius poisoning. Analysis of cases in the literature. Nephrologie 22:167–173
Wornle M, Angstwurm MW, Sitter T (2004) Treatment of intoxication with Cortinarius speciosissimus using an antioxidant therapy. Am J Kidney Dis 43:e3–6
Hassan AM, Sheashaa HA, Fattah MF, Ibrahim AZ, Gaber OA, Sobh MA (2006) Study of ochratoxin A as an environmental risk that causes renal injury in breast-fed Egyptian infants. Pediatr Nephrol 21:102–105
Saviuc P, Danel V (2006) New syndromes in mushroom poisoning. Toxicol Rev 25:199–209
Bedry R, Baudrimont I, Deffieux G, Creppy EE, Pomies JP, Ragnaud JM, Dupon M, Neau D, Gabinski C, De Witte S, Chapalain JC, Godeau P, Beylot J (2001) Wild-mushroom intoxication as a cause of rhabdomyolysis. N Engl J Med 345:798–802
Xuan BH, Thi TX, Nguyen ST, Goldfarb DS, Stokes MB, Rabenou RA (2003) Ichthyotoxic ARF after fish gallbladder ingestion: a large case series from Vietnam. Am J Kidney Dis 41:220–224
Debelle FD, Vanherweghem JL, Nortier JL (2008) Aristolochic acid nephropathy: a worldwide problem. Kidney Int 74:158–169
Lee S, Lee T, Lee B, Choi H, Yang M, Ihm CG, Kim M (2004) Fanconi’s syndrome and subsequent progressive renal failure caused by a Chinese herb containing aristolochic acid. Nephrology (Carlton) 9:126–129
Grollman AP, Shibutani S, Moriya M, Miller F, Wu L, Moll U, Suzuki N, Fernandes A, Rosenquist T, Medverec Z, Jakovina K, Brdar B, Slade N, Turesky RJ, Goodenough AK, Rieger R, Vukelic M, Jelakovic B (2007) Aristolochic acid and the etiology of endemic (Balkan) nephropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:12129–12134
Debelle F, Nortier J (2006) Nephropathy caused by Chinese plants and aristolochic acids: from clinical observation to experimental model. Bull Mem Acad R Med Belg 161:327–333
Hong YT, Fu LS, Chung LH, Hung SC, Huang YT, Chi CS (2006) Fanconi’s syndrome, interstitial fibrosis and renal failure by aristolochic acid in Chinese herbs. Pediatr Nephrol 21:577–579
de Jonge H, Vanrenterghem Y (2008) Aristolochic acid: the common culprit of Chinese herbs nephropathy and Balkan endemic nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:39–41
Nortier JL, Vanherweghem JL (2007) For patients taking herbal therapy—lessons from aristolochic acid nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 22:1512–1517
Cosyns JP, Dehoux JP, Guiot Y, Goebbels RM, Robert A, Bernard AM, van Ypersele de Strihou C (2001) Chronic aristolochic acid toxicity in rabbits: a model of Chinese herbs nephropathy? Kidney Int 59:2164–2173
Li X, Wang H (2004) Aristolochic acid nephropathy: what we know and what we have to do. Nephrology (Carlton) 9:109–111
Barrett B, Kiefer D, Rabago D (1999) Assessing the risks and benefits of herbal medicine: an overview of scientific evidence. Altern Ther Health Med 5:40–49
Gabardi S, Munz K, Ulbricht C (2007) A review of dietary supplement-induced renal dysfunction. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2:757–765
Jha V, Chugh KS (2003) Nephropathy associated with animal, plant, and chemical toxins in the tropics. Semin Nephrol 23:49–65
Adelekun TA, Ekwere TR, Akinsola A (1999) The pattern of acute toxic nephropathy in Ife, Nigeria. West Afr J Med 18:60–63
Isnard Bagnis C, Deray G, Baumelou A, Le Quintrec M, Vanherweghem JL (2004) Herbs and the kidney. Am J Kidney Dis 44:1–11
Bourquia A, Jabrane AJ, Ramdani B, Zaid D (1988) Systemic toxicity of paraphenylenediamine. 4 cases. Presse Med 17:1798–1800
Bolley R, Zulke C, Kammerl M, Fischereder M, Kramer BK (2002) Tacrolimus-induced nephrotoxicity unmasked by induction of the CYP3A4 system with St John’s wort. Transplantation 73:1009
Knight EL, Stampfer MJ, Hankinson SE, Spiegelman D, Curhan GC (2003) The impact of protein intake on renal function decline in women with normal renal function or mild renal insufficiency. Ann Intern Med 138:460–467
Hoogeveen EK, Kostense PJ, Jager A, Heine RJ, Jakobs C, Bouter LM, Donker AJ, Stehouwer CD (1998) Serum homocysteine level and protein intake are related to risk of microalbuminuria: the Hoorn Study. Kidney Int 54:203–209
Uribarri J, Tuttle KR (2006) Advanced glycation end products and nephrotoxicity of high-protein diets. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1:1293–1299
Langman CB, Alon U, Ingelfinger J, Englund M, Saland JM, Somers MJ, Stapleton FB, Sibu NO, Cochat P, Wong W, Eke FU, Satlin L, Salusky I (2009) A position statement on kidney disease from powdered infant formula-based melamine exposure in Chinese infants. Pediatr Nephrol doi:10.1007/s00467-009-1129-6
Melnick RL, Boorman GA, Haseman JK, Montali RJ, Huff J (1984) Urolithiasis and bladder carcinogenicity of melamine in rodents. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 72:292–303
Thompson ME, Lewin-Smith MR, Kalasinsky VF, Pizzolato KM, Fleetwood ML, McElhaney MR, Johnson TO (2008) Characterization of melamine-containing and calcium oxalate crystals in three dogs with suspected pet food-induced nephrotoxicosis. Vet Pathol 45:417–426
Cianciolo RE, Bischoff K, Ebel JG, Van Winkle TJ, Goldstein RE, Serfilippi LM (2008) Clinicopathologic, histologic, and toxicologic findings in 70 cats inadvertently exposed to pet food contaminated with melamine and cyanuric acid. J Am Vet Med Assoc 233:729–737
Hui-Stickle S, Brewer ED, Goldstein SL (2005) Pediatric ARF epidemiology at a tertiary care center from 1999 to 2001. Am J Kidney Dis 45:96–101
Askenazi DJ, Feig DI, Graham NM, Hui-Stickle S, Goldstein SL (2006) 3–5 year longitudinal follow-up of pediatric patients after acute renal failure. Kidney Int 69:184–189
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bacchetta, J., Dubourg, L., Juillard, L. et al. Non-drug-induced nephrotoxicity. Pediatr Nephrol 24, 2291–2300 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1180-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1180-3