Abstract
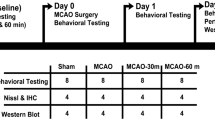
There is evidence that physical activity is associated with decreased brain injury resulting from transient middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion. We investigated whether exercise could reduce stroke-induced brain inflammatory injury and its associated mediators. Sprague Dawley rats (3 months old) were subjected to 30 min exercise on a treadmill each day for 1–3 weeks. Stroke, in exercised and non-exercised animals, was then induced by a 2-h MCA occlusion followed by 48 h of reperfusion using an intraluminal filament. Endothelial expression of the intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and leukocyte infiltration were determined by immunocytochemistry. Expressions of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and ICAM-1 mRNA were detected using a real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction in ischemic rats with or without exercise, and in non-ischemic control rats following exercise. Expression of TNF-α increased after exercise for 2 and 3 weeks. The overexpression of TNF-α was not further elevated in 3-week exercised rats subjected to a transient MCA occlusion and 6 or 12 h of reperfusion, as compared to that in non-exercised rats. Furthermore, ICAM-1 mRNA expression remained at significantly (P<0.01) low levels in exercised animals during ischemia/reperfusion. Pre-ischemic exercise significantly (P<0.01) reduced numbers of ICAM-1-positive vessels and infiltrating leukocytes in the frontoparietal cortex and dorsolateral striatum in ischemic rats after 48 h of reperfusion. Exercised ischemic rats demonstrated an 11±7% infarct volume of contralateral hemisphere as compared to a 52±3% volume in non-exercised ischemic rats. The data suggests that exercise inhibits inflammatory injury (i.e., decreased expression of inflammatory mediators and reduced accumulation of leukocytes) during reperfusion, leading to reduced brain damage. Chronically increased expression of TNF-α during exercise prevent the same downstream inflammatory events as does acutely elevated TNF-α after ischemia/reperfusion.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang ET, Wong PT, Moochhala S, Ng YK (2003) Neuroprotection associated with running: is it a result of increased endogenous neurotrophic factors? Neuroscience 118:335–345
Ay I, Sugimori H, Finklestein SP (2001) Intravenous basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) decreases DNA fragmentation and prevents downregulation of Bcl-2 expression in the ischemic brain following middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 87:71–80
Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ (1999) Inflammatory mediators and stroke: new opportunities for novel therapeutics. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 19:819–834
Barone FC, Hillegass LM, Price WJ, White RF, Lee EV, Feuerstein GZ, Sarau HM, Clark RK, Griswold DE (1991) Polymorphonuclear leukocyte infiltration into cerebral focal ischemic tissue: myeloperoxidase activity assay and histologic verification. J Neurosci Res 29:336–345
Belayev L, Alonso OF, Busto R, Zhao W, Ginsberg MD (1996) Middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat by intraluminal suture. Neurological and pathological evaluation of an improved model. Stroke 27:1616–1622
Berti R, Williams AJ, Moffett JR, Hale SL, Velarde LC, Elliott PJ, Yao C, Dave JR, Tortella FC (2002) Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory gene expression associated with ischemia-reperfusion brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:1068–1079
Black JE, Isaacs KR, Anderson BJ, Alcantara AA, Greenough WT (1990) Learning causes synaptogenesis, whereas motor activity causes angiogenesis, in cerebellar cortex of adult rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:5568–5572
Black JE, Zelazny AM, Greenough WT (1991) Capillary and mitochondrial support of neural plasticity in adult rat visual cortex. Exp Neurol 111:204–209
Boero JA, Ascher J, Arregui A, Rovainen C, Woolsey TA (1999) Increased brain capillaries in chronic hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 86:1211–1219
Botchkina GI, Meistrell ME, Botchkina IL, Tracey KJ (1997) Expression of TNF and TNF receptors (p55 and p75) in the rat brain after focal cerebral ischemia. Mol Med 3:765–781
Bruce AJ, Boling W, Kindy MS, Peschon J, Kraemer PJ, Carpenter MK, Holtsberg FW, Mattson MP (1996) Altered neuronal and microglial responses to excitotoxic and ischemic brain injury in mice lacking TNF receptors. Nat Med 2:788–794
Carroll JE, Hess DC, Howard EF, Hill WD (2000) Is nuclear factor-kappaB a good treatment target in brain ischemia/reperfusion injury? NeuroReport 11:R1–R4
Chandrasekar B, Streitman JE, Colston JT, Freeman GL (1998) Inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B attenuates proinflammatory cytokine and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in postischemic myocardium. Biochim Biophys Acta 1406:91–106
Chatzipanteli K, Alonso OF, Kraydieh S, Dietrich WD (2000) Importance of posttraumatic hypothermia and hyperthermia on the inflammatory response after fluid percussion brain injury: biochemical and immunocytochemical studies. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:531–542
Cotman CW, Engesser C (2002) Exercise enhances and protects brain function. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 30:75–79
Del Zoppo GJ, Becker KJ, Hallenbeck JM (2001) Inflammation after stroke: is it harmful? Arch Neurol 58:669–672
Ding Y, Li J, Rafols JA, Phillis JW, Diaz FG (2002) Pre-reperfusion flushing of ischemic territory reduces inflammatory injury following transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Stroke 33:2492–2498
Ding Y, Li J, Rafols JA, Clark J, Phillis JW, Diaz FG (2003) Pre-ischemic motor exercise reduces ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats that correlateds with regional angiogenesis and cellular expression of neurotrophin. Stroke 34:240–241
Ding Y, Young C, Li C, Luan X, McAllister JP, II, Clark J, Diaz FG (2003) Reduced inflammatory mediator expression by pre-reperfusion infusion into ischemic territory: a real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis. Neurosci Lett 353:173–176
Ding Y, Li J, Luan X, Ding YH, Lai Q, Rafols JA, Phillis JW, Clark J, Diaz FG (2004) Exercise pre-conditioning reduces brain damage in ischemic rats via regional angiogenesis and cellular overexpression of neurotrophin. Neuroscience 124:583–591
Dirnagl U, Iadecola C, Moskowitz MA (1999) Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends Neurosci 22:391–397
Domenech RJ, Macho P, Velez D, Sanchez G, Liu X, Dhalla N (1998) Tachycardia preconditions infarct size in dogs: role of adenosine and protein kinase C. Circulation 97:786–794
Feuerstein GZ, Wang X (2001) Inflammation and stroke: benefits without harm? Arch Neurol 58:672–674
Fisher M, Meadows ME, Do T, Weise J, Trubetskoy V, Charette M, Finklestein SP (1995) Delayed treatment with intravenous basic fibroblast growth factor reduces infarct size following permanent focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 15:953–959
Garcia JH, Liu KF, Yoshida Y, Lian J, Chen S, Zoppo GJ del (1994) Influx of leukocytes and platelets in an evolving brain infarct (Wistar rat). Am J Pathol 144:188–199
Gibson UE, Heid CA, Williams PM (1996) A novel method for real time quantitative RT-PCR. Genome Res 6:995–1001
Ginis I, Schweizer U, Brenner M, Liu J, Azzam N, Spatz M, Hallenbeck JM (1999) TNF-alpha pretreatment prevents subsequent activation of cultured brain cells with TNF-alpha and hypoxia via ceramide. Am J Physiol 276:C1171–C1183
Ginis I, Hallenbeck JM, Liu J, Spatz M, Jaiswal R, Shohami E (2000) Tumor necrosis factor and reactive oxygen species cooperative cytotoxicity is mediated via inhibition of NF-kappaB. Mol Med 6:1028–1041
Ginis I, Jaiswal R, Klimanis D, Liu J, Greenspon J, Hallenbeck JM (2002) TNF-alpha-induced tolerance to ischemic injury involves differential control of NF-kappaB transactivation: the role of NF-kappaB association with p300 adaptor. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:142–152
Gomez M, Bequet F, Berthelot M, Chennaoui M, Guezennec CY (2001) Site-dependent effects of an acute intensive exercise on extracellular 5-HT and 5-HIAA levels in rat brain. Neurosci Lett 301:143–146
Gomez P, Dao L, So V (1997) Physical exercise induces FGF-2 and its mRNA in the hippocampus. Brain Res 764:1–8
Hess DC, Howard E, Cheng C, Carroll J, Hill WD, Hsu CY (2000) Hypertonic mannitol loading of NF-kappaB transcription factor decoys in human brain microvascular endothelial cells blocks upregulation of ICAM-1. Stroke 31:1179–1186
Hiratsuka M, Agatsuma Y, Mizugaki M (1999) Rapid detection of CYP2C9*3 alleles by real-time fluorescence PCR based on SYBR Green. Mol Genet Metab 68:357–362
Howard EF, Chen Q, Cheng C, Carroll JE, Hess D (1998) NF-kappa B is activated and ICAM-1 gene expression is upregulated during reoxygenation of human brain endothelial cells. Neurosci Lett 248:199–203
Ickes BR, Pham TM, Sanders LA, Albeck DS, Mohammed AH, Granholm AC (2000) Long-term environmental enrichment leads to regional increases in neurotrophin levels in rat brain. Exp Neurol 164:45–52
Isaacs KR, Anderson BJ, Alcantara AA, Black JE, Greenough WT (1992) Exercise and the brain: angiogenesis in the adult rat cerebellum after vigorous physical activity and motor skill learning. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 12:110–119
Jean WC, Spellman SR, Nussbaum ES, Low WC (1998) Reperfusion injury after focal cerebral ischemia: the role of inflammation and the therapeutic horizon. Neurosurgery 43:1382–1396
Jiang N, Finklestein SP, Do T, Caday CG, Charette M, Chopp M (1996) Delayed intravenous administration of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) reduces infarct volume in a model of focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in the rat. J Neurol Sci 139:173–179
Kleim JA, Cooper NR, VandenBerg PM (2002) Exercise induces angiogenesis but does not alter movement representations within rat motor cortex. Brain Res 934:1–6
Kleim JA, Jones TA, Schallert T (2003) Motor enrichment and the induction of plasticity before or after brain injury. Neurochem Res 28:1757–1769
Koketsu N, Berlove DJ, Moskowitz MA, Kowall NW, Caday CG, Finklestein SP (1994) Pretreatment with intraventricular basic fibroblast growth factor decreases infarct size following focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Ann Neurol 35:451–457
LaManna JC, Vendel LM, Farrell RM (1992) Brain adaptation to chronic hypobaric hypoxia in rats. J Appl Physiol 72:2238–2243
Ledebur HC, Parks TP (1995) Transcriptional regulation of the intercellular adhesion molecule-1 gene by inflammatory cytokines in human endothelial cells. Essential roles of a variant NF-kappa B site and p65 homodimers. J Biol Chem 270:933–943
Li J, Luan X, Clark J, Rafols JA, Ding Y (2004) Neuroprotection against transient cerebral ischemia by exercise pre-conditioning in rats. Neurol Res 26:404–408
Maybaum S, Ilan M, Mogilevsky J, Tzivoni D (1996) Improvement in ischemic parameters during repeated exercise testing: a possible model for myocardial preconditioning. Am J Cardiol 78:1087–1091
Neeper SA, Gomez P, Choi J, Cotman C (1995) Exercise and brain neurotrophins. Nature 373:109
Neeper SA, Gomez P, Choi J, Cotman CW (1996) Physical activity increases mRNA for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor in rat brain. Brain Res 726:49–56
Ohtsuki T, Ruetzler CA, Tasaki K, Hallenbeck JM (1996) Interleukin-1 mediates induction of tolerance to global ischemia in gerbil hippocampal CA1 neurons. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:1137–1142
Okada Y, Copeland BR, Mori E, Tung MM, Thomas WS, Zoppo GJ del (1994) P-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression after focal brain ischemia and reperfusion. Stroke 25:202–211
Pagliari R, Peyrin L (1995) Norepinephrine release in the rat frontal cortex under treadmill exercise: a study with microdialysis. J Appl Physiol 78:2121–2130
Radak Z, Sasvari M, Nyakas C, Pucsok J, Nakamoto H, Goto S (2000) Exercise preconditioning against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage in proteins of rat myocardium. Arch Biochem Biophys 376:248–251
Radak Z, Sasvari M, Nyakas C, Taylor AW, Ohno H, Nakamoto H, Goto S (2000) Regular training modulates the accumulation of reactive carbonyl derivatives in mitochondrial and cytosolic fractions of rat skeletal muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys 383:114–118
Rahman A, Anwar KN, True AL, Malik AB (1999) Thrombin-induced p65 homodimer binding to downstream NF-kappa B site of the promoter mediates endothelial ICAM-1 expression and neutrophil adhesion. J Immunol 162:5466–5476
Read MA, Whitley MZ, Williams AJ, Collins T (1994) NF-kappa B and I kappa B alpha: an inducible regulatory system in endothelial activation. J Exp Med 179:503–512
Ren JM, Finklestein SP (1997) Time window of infarct reduction by intravenous basic fibroblast growth factor in focal cerebral ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol 327:11–16
Ritter LS, Orozco JA, Coull BM, McDonagh PF, Rosenblum WI (2000) Leukocyte accumulation and hemodynamic changes in the cerebral microcirculation during early reperfusion after stroke. Stroke 31:1153–1161
Schabitz WR, Schwab S, Spranger M, Hacke W (1997) Intraventricular brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces infarct size after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17:500–506
Stanimirovic D, Satoh K (2000) Inflammatory mediators of cerebral endothelium: a role in ischemic brain inflammation. Brain Pathol 10:113–126
Stummer W, Weber K, Tranmer B, Baethmann A, Kempski O (1994) Reduced mortality and brain damage after locomotor activity in gerbil forebrain ischemia. Stroke 25:1862–1869
Swain RA, Harris AB, Wiener EC, Dutka MV, Morris HD, Theien BE, Konda S, Engberg K, Lauterbur PC, Greenough WT (2003) Prolonged exercise induces angiogenesis and increases cerebral blood volume in primary motor cortex of the rat. Neuroscience 117:1037–1046
Swanson RA, Morton MT, Tsao-Wu G, Savalos RA, Davidson C, Sharp FR (1990) A semiautomated method for measuring brain infarct volume. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 10:290–293
Tasaki K, Ruetzler CA, Ohtsuki T, Martin D, Nawashiro H, Hallenbeck JM (1997) Lipopolysaccharide pre-treatment induces resistance against subsequent focal cerebral ischemic damage in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Brain Res 748:267–270
Tomai F, Crea F, Chiariello L, Gioffre PA (1999) Ischemic preconditioning in humans: models, mediators, and clinical relevance. Circulation 100:559–563
Tracey KJ, Vlassara H, Cerami A (1989) Cachectin/tumour necrosis factor. Lancet 1:1122–1126
Vissing J, Andersen M, Diemer NH (1996) Exercise-induced changes in local cerebral glucose utilization in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:729–736
Wang RY, Yang YR, Yu SM (2001) Protective effects of treadmill training on infarction in rats. Brain Res 922:140–143
Wang X, Li X, Currie RW, Willette RN, Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ (2000) Application of real-time polymerase chain reaction to quantitate induced expression of interleukin-1beta mRNA in ischemic brain tolerance. J Neurosci Res 59:238–246
Wang X, Li X, Erhardt JA, Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ (2000) Detection of tumor necrosis factor-alpha mRNA induction in ischemic brain tolerance by means of real-time polymerase chain reaction. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:15–20
Yamashita K, Wiessner C, Lindholm D, Thoenen H, Hossmann KA (1997) Post-occlusion treatment with BDNF reduces infarct size in a model of permanent occlusion of the middle cerebral artery in rat. Metab Brain Dis 12:271–280
Yamashita N, Hoshida S, Otsu K, Taniguchi N, Kuzuya T, Hori M (1999) Monophosphoryl lipid A provides biphasic cardioprotection against ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rat hearts. Br J Pharmacol 128:412–418
Yanamoto H, Hashimoto N, Nagata I, Kikuchi H (1998) Infarct tolerance against temporary focal ischemia following spreading depression in rat brain. Brain Res 784:239–249
Yanamoto H, Nagata I, Sakata M, Zhang Z, Tohnai N, Sakai H, Kikuchi H (2000) Infarct tolerance induced by intra-cerebral infusion of recombinant brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Brain Res 859:240–248
Zea Longa Z, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
Zhang RL, Chopp M, Chen H, Garcia JH (1994) Temporal profile of ischemic tissue damage, neutrophil response, and vascular plugging following permanent and transient (2H) middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J Neurol Sci 125:3–10
Zhang Z, Chopp M (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietins in focal cerebral ischemia. Trends Cardiovasc Med 12:62–66
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Qin Lai for his help in the statistical analysis, to Mr. Yandong Zhou for his help in preparation of the manuscript. This work was supported partially by an American Heart Association Midwest Affiliate Grant in Aid and Wayne State University Research Stimulation Fund to Yuchuan Ding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, YH., Young, C.N., Luan, X. et al. Exercise preconditioning ameliorates inflammatory injury in ischemic rats during reperfusion. Acta Neuropathol 109, 237–246 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-004-0943-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-004-0943-y