Abstract
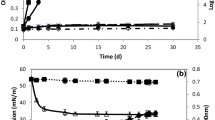
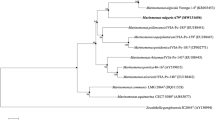
Strain SM1 was isolated as a biosurfactant-producing microorganism from seawater and presumptively identified as Myroides sp., based on morphology, biochemical characteristics and 16S rDNA sequence. The strain produced surface-active compounds in marine broth, which were purified, using emulsification activity for n-hexadecane as an indicator. The purified compounds were identified by thin-layer chromatography, 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra and fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry as cholic acid, deoxycholic acid and their glycine conjugates. Type strains of the genus Myroides, M. odoratus JCM7458 and M. odoramitimus JCM7460, also produced these compounds. Myroides sp. strain SM1 possessed a biosynthetic route to cholic acid from cholesterol. Thus, bile acids were found as new products of prokaryotic cells, genus Myroides.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrus G, Ilkoy E, Jekkel A, Horvath G, Bocskei Z (1995) Microbial transformation of beta-sitosterol and stigmasterol into 26-oxygenated derivatives. Steroids 60:621–625
Av-Gay Y, Sobouti R (2000) Cholesterol is accumulated by mycobacteria but its degradation is limited to non-pathogenic fast-growing mycobacteria. Can J Microbiol 46:826–831
Dayal B, Ertel NH, Padia J, Rapole KR, Salen G (1997) 7β-Hydroxy bile alcohols: facile synthesis and 2D 1H NMR studies of 5β-cholestqane-3α, 7β, 12α, 25-tetrol. Steroids 62:409–414
Gonzalez CJ, Santos JA, Garcia-Lopez ML, Otero A (2000) Psychrobacters and related bacteria in freshwater fish. J Food Prot 63:315–321
Karlaganis G, Bradley SE, Boyer JL, Batta AK, Salen G, Egestad B, Sjövall J (1989) A bile alcohol sulfate as a major component in the bile of the small skate (Raja erinacea). J Lipid Res 30:317–322
Kurdi P, Veen HW van, Tanaka H, Mierau I, Konings WN, Tannock GW, Tomita F, Yokota A (2000) Cholic acid is accumulated spontaneously, driven by membrane ΔpH, in many lactobacilli. J Bacteriol 182:6525–6528
Kurdi P, Tanaka H, Veen HW van, Asano K, Tomita F, Yokota A (2003) Cholic acid accumulation and its diminution by short-chain fatty acids in bifidobacteria. Microbiology 149:2031–2037
Lamb DC, Kelly DE, Manning NJ, Kelly SL (1998) A sterol biosynthetic pathway in Mycobacterium. FEBS Lett 437:142–144
Mahato SB, Baneriee S, Podder S (1988) Oxidative side-chain and ring fision of pregnanes by Arthrobacter simplex. Biochem J 255:769–774
Matsuzaki Y, Bouscarel B, Ikegami T, Honda A, Doy M, Ceryak S, Fukushima S, Yoshida S, Shoda J, Tanaka N (2002) Selective inhibition of CYP27A1 and of chenodeoxycholic acid synthesis in cholestatic hamster liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 1588:139–148
Miyamoto M, Matsumoto J, Iwaya T, Itagaki E (1995) Bacterial steroid monooxigenase catalyzing the Baeyer–Villiger oxidation of C21-ketosteroids from Rhodococcus rhodochrous: the isolation and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta 1251:115–124
Passeri A, Lang S, Wagner F, Wray V (1991) Marine biosurfactants, II. Production and characterization of an anionic trehalose tetraester from the marine bacterium Arthrobacter sp. EK1. Z Naturforsch 46c:204–209
Poralla K (2001) The changing path of hopanoid research: from condensing lipids to new membrane enzymes. In: Braun V, Götz F (eds) Microbial fundamentals of biotechnology. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, pp 263–281
Rochelle PA, Will JAK, Fry JC, Jenkins GJS, Parkes RJ, Turley CM, Weightman AJ (1995) Extraction and amplification of 16S rRNA genes from deep marine sediments and seawater to assess bacterial community diversity. In: Trevors JT, Elsas JD van (eds) Nucleic acids in the environment. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 219–239
Small DM, Penkett SA, Chapman D (1969) Studies on simple and mixed bile salt micelles by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochem Biophys Acta 176:178–189
Spiteller D, Dettner K, Boland W (2000) Gut bacteria may be involved in interactions between plants, herbivores and their predators: microbial biosynthesis of N-acylglutamine surfactants as elicitors of plant volatiles. Biol Chem 381:755–762
Vancanneyt M, Segers P, Torck U, Hoste B, Bernardet JF, Vandamme P, Kersters K (1996) Reclassification of Flavobacterium odoratum (Stutzer 1929) strains to a new genus, Myroides, as Myroides odoratus comb. nov. and Myroides odoramitimus sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:926–932
Waterhous DV, Barnes S, Muccio DD (1985) Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of bile acids. Development of two-dimensional NMR methods for the elucidation of proton resonance assignments for five common hydroxylated bile acids, and their parentbile acid, 5 beta-cholanoic acid. J Lipid Res 26:1068–1078
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the JSPS-NRCT Core University Program for providing a scholarship to S.M., to The Nihonseimei Foundation for a grant to F.K. and to the Marine Biotechnology Institute, Iwate, Japan, for their kind supply of weathered crude oil. The authors express their thanks to the SC-NMR laboratory of Okayama University and the MS Laboratory of the Faculty of Agriculture, Okayama University, for assistance in the 1H-NMR and MS experiments, respectively
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maneerat, S., Nitoda, T., Kanzaki, H. et al. Bile acids are new products of a marine bacterium, Myroides sp. strain SM1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67, 679–683 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1777-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1777-1