Abstract
Through four decades’ development, DNA sequencing has inched into the era of single-molecule sequencing (SMS), or the third-generation sequencing (TGS), as represented by two distinct technical approaches developed independently by Pacific Bioscience (PacBio) and Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT). Historically, each generation of sequencing technologies was marked by innovative technological achievements and novel applications. Long reads (LRs) are considered as the most advantageous feature of SMS shared by both PacBio and ONT to distinguish SMS from next-generation sequencing (NGS, or the second-generation sequencing) and Sanger sequencing (the first-generation sequencing). Long reads overcome the limitations of NGS and drastically improves the quality of genome assembly. Besides, ONT also contributes several unique features including ultra-long reads (ULRs) with read length above 300 kb and some close to 1 million bp, direct RNA sequencing and superior portability as made possible by pocket-sized MinION sequencer. Here, we review the history of DNA sequencing technologies and associated applications, with a special focus on the advantages as well as the limitations of ULR sequencing in genome assembly.

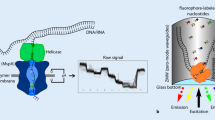
Figure reproduced by copyright permission of AAAS



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkan C, Sajjadian S, Eichler EE (2011) Limitations of next-generation genome sequence assembly. Nat Methods 8:61–65. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1527
Ambardar S, Gowda M (2018) High-resolution full-length HLA typing method using third generation (Pac-Bio SMRT) sequencing technology. Methods Mol Biol 1802:135–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8546-3_9
Ameur A, Kloosterman WP, Hestand MS (2019) Single-molecule sequencing: towards clinical applications. Trends Biotechnol 37:72–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2018.07.013
Antipov D, Korobeynikov A, McLean JS, Pevzner PA (2016) hybridSPAdes: an algorithm for hybrid assembly of short and long reads. Bioinformatics 32:1009–1015. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv688
Ardui S, Ameur A, Vermeesch JR, Hestand MS (2018) Single molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing comes of age: applications and utilities for medical diagnostics. Nucleic Acids Res 46:2159–2168. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky066
Ashley EA (2016) Towards precision medicine. Nat Rev Genet 17:507–522. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2016.86
Bahlo M, Bennett MF, Degorski P, Tankard RM, Delatycki MB, Lockhart PJ (2018) Recent advances in the detection of repeat expansions with short-read next-generation sequencing. F1000Res 7(F1000 Faculty Rev):736. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.13980.1
Bayega A, Wang YC, Oikonomopoulos S, Djambazian H, Fahiminiya S, Ragoussis J (2018) Transcript profiling using long-read sequencing technologies. Methods Mol Biol 1783:121–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7834-2_6
Benner S, Chen RJ, Wilson NA, Abu-Shumays R, Hurt N, Lieberman KR, Deamer DW, Dunbar WB, Akeson M (2007) Sequence-specific detection of individual DNA polymerase complexes in real time using a nanopore. Nat Nanotechnol 2:718–724. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2007.344
Boldogkoi Z, Moldovan N, Balazs Z, Snyder M, Tombacz D (2019) Long-read sequencing—a powerful tool in viral transcriptome research. Trends Microbiol 27:578–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2019.01.010
Boza V, Brejova B, Vinar T (2017) DeepNano: deep recurrent neural networks for base calling in MinION nanopore reads. PLoS One 12:e0178751. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0178751
Byrne A, Beaudin AE, Olsen HE, Jain M, Cole C, Palmer T, DuBois RM, Forsberg EC, Akeson M, Vollmers C (2017) Nanopore long-read RNAseq reveals widespread transcriptional variation among the surface receptors of individual B cells. Nat Commun 8:16027. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms16027
Chaisson MJ, Wilson RK, Eichler EE (2015) Genetic variation and the de novo assembly of human genomes. Nat Rev Genet 16:627–640. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3933
Chin FY, Leung HC, Yiu SM (2014) Sequence assembly using next generation sequencing data–challenges and solutions. Sci China Life Sci 57:1140–1148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-014-4752-9
Chin CS, Peluso P, Sedlazeck FJ, Nattestad M, Concepcion GT, Clum A, Dunn C, O’Malley R, Figueroa-Balderas R, Morales-Cruz A, Cramer GR, Delledonne M, Luo C, Ecker JR, Cantu D, Rank DR, Schatz MC (2016) Phased diploid genome assembly with single-molecule real-time sequencing. Nat Methods 13:1050–1054. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4035
Clark TA, Spittle KE, Turner SW, Korlach J (2011) Direct detection and sequencing of damaged DNA bases. Genome Integr 2:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/2041-9414-2-10
Clarke J, Wu HC, Jayasinghe L, Patel A, Reid S, Bayley H (2009) Continuous base identification for single-molecule nanopore DNA sequencing. Nat Nanotechnol 4:265–270. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2009.12
Costa-Silva J, Domingues D, Lopes FM (2017) RNA-Seq differential expression analysis: an extended review and a software tool. PLoS One 12:e0190152. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190152
Cretu Stancu M, van Roosmalen MJ, Renkens I, Nieboer MM, Middelkamp S, de Ligt J, Pregno G, Giachino D, Mandrile G, Espejo Valle-Inclan J, Korzelius J, de Bruijn E, Cuppen E, Talkowski ME, Marschall T, de Ridder J, Kloosterman WP (2017) Mapping and phasing of structural variation in patient genomes using nanopore sequencing. Nat Commun 8:1326. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01343-4
De Coster W, D’Hert S, Schultz DT, Cruts M, Van Broeckhoven C (2018) NanoPack: visualizing and processing long-read sequencing data. Bioinformatics 34:2666–2669. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty149
de Koning AP, Gu W, Castoe TA, Batzer MA, Pollock DD (2011) Repetitive elements may comprise over two-thirds of the human genome. PLoS Genet 7:e1002384. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002384
De Roeck A, De Coster W, Bossaerts L, Cacace R, De Pooter T, Van Dongen J, D’Hert S, De Rijk P, Strazisar M, Van Broeckhoven C, Sleegers K (2018) Accurate characterization of expanded tandem repeat length and sequence through whole genome long-read sequencing on PromethION. BioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/439026
De Roeck A, Van Broeckhoven C, Sleegers K (2019) The role of ABCA7 in Alzheimer’s disease: evidence from genomics, transcriptomics and methylomics. Acta Neuropathol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-019-01994-1
Delaneau O, Howie B, Cox AJ, Zagury JF, Marchini J (2013) Haplotype estimation using sequencing reads. Am J Hum Genet 93:687–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.09.002
Deonovic B, Wang Y, Weirather J, Wang XJ, Au KF (2017) IDP-ASE: haplotyping and quantifying allele-specific expression at the gene and gene isoform level by hybrid sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res 45:e32. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1076
Depledge DP, Srinivas KP, Sadaoka T, Bready D, Mori Y, Placantonakis DG, Mohr I, Wilson AC (2019) Direct RNA sequencing on nanopore arrays redefines the transcriptional complexity of a viral pathogen. Nat Commun 10:754. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08734-9
Deurenberg RH, Bathoorn E, Chlebowicz MA, Couto N, Ferdous M, Garcia-Cobos S, Kooistra-Smid AM, Raangs EC, Rosema S, Veloo AC, Zhou K, Friedrich AW, Rossen JW (2017) Application of next generation sequencing in clinical microbiology and infection prevention. J Biotechnol 243:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.12.022
Duitama J, Zablotskaya A, Gemayel R, Jansen A, Belet S, Vermeesch JR, Verstrepen KJ, Froyen G (2014) Large-scale analysis of tandem repeat variability in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res 42:5728–5741. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku212
Ebbert MTW, Farrugia SL, Sens JP, Jansen-West K, Gendron TF, Prudencio M, McLaughlin IJ, Bowman B, Seetin M, DeJesus-Hernandez M, Jackson J, Brown PH, Dickson DW, van Blitterswijk M, Rademakers R, Petrucelli L, Fryer JD (2018) Long-read sequencing across the C9orf72 ‘GGGGCC’ repeat expansion: implications for clinical use and genetic discovery efforts in human disease. Mol Neurodegener 13:46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-018-0274-4
Eberle MA, Fritzilas E, Krusche P, Kallberg M, Moore BL, Bekritsky MA, Iqbal Z, Chuang HY, Humphray SJ, Halpern AL, Kruglyak S, Margulies EH, McVean G, Bentley DR (2017) A reference data set of 5.4 million phased human variants validated by genetic inheritance from sequencing a three-generation 17-member pedigree. Genome Res 27:157–164. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.210500.116
Eid J, Fehr A, Gray J, Luong K, Lyle J, Otto G, Peluso P, Rank D, Baybayan P, Bettman B, Bibillo A, Bjornson K, Chaudhuri B, Christians F, Cicero R, Clark S, Dalal R, Dewinter A, Dixon J, Foquet M, Gaertner A, Hardenbol P, Heiner C, Hester K, Holden D, Kearns G, Kong X, Kuse R, Lacroix Y, Lin S, Lundquist P, Ma C, Marks P, Maxham M, Murphy D, Park I, Pham T, Phillips M, Roy J, Sebra R, Shen G, Sorenson J, Tomaney A, Travers K, Trulson M, Vieceli J, Wegener J, Wu D, Yang A, Zaccarin D, Zhao P, Zhong F, Korlach J, Turner S (2009) Real-time DNA sequencing from single polymerase molecules. Science 323:133–138. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1162986
Erlich RL, Jia X, Anderson S, Banks E, Gao X, Carrington M, Gupta N, DePristo MA, Henn MR, Lennon NJ, de Bakker PI (2011) Next-generation sequencing for HLA typing of class I loci. BMC Genomics 12:42. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-42
Euskirchen P, Bielle F, Labreche K, Kloosterman WP, Rosenberg S, Daniau M, Schmitt C, Masliah-Planchon J, Bourdeaut F, Dehais C, Marie Y, Delattre JY, Idbaih A (2017) Same-day genomic and epigenomic diagnosis of brain tumors using real-time nanopore sequencing. Acta Neuropathol 134:691–703. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-017-1743-5
Fragouli E, Katz-Jaffe M, Alfarawati S, Stevens J, Colls P, Goodall NN, Tormasi S, Gutierrez-Mateo C, Prates R, Schoolcraft WB, Munne S, Wells D (2010) Comprehensive chromosome screening of polar bodies and blastocysts from couples experiencing repeated implantation failure. Fertil Steril 94:875–887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.04.053
Fragouli E, Alfarawati S, Daphnis DD, Goodall NN, Mania A, Griffiths T, Gordon A, Wells D (2011) Cytogenetic analysis of human blastocysts with the use of FISH, CGH and aCGH: scientific data and technical evaluation. Hum Reprod 26:480–490. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deq344
Friedenthal J, Maxwell SM, Munne S, Kramer Y, McCulloh DH, McCaffrey C, Grifo JA (2018) Next generation sequencing for preimplantation genetic screening improves pregnancy outcomes compared with array comparative genomic hybridization in single thawed euploid embryo transfer cycles. Fertil Steril 109:627–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.12.017
Gardy JL, Loman NJ (2018) Towards a genomics-informed, real-time, global pathogen surveillance system. Nat Rev Genet 19:9–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2017.88
Giampaoli S, Alessandrini F, Frajese GV, Guglielmi G, Tagliabracci A, Berti A (2018) Environmental microbiology: perspectives for legal and occupational medicine. Leg Med (Tokyo) 35:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.legalmed.2018.09.014
Gießelmann P, Brändl B, Raimondeau E, Bowen R, Rohrandt C, Tandon R, Kretzmer H, Assum G, Galonska C, Siebert R, Ammerpohl O, Heron A, Schneider SA, Ladewig J, Koch P, Schuldt BM, Graham JE, Meissner A, Müller F-J (2018) Repeat expansion and methylation state analysis with nanopore sequencing. BioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/480285
Giordano F, Aigrain L, Quail MA, Coupland P, Bonfield JK, Davies RM, Tischler G, Jackson DK, Keane TM, Li J, Yue JX, Liti G, Durbin R, Ning Z (2017) De novo yeast genome assemblies from MinION, PacBio and MiSeq platforms. Sci Rep 7:3935. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03996-z
Goodwin S, McPherson JD, McCombie WR (2016) Coming of age: ten years of next-generation sequencing technologies. Nat Rev Genet 17:333–351. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2016.49
Greninger AL, Naccache SN, Federman S, Yu G, Mbala P, Bres V, Stryke D, Bouquet J, Somasekar S, Linnen JM, Dodd R, Mulembakani P, Schneider BS, Muyembe-Tamfum JJ, Stramer SL, Chiu CY (2015) Rapid metagenomic identification of viral pathogens in clinical samples by real-time nanopore sequencing analysis. Genome Med 7:99. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-015-0220-9
Guan P, Sung WK (2016) Structural variation detection using next-generation sequencing data: a comparative technical review. Methods 102:36–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2016.01.020
Hansen S, Faye O, Sanabani SS, Faye M, Bohlken-Fascher S, Faye O, Sall AA, Bekaert M, Weidmann M, Czerny CP, Abd El Wahed A (2018) Combination random isothermal amplification and nanopore sequencing for rapid identification of the causative agent of an outbreak. J Clin Virol 106:23–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2018.07.001
Hartel AJW, Shekar S, Ong P, Schroeder I, Thiel G, Shepard KL (2019) High bandwidth approaches in nanopore and ion channel recordings—a tutorial review. Anal Chim Acta 1061:13–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.01.034
Hedges DJ, Hamilton-Nelson KL, Sacharow SJ, Nations L, Beecham GW, Kozhekbaeva ZM, Butler BL, Cukier HN, Whitehead PL, Ma D, Jaworski JM, Nathanson L, Lee JM, Hauser SL, Oksenberg JR, Cuccaro ML, Haines JL, Gilbert JR, Pericak-Vance MA (2012) Evidence of novel fine-scale structural variation at autism spectrum disorder candidate loci. Mol Autism 3:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/2040-2392-3-2
Hoenen T, Groseth A, Rosenke K, Fischer RJ, Hoenen A, Judson SD, Martellaro C, Falzarano D, Marzi A, Squires RB, Wollenberg KR, de Wit E, Prescott J, Safronetz D, van Doremalen N, Bushmaker T, Feldmann F, McNally K, Bolay FK, Fields B, Sealy T, Rayfield M, Nichol ST, Zoon KC, Massaquoi M, Munster VJ, Feldmann H (2016) Nanopore sequencing as a rapidly deployable ebola outbreak tool. Emerg Infect Dis 22:331–334. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2202.151796
Hoper D, Mettenleiter TC, Beer M (2016) Metagenomic approaches to identifying infectious agents. Rev Sci Tech 35:83–93. https://doi.org/10.20506/rst.35.1.2419
Hosomichi K, Shiina T, Tajima A, Inoue I (2015) The impact of next-generation sequencing technologies on HLA research. J Hum Genet 60:665–673. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2015.102
Huddleston J, Chaisson MJP, Steinberg KM, Warren W, Hoekzema K, Gordon D, Graves-Lindsay TA, Munson KM, Kronenberg ZN, Vives L, Peluso P, Boitano M, Chin CS, Korlach J, Wilson RK, Eichler EE (2017) Discovery and genotyping of structural variation from long-read haploid genome sequence data. Genome Res 27:677–685. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.214007.116
Istace B, Friedrich A, d’Agata L, Faye S, Payen E, Beluche O, Caradec C, Davidas S, Cruaud C, Liti G, Lemainque A, Engelen S, Wincker P, Schacherer J, Aury JM (2017) de novo assembly and population genomic survey of natural yeast isolates with the Oxford Nanopore MinION sequencer. Gigascience 6:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giw018
Jain M, Koren S, Miga KH, Quick J, Rand AC, Sasani TA, Tyson JR, Beggs AD, Dilthey AT, Fiddes IT, Malla S, Marriott H, Nieto T, O’Grady J, Olsen HE, Pedersen BS, Rhie A, Richardson H, Quinlan AR, Snutch TP, Tee L, Paten B, Phillippy AM, Simpson JT, Loman NJ, Loose M (2018) Nanopore sequencing and assembly of a human genome with ultra-long reads. Nat Biotechnol 36:338–345. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.4060
Jayakumar V, Sakakibara Y (2019) Comprehensive evaluation of non-hybrid genome assembly tools for third-generation PacBio long-read sequence data. Brief Bioinform 20:866–876. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbx147
Judge K, Harris SR, Reuter S, Parkhill J, Peacock SJ (2015) Early insights into the potential of the Oxford Nanopore MinION for the detection of antimicrobial resistance genes. J Antimicrob Chemother 70:2775–2778. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkv206
Kafetzopoulou LE, Efthymiadis K, Lewandowski K, Crook A, Carter D, Osborne J, Aarons E, Hewson R, Hiscox JA, Carroll MW, Vipond R, Pullan ST (2018) Assessment of metagenomic Nanopore and Illumina sequencing for recovering whole genome sequences of chikungunya and dengue viruses directly from clinical samples. Euro Surveill. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.es.2018.23.50.1800228
Kafetzopoulou LE, Pullan ST, Lemey P, Suchard MA, Ehichioya DU, Pahlmann M, Thielebein A, Hinzmann J, Oestereich L, Wozniak DM, Efthymiadis K, Schachten D, Koenig F, Matjeschk J, Lorenzen S, Lumley S, Ighodalo Y, Adomeh DI, Olokor T, Omomoh E, Omiunu R, Agbukor J, Ebo B, Aiyepada J, Ebhodaghe P, Osiemi B, Ehikhametalor S, Akhilomen P, Airende M, Esumeh R, Muoebonam E, Giwa R, Ekanem A, Igenegbale G, Odigie G, Okonofua G, Enigbe R, Oyakhilome J, Yerumoh EO, Odia I, Aire C, Okonofua M, Atafo R, Tobin E, Asogun D, Akpede N, Okokhere PO, Rafiu MO, Iraoyah KO, Iruolagbe CO, Akhideno P, Erameh C, Akpede G, Isibor E, Naidoo D, Hewson R, Hiscox JA, Vipond R, Carroll MW, Ihekweazu C, Formenty P, Okogbenin S, Ogbaini-Emovon E, Gunther S, Duraffour S (2019) Metagenomic sequencing at the epicenter of the Nigeria 2018 Lassa fever outbreak. Science 363:74–77. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau9343
Keller MW, Rambo-Martin BL, Wilson MM, Ridenour CA, Shepard SS, Stark TJ, Neuhaus EB, Dugan VG, Wentworth DE, Barnes JR (2018) Direct RNA sequencing of the coding complete influenza a virus genome. Sci Rep 8:14408. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32615-8
Koren S, Schatz MC, Walenz BP, Martin J, Howard JT, Ganapathy G, Wang Z, Rasko DA, McCombie WR, Jarvis ED, Adam MP (2012) Hybrid error correction and de novo assembly of single-molecule sequencing reads. Nat Biotechnol 30:693–700. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2280
Koren S, Walenz BP, Berlin K, Miller JR, Bergman NH, Phillippy AM (2017) Canu: scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res 27:722–736. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.215087.116
Lang K, Surendranath V, Quenzel P, Schofl G, Schmidt AH, Lange V (2018) Full-length HLA class I genotyping with the MinION nanopore sequencer. Methods Mol Biol 1802:155–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8546-3_10
Laver TW, Caswell RC, Moore KA, Poschmann J, Johnson MB, Owens MM, Ellard S, Paszkiewicz KH, Weedon MN (2016) Pitfalls of haplotype phasing from amplicon-based long-read sequencing. Sci Rep 6:21746. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21746
Lee E, Illingworth P, Wilton L, Chambers GM (2015a) The clinical effectiveness of preimplantation genetic diagnosis for aneuploidy in all 24 chromosomes (PGD-A): systematic review. Hum Reprod 30:473–483. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deu303
Lee HL, McCulloh DH, Hodes-Wertz B, Adler A, McCaffrey C, Grifo JA (2015b) In vitro fertilization with preimplantation genetic screening improves implantation and live birth in women age 40 through 43. J Assist Reprod Genet 32:435–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-014-0417-7
Li H (2016) Minimap and miniasm: fast mapping and de novo assembly for noisy long sequences. Bioinformatics 32:2103–2110. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw152
Lin Y, Yuan J, Kolmogorov M, Shen MW, Chaisson M, Pevzner PA (2016) Assembly of long error-prone reads using de Bruijn graphs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:E8396–E8405. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1604560113
Liu L, Li Y, Li S, Hu N, He Y, Pong R, Lin D, Lu L, Law M (2012) Comparison of next-generation sequencing systems. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:251364. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/251364
Liu X, Mei W, Soltis PS, Soltis DE, Barbazuk WB (2017) Detecting alternatively spliced transcript isoforms from single-molecule long-read sequences without a reference genome. Mol Ecol Resour 17:1243–1256. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12670
Liu C, Xiao F, Hoisington-Lopez J, Lang K, Quenzel P, Duffy B, Mitra RD (2018) Accurate typing of human leukocyte antigen class i genes by oxford nanopore sequencing. J Mol Diagn 20:428–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmoldx.2018.02.006
Loomis EW, Eid JS, Peluso P, Yin J, Hickey L, Rank D, McCalmon S, Hagerman RJ, Tassone F, Hagerman PJ (2013) Sequencing the unsequenceable: expanded CGG-repeat alleles of the fragile X gene. Genome Res 23:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.141705.112
Lu H, Giordano F, Ning Z (2016) Oxford nanopore MinION sequencing and genome assembly. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 14:265–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2016.05.004
Macintyre G, Ylstra B, Brenton JD (2016) Sequencing structural variants in cancer for precision therapeutics. Trends Genet 32:530–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2016.07.002
Manrao EA, Derrington IM, Laszlo AH, Langford KW, Hopper MK, Gillgren N, Pavlenok M, Niederweis M, Gundlach JH (2012) Reading DNA at single-nucleotide resolution with a mutant MspA nanopore and phi29 DNA polymerase. Nat Biotechnol 30:349–353. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2171
Mardis ER (2013) Next-generation sequencing platforms. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif) 6:287–303. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-anchem-062012-092628
Martin JA, Wang Z (2011) Next-generation transcriptome assembly. Nat Rev Genet 12:671–682. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3068
Maxam AM, Gilbert W (1977) A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:560–564
McGinty RJ, Rubinstein RG, Neil AJ, Dominska M, Kiktev D, Petes TD, Mirkin SM (2017) Nanopore sequencing of complex genomic rearrangements in yeast reveals mechanisms of repeat-mediated double-strand break repair. Genome Res 27:2072–2082. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.228148.117
McIntyre ABR, Alexander N, Grigorev K, Bezdan D, Sichtig H, Chiu CY, Mason CE (2019) Single-molecule sequencing detection of N6-methyladenine in microbial reference materials. Nat Commun 10:579. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08289-9
Merker JD, Wenger AM, Sneddon T, Grove M, Zappala Z, Fresard L, Waggott D, Utiramerur S, Hou Y, Smith KS, Montgomery SB, Wheeler M, Buchan JG, Lambert CC, Eng KS, Hickey L, Korlach J, Ford J, Ashley EA (2018) Long-read genome sequencing identifies causal structural variation in a Mendelian disease. Genet Med 20:159–163. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2017.86
Mitsuhashi S, Nakagawa S, Takahashi Ueda M, Imanishi T, Frith MC, Mitsuhashi H (2017) Nanopore-based single molecule sequencing of the D4Z4 array responsible for facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Sci Rep 7:14789. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13712-6
Mousavi N, Shleizer-Burko S, Gymrek M (2018) Profiling the genome-wide landscape of tandem repeat expansions. BioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/361162
Nair SS, Luu PL, Qu W, Maddugoda M, Huschtscha L, Reddel R, Chenevix-Trench G, Toso M, Kench JG, Horvath LG, Hayes VM, Stricker PD, Hughes TP, White DL, Rasko JEJ, Wong JJ, Clark SJ (2018) Guidelines for whole genome bisulphite sequencing of intact and FFPET DNA on the Illumina HiSeq X Ten. Epigenetics Chromatin 11:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13072-018-0194-0
Ozaki Y, Suzuki S, Kashiwase K, Shigenari A, Okudaira Y, Ito S, Masuya A, Azuma F, Yabe T, Morishima S, Mitsunaga S, Satake M, Ota M, Morishima Y, Kulski JK, Saito K, Inoko H, Shiina T (2015) Cost-efficient multiplex PCR for routine genotyping of up to nine classical HLA loci in a single analytical run of multiple samples by next generation sequencing. BMC Genomics 16:318. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1514-4
Pang AW, MacDonald JR, Pinto D, Wei J, Rafiq MA, Conrad DF, Park H, Hurles ME, Lee C, Venter JC, Kirkness EF, Levy S, Feuk L, Scherer SW (2010) Towards a comprehensive structural variation map of an individual human genome. Genome Biol 11:R52. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-5-r52
Payne A, Holmes N, Rakyan V, Loose M (2018) BulkVis: a graphical viewer for Oxford nanopore bulk FAST5 files. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty841
Petersen BS, Fredrich B, Hoeppner MP, Ellinghaus D, Franke A (2017) Opportunities and challenges of whole-genome and -exome sequencing. BMC Genet 18:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-017-0479-5
Profaizer T, Lazar-Molnar E, Close DW, Delgado JC, Kumanovics A (2016) HLA genotyping in the clinical laboratory: comparison of next-generation sequencing methods. HLA 88:14–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/tan.12850
Quick J, Loman NJ, Duraffour S, Simpson JT, Severi E, Cowley L, Bore JA, Koundouno R, Dudas G, Mikhail A, Ouedraogo N, Afrough B, Bah A, Baum JH, Becker-Ziaja B, Boettcher JP, Cabeza-Cabrerizo M, Camino-Sanchez A, Carter LL, Doerrbecker J, Enkirch T, Dorival IGG, Hetzelt N, Hinzmann J, Holm T, Kafetzopoulou LE, Koropogui M, Kosgey A, Kuisma E, Logue CH, Mazzarelli A, Meisel S, Mertens M, Michel J, Ngabo D, Nitzsche K, Pallash E, Patrono LV, Portmann J, Repits JG, Rickett NY, Sachse A, Singethan K, Vitoriano I, Yemanaberhan RL, Zekeng EG, Trina R, Bello A, Sall AA, Faye O, Faye O, Magassouba N, Williams CV, Amburgey V, Winona L, Davis E, Gerlach J, Washington F, Monteil V, Jourdain M, Bererd M, Camara A, Somlare H, Camara A, Gerard M, Bado G, Baillet B, Delaune D, Nebie KY, Diarra A, Savane Y, Pallawo RB, Gutierrez GJ, Milhano N, Roger I, Williams CJ, Yattara F, Lewandowski K, Taylor J, Rachwal P, Turner D, Pollakis G, Hiscox JA, Matthews DA, O’Shea MK, Johnston AM, Wilson D, Hutley E, Smit E, Di Caro A, Woelfel R, Stoecker K, Fleischmann E, Gabriel M, Weller SA, Koivogui L, Diallo B, Keita S, Rambaut A, Formenty P et al (2016) Real-time, portable genome sequencing for Ebola surveillance. Nature 530:228–232. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16996
Quinlan AR, Hall IM (2012) Characterizing complex structural variation in germline and somatic genomes. Trends Genet 28:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2011.10.002
Rand AC, Jain M, Eizenga JM, Musselman-Brown A, Olsen HE, Akeson M, Paten B (2017) Mapping DNA methylation with high-throughput nanopore sequencing. Nat Methods 14:411–413. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4189
Raymond CK, Subramanian S, Paddock M, Qiu R, Deodato C, Palmieri A, Chang J, Radke T, Haugen E, Kas A, Waring D, Bovee D, Stacy R, Kaul R, Olson MV (2005) Targeted, haplotype-resolved resequencing of long segments of the human genome. Genomics 86:759–766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2005.08.013
Rhoads A, Au KF (2015) pacbio sequencing and its applications. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 13:278–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2015.08.002
Rovelet-Lecrux A, Hannequin D, Raux G, Le Meur N, Laquerriere A, Vital A, Dumanchin C, Feuillette S, Brice A, Vercelletto M, Dubas F, Frebourg T, Campion D (2006) APP locus duplication causes autosomal dominant early-onset Alzheimer disease with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Nat Genet 38:24–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1718
Salzberg SL, Yorke JA (2005) Beware of mis-assembled genomes. Bioinformatics 21:4320–4321. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti769
Sanger F, Coulson AR (1975) A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol 94:441–448
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Sasazuki T, Inoko H, Morishima S, Morishima Y (2016) Gene map of the HLA region, graves’ disease and hashimoto thyroiditis, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Adv Immunol 129:175–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ai.2015.08.003
Scheben A, Batley J, Edwards D (2017) Genotyping-by-sequencing approaches to characterize crop genomes: choosing the right tool for the right application. Plant Biotechnol J 15:149–161. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12645
Schmutz J, Wheeler J, Grimwood J, Dickson M, Yang J, Caoile C, Bajorek E, Black S, Chan YM, Denys M, Escobar J, Flowers D, Fotopulos D, Garcia C, Gomez M, Gonzales E, Haydu L, Lopez F, Ramirez L, Retterer J, Rodriguez A, Rogers S, Salazar A, Tsai M, Myers RM (2004) Quality assessment of the human genome sequence. Nature 429:365–368. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02390
Sedlazeck FJ, Rescheneder P, Smolka M, Fang H, Nattestad M, von Haeseler A, Schatz MC (2018) Accurate detection of complex structural variations using single-molecule sequencing. Nat Methods 15:461–468. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-018-0001-7
Seo JS, Rhie A, Kim J, Lee S, Sohn MH, Kim CU, Hastie A, Cao H, Yun JY, Kim J, Kuk J, Park GH, Kim J, Ryu H, Kim J, Roh M, Baek J, Hunkapiller MW, Korlach J, Shin JY, Kim C (2016) De novo assembly and phasing of a Korean human genome. Nature 538:243–247. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20098
Shi L, Guo Y, Dong C, Huddleston J, Yang H, Han X, Fu A, Li Q, Li N, Gong S, Lintner KE, Ding Q, Wang Z, Hu J, Wang D, Wang F, Wang L, Lyon GJ, Guan Y, Shen Y, Evgrafov OV, Knowles JA, Thibaud-Nissen F, Schneider V, Yu CY, Zhou L, Eichler EE, So KF, Wang K (2016) Long-read sequencing and de novo assembly of a Chinese genome. Nat Commun 7:12065. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12065
Simpson JT, Workman RE, Zuzarte PC, David M, Dursi LJ, Timp W (2017) Detecting DNA cytosine methylation using nanopore sequencing. Nat Methods 14:407–410. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4184
Smith ZD, Gu H, Bock C, Gnirke A, Meissner A (2009) High-throughput bisulfite sequencing in mammalian genomes. Methods 48:226–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2009.05.003
Spies N, Weng Z, Bishara A, McDaniel J, Catoe D, Zook JM, Salit M, West RB, Batzoglou S, Sidow A (2017) Genome-wide reconstruction of complex structural variants using read clouds. Nat Methods 14:915–920. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4366
Steijger T, Abril JF, Engstrom PG, Kokocinski F, Consortium R, Hubbard TJ, Guigo R, Harrow J, Bertone P (2013) Assessment of transcript reconstruction methods for RNA-seq. Nat Methods 10:1177–1184. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2714
Sudmant PH, Rausch T, Gardner EJ, Handsaker RE, Abyzov A, Huddleston J, Zhang Y, Ye K, Jun G, Fritz MH, Konkel MK, Malhotra A, Stutz AM, Shi X, Casale FP, Chen J, Hormozdiari F, Dayama G, Chen K, Malig M, Chaisson MJP, Walter K, Meiers S, Kashin S, Garrison E, Auton A, Lam HYK, Mu XJ, Alkan C, Antaki D, Bae T, Cerveira E, Chines P, Chong Z, Clarke L, Dal E, Ding L, Emery S, Fan X, Gujral M, Kahveci F, Kidd JM, Kong Y, Lameijer EW, McCarthy S, Flicek P, Gibbs RA, Marth G, Mason CE, Menelaou A, Muzny DM, Nelson BJ, Noor A, Parrish NF, Pendleton M, Quitadamo A, Raeder B, Schadt EE, Romanovitch M, Schlattl A, Sebra R, Shabalin AA, Untergasser A, Walker JA, Wang M, Yu F, Zhang C, Zhang J, Zheng-Bradley X, Zhou W, Zichner T, Sebat J, Batzer MA, McCarroll SA, Genomes Project C, Mills RE, Gerstein MB, Bashir A, Stegle O, Devine SE, Lee C, Eichler EE, Korbel JO (2015) An integrated map of structural variation in 2,504 human genomes. Nature 526:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15394
Tattini L, D’Aurizio R, Magi A (2015) Detection of genomic structural variants from next-generation sequencing data. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 3:92. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2015.00092
Tewhey R, Bansal V, Torkamani A, Topol EJ, Schork NJ (2011) The importance of phase information for human genomics. Nat Rev Genet 12:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2950
Traherne JA (2008) Human MHC architecture and evolution: implications for disease association studies. Int J Immunogenet 35:179–192. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-313X.2008.00765.x
Travers KJ, Chin CS, Rank DR, Eid JS, Turner SW (2010) A flexible and efficient template format for circular consensus sequencing and SNP detection. Nucleic Acids Res 38:e159. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq543
Treangen TJ, Salzberg SL (2011) Repetitive DNA and next-generation sequencing: computational challenges and solutions. Nat Rev Genet 13:36–46. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3117
Trowsdale J (1993) Genomic structure and function in the MHC. Trends Genet 9:117–122
Tubio JM (2015) Somatic structural variation and cancer. Brief Funct Genomics 14:339–351. https://doi.org/10.1093/bfgp/elv016
Turner TR, Hayhurst JD, Hayward DR, Bultitude WP, Barker DJ, Robinson J, Madrigal JA, Mayor NP, Marsh SGE (2018) Single molecule real-time DNA sequencing of HLA genes at ultra-high resolution from 126 international HLA and immunogenetics workshop cell lines. HLA 91:88–101. https://doi.org/10.1111/tan.13184
Ulahannan D, Kovac MB, Mulholland PJ, Cazier JB, Tomlinson I (2013) Technical and implementation issues in using next-generation sequencing of cancers in clinical practice. Br J Cancer 109:827–835. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2013.416
Usdin K (2008) The biological effects of simple tandem repeats: lessons from the repeat expansion diseases. Genome Res 18:1011–1019. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.070409.107
Vaser R, Sovic I, Nagarajan N, Sikic M (2017) Fast and accurate de novo genome assembly from long uncorrected reads. Genome Res 27:737–746. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.214270.116
Wang C, Krishnakumar S, Wilhelmy J, Babrzadeh F, Stepanyan L, Su LF, Levinson D, Fernandez-Vina MA, Davis RW, Davis MM, Mindrinos M (2012) High-throughput, high-fidelity HLA genotyping with deep sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:8676–8681. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1206614109
Warnecke PM, Stirzaker C, Song J, Grunau C, Melki JR, Clark SJ (2002) Identification and resolution of artifacts in bisulfite sequencing. Methods 27:101–107
Wei S, Weiss ZR, Gaur P, Forman E, Williams Z (2018) Rapid preimplantation genetic screening using a handheld, nanopore-based DNA sequencer. Fertil Steril 110(910–916):e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.06.014
Weirather JL, Afshar PT, Clark TA, Tseng E, Powers LS, Underwood JG, Zabner J, Korlach J, Wong WH, Au KF (2015) Characterization of fusion genes and the significantly expressed fusion isoforms in breast cancer by hybrid sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res 43:e116. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv562
Weirather JL, de Cesare M, Wang Y, Piazza P, Sebastiano V, Wang XJ, Buck D, Au KF (2017) Comprehensive comparison of pacific biosciences and oxford nanopore technologies and their applications to transcriptome analysis. F1000Res 6:100. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.10571.2
Xiao CL, Zhu S, He M, Chen Zhang Q, Chen Y, Yu G, Liu J, Xie SQ, Luo F, Liang Z, Wang DP, Bo XC, Gu XF, Wang K, Yan GR (2018) N(6)-methyladenine DNA modification in the human genome. Mol Cell 71(306–318):e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.015
Yang Z, Lin J, Zhang J, Fong WI, Li P, Zhao R, Liu X, Podevin W, Kuang Y, Liu J (2015) Randomized comparison of next-generation sequencing and array comparative genomic hybridization for preimplantation genetic screening: a pilot study. BMC Med Genomics 8:30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-015-0110-4
Yuan Y, Bayer PE, Batley J, Edwards D (2017) Improvements in genomic technologies: application to crop genomics. Trends Biotechnol 35:547–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2017.02.009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest declared by MKM and KPC. MW works in a company which provides Nanopore services.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Midha, M.K., Wu, M. & Chiu, KP. Long-read sequencing in deciphering human genetics to a greater depth. Hum Genet 138, 1201–1215 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-019-02064-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-019-02064-y