Abstract
Background
The finite life of non-rechargeable batteries powering implantable pulse generators (IPG) necessitates their periodic replacement. Children receiving deep brain stimulation (DBS) may require frequent battery changes over their treatment lifetime.
Objectives
We aimed to determine the battery life of IPGs used in pallidal DBS for the treatment of dystonia in children and young people.
Methods
We make use of a review of case notes of all children and young people undergoing DBS surgery at our institution from June 2005 to May 2010.
Results
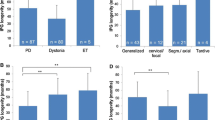
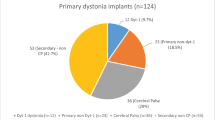
A total of 54 children and young people underwent surgery on at least one occasion, with a total of 76 IPGs implanted. Replacement IPGs due to battery failure were required in 15 out of 54 (27.8%). The average time to battery failure was 24.5 ± 2.9 months (95% confidence interval), with a range of 13–39 months. Battery life was significantly longer in primary compared to subsequent IPGs. No difference in longevity was seen between different IPG devices.
Conclusions
IPG battery life may be short in children and young people receiving treatment for dystonia. These findings highlight the potential benefits of the recently introduced rechargeable neurostimulators.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allert N, Kirsch H, Weirich W, Karbe H (2009) Stability of symptom control after replacement of impulse generators for deep brain stimulation. J Neurosurg 110:1274–1277
Alterman RL, Miravite J, Weisz D, Shils JL, Bressman SB, Tagliati M (2007) Sixty hertz pallidal deep brain stimulation for primary torsion dystonia. Neurology 69:681–688
Alterman RL, Shils JL, Miravite J, Tagliati M (2007) Lower stimulation frequency can enhance tolerability and efficacy of pallidal deep brain stimulation for dystonia. Mov Disord 22:366–368
Andrews C, Aviles-Olmos I, Hariz M, Foltynie T (2010) Which patients with dystonia benefit from deep brain stimulation? A metaregression of individual patient outcomes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81:1383–1389
Anheim M, Fraix V, Chabardes S, Krack P, Benabid AL, Pollak P (2007) Lifetime of Itrel II pulse generators for subthalamic nucleus stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 22:2436–2439
Anheim M, Vercueil L, Fraix V, Chabardes S, Seigneuret E, Krack P, Benabid AL, Vidailhet M, Pollak P (2008) Early stimulation of DYT1 primary generalized dystonia prevents from its secondary irreversible complications. Mov Disord 23:2261–2263
Blahak C, Capelle HH, Baezner H, Kinfe TM, Hennerici MG, Krauss JK (2011) Battery lifetime in pallidal deep brain stimulation for dystonia. Eur J Neurol 18:872–875
Chou KL, Siderowf AD, Jaggi JL, Liang GS, Baltuch GH (2004) Unilateral battery depletion in Parkinson’s disease patients treated with bilateral subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation may require urgent surgical replacement. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 82:153–155
Coubes P, Cif L, El Fertit H, Hemm S, Vayssiere N, Serrat S, Picot MC, Tuffery S, Claustres M, Echenne B, Frerebeau P (2004) Electrical stimulation of the globus pallidus internus in patients with primary generalized dystonia: long-term results. J Neurosurg 101:189–194
Goto S, Mita S, Ushio Y (2002) Bilateral pallidal stimulation for cervical dystonia. An optimal paradigm from our experiences. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 79:221–227
Halbig TD, Gruber D, Kopp UA, Schneider GH, Trottenberg T, Kupsch A (2005) Pallidal stimulation in dystonia: effects on cognition, mood, and quality of life. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:1713–1716
Isaias IU, Alterman RL, Tagliati M (2008) Outcome predictors of pallidal stimulation in patients with primary dystonia: the role of disease duration. Brain 131:1895–1902
Isaias IU, Alterman RL, Tagliati M (2009) Deep brain stimulation for primary generalized dystonia: long-term outcomes. Arch Neurol 66:465–470
Krause M, Fogel W, Kloss M, Rasche D, Volkmann J, Tronnier V (2004) Pallidal stimulation for dystonia. Neurosurgery 55:1361–1368
Kupsch A, Benecke R, Muller J, Trottenberg T, Schneider GH, Poewe W, Eisner W, Wolters A, Muller JU, Deuschl G, Pinsker MO, Skogseid IM, Roeste GK, Vollmer-Haase J, Brentrup A, Krause M, Tronnier V, Schnitzler A, Voges J, Nikkhah G, Vesper J, Naumann M, Volkmann J (2006) Pallidal deep-brain stimulation in primary generalized or segmental dystonia. N Engl J Med 355:1978–1990
Moro E, Piboolnurak P, Arenovich T, Hung SW, Poon YY, Lozano AM (2009) Pallidal stimulation in cervical dystonia: clinical implications of acute changes in stimulation parameters. Eur J Neurol 16:506–512
Ondo WG, Meilak C, Vuong KD (2007) Predictors of battery life for the Activa Soletra 7426 Neurostimulator. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 13:240–242
Parr JR, Green AL, Joint C, Andrew M, Gregory RP, Scott RB, McShane MA, Aziz TZ (2007) Deep brain stimulation in childhood: an effective treatment for early onset idiopathic generalised dystonia. Arch Dis Child 92:708–711
Van Buyten JP, Fowo S, Spincemaille GH, Tronnier V, Beute G, Pallares JJ, Naous H, Zucco F, Krauss JK, De Andres J, Buchser E, Costantini A, Lazorthes Y (2008) The restore rechargeable, implantable neurostimulator: handling and clinical results of a multicenter study. Clin J Pain 24:325–334
Vasques X, Cif L, Gonzalez V, Nicholson C, Coubes P (2009) Factors predicting improvement in primary generalized dystonia treated by pallidal deep brain stimulation. Mov Disord 24:846–853
Vidailhet M, Vercueil L, Houeto JL, Krystkowiak P, Benabid AL, Cornu P, Lagrange C, du Tezenas MS, Dormont D, Grand S, Blond S, Detante O, Pillon B, Ardouin C, Agid Y, Destee A, Pollak P (2005) Bilateral deep-brain stimulation of the globus pallidus in primary generalized dystonia. N Engl J Med 352:459–467
Vidailhet M, Vercueil L, Houeto JL, Krystkowiak P, Lagrange C, Yelnik J, Bardinet E, Benabid AL, Navarro S, Dormont D, Grand S, Blond S, Ardouin C, Pillon B, Dujardin K, Hahn-Barma V, Agid Y, Destee A, Pollak P (2007) Bilateral, pallidal, deep-brain stimulation in primary generalised dystonia: a prospective 3 year follow-up study. Lancet Neurol 6:223–229
Vidailhet M, Yelnik J, Lagrange C, Fraix V, Grabli D, Thobois S, Burbaud P, Welter ML, Xie-Brustolin J, Braga MC, Ardouin C, Czernecki V, Klinger H, Chabardes S, Seigneuret E, Mertens P, Cuny E, Navarro S, Cornu P, Benabid AL, Le Bas JF, Dormont D, Hermier M, Dujardin K, Blond S, Krystkowiak P, Destee A, Bardinet E, Agid Y, Krack P, Broussolle E, Pollak P (2009) Bilateral pallidal deep brain stimulation for the treatment of patients with dystonia-choreoathetosis cerebral palsy: a prospective pilot study. Lancet Neurol 8:709–717
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Guy’s and St Thomas’ Charity: Project Number G06070.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lumsden, D.E., Kaminska, M., Tustin, K. et al. Battery life following pallidal deep brain stimulation (DBS) in children and young people with severe primary and secondary dystonia. Childs Nerv Syst 28, 1091–1097 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1728-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1728-6