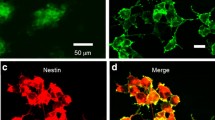
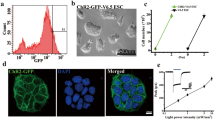
Abstract
Modulation of stem cell proliferation is a crucial aspect of neural developmental biology and regenerative medicine. To investigate the effect of optical stimulation on neural stem cell proliferation, cells transduced with channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) were used to analyze changes in cell proliferation and cell cycle distribution after light stimulation. Blue light significantly inhibited cell proliferation and affected the cell cycle, which increased the percentage of cells in G1 phase and reduced the percentage in S phase. It is likely that the influence of blue light on cell proliferation and the cell cycle was mediated by membrane depolarization, which induced accumulation of p21 and p27 proteins. Our data provide additional specific evidence that membrane depolarization may inhibit neural stem cell proliferation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biagiotti T, D’Amico M, Marzi I, Di Gennaro P, Arcangeli A, Wanke E, Olivotto M (2006) Cell renewing in neuroblastoma: electrophysiological and immunocytochemical characterization of stem cells and derivatives. Stem Cells 24:443–453
Boyden ES, Zhang F, Bamberg E, Nagel G, Deisseroth K (2005) Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity. Nat Neurosci 8:1263–1268
Cai J, Cheng A, Luo Y, Lu C, Mattson MP, Rao MS, Furukawa K (2004) Membrane properties of rat embryonic multipotent neural stem cells. J Neurochem 88:212–226
Chiu S (1991) Functions and distribution of voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels in mammalian Schwann cells. Glia 4:541–558
Cho T, Bae JH, Choi HB, Kim SS, McLarnon JG, Suh-Kim H, Kim SU, Min CK (2002) Human neural stem cells: electrophysiological properties of voltage-gated ion channels. Neuroreport 13:1447–1452
Coqueret O (2003) New roles for p21 and p27 cell-cycle inhibitors: a function for each cell compartment? Trends Cell Biol 13:65–70
Deisseroth K, Singla S, Toda H, Monje M, Palmer TD, Malenka RC (2004) Excitation-neurogenesis coupling in adult neural stem/progenitor cells. Neuron 42:535–552
Fang F, Orend G, Watanabe N, Hunter T, Ruoslahti E (1996) Dependence of cyclin E-CDK2 kinase activity on cell anchorage. Science 271:499–502
Flax JD, Aurora S, Yang C, Simonin C, Wills AM, Billinghurst LL, Jendoubi M, Sidman RL, Wolfe JH, Kim SU (1998) Engraftable human neural stem cells respond to development cues, replace neurons, and express foreign genes. Nat Biotechnol 16:1033–1039
Ghiani CA, Yuan X, Eisen AM, Knutson PL, DePinho RA, McBain CJ, Gallo V (1999) Voltage-activated K+ channels and membrane depolarization regulate accumulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p27(Kip1) and p21(CIP1) in glial progenitor cells. J Neurosci 19:5380–5392
He XB, Yi SH, Rhee YH, Kim H, Han YM, Lee SH, Lee H, Park CH, Lee YS, Richardson E, Kim BW (2011) Prolonged membrane depolarization enhances midbrain dopamine neuron differentiation via epigenetic histone modifications. Stem Cells 29:1861–1873
Heubach JF, Graf EM, Leutheuser J, Bock M, Balana B, Zahanich I, Christ T, Boxberger S, Wettwer E, Ravens U (2004) Electrophysiological properties of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Physiol 554:659–672
Knutson P, Ghiani CA, Zhou JM, Gallo V, McBain CJ (1997) K+ channel expression and cell proliferation are regulated by intracellular sodium and membrane depolarization in oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. J Neurosci 17:2669–2682
Lau YT, Wong CK, Luo J, Leung LH, Tsang PF, Bian ZX, Tsang SY (2011) Effects of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channel blockers on the proliferation and cell cycle progression of embryonic stem cells. Pflugers Arch 461:191–202
Li M, Wang B, Lin W (2008) Cl-channel blockers inhibit cell proliferation and arrest the cell cycle of human ovarian cancer cells. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol 29:267–271
Liu X, Wang Q, Haydar TF, Bordey A (2005) Nonsynaptic GABA signaling in postnatal subventricular zone controls proliferation of GFAP-expressing progenitors. Nat Neurosci 8:1179–1187
Lloyd AC, Obermüller F, Staddon S, Barth CF, McMahon M, Land H (1997) Cooperating oncogenes converge to regulate cyclin/cdk complexes. Genes Dev 11:663–677
MacFarlane SN, Sontheimer H (2000) Changes in ion channel expression accompany cell cycle progression of spinal cord astrocytes. Glia 30:39–48
Miesenbock G (2011) Optogenetic control of cells and circuits. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27:731–758
Momose-Sato Y, Sato K, Kinoshita M (2007) Spontaneous depolarization waves of multiple origins in the embryonic rat CNS. Eur J Neurosci 25:929–944
Nagel G, Szellas T, Huhn W, Kateriya S, Adeishvili N, Berthold P, Ollig D, Hegemann P, Bamberg E (2003) Channelrhodopsin-2, a directly light-gated cation-selective membrane channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13940–13945
Porlan E, Morante-Redolat JM, Marqués-Torrejón MÁ, Andreu-Agulló C, Carneiro C, Gómez-Ibarlucea E, Soto A, Vidal A, Ferrón SR, Fariñas I (2013) Transcriptional repression of Bmp2 by p21Waf1/Cip1 links quiescence to neural stem cell maintenance. Nat Neurosci 16:1567–1575
Rein ML, Deussing JM (2011) The optogenetic (r)evolution. Mol Genet Genom
Roovers K, Assoian RK (2000) Integrating the MAP kinase signal into the G 1 phase cell cycle machinery. Bioessays 22:818–826
Ross ME (1996) Cell division and the nervous system: regulating the cycle from neural differentiation to death. Trends Neurosci 19:62–68
Sewing A, Wiseman B, Lloyd AC, Land H (1997) High-intensity Raf signal causes cell cycle arrest mediated by p21Cip1. Mol Cell Biol 17:5588–5597
Snyder EY, Deitcher DL, Walsh C, Arnold-Aldea S, Hartwieg EA, Cepko CL (1992) Multipotent neural cell lines can engraft and participate in development of mouse cerebellum. Cell 68:33–51
Spitzer NC (2006) Electrical activity in early neuronal development. Nature 444:707–712
Stroh A, Tsai HC, Wang LP, Zhang F, Kressel J, Aravanis A, Santhanam N, Deisseroth K, Konnerth A, Schneider MB (2011) Tracking stem cell differentiation in the setting of automated optogenetic stimulation. Stem Cells 29:78–88
Sundelacruz S, Levin M, Kaplan DL (2009) Role of membrane potential in the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation. Stem Cell Rev 5:231–246
Toettcher JE, Voigt CA, Weiner OD, Lim WA (2011) The promise of optogenetics in cell biology: interrogating molecular circuits in space and time. Nat Methods 8:35–38
Tonnesen J, Parish CL, Sorensen AT, Andersson A, Lundberg C, Deisseroth K, Arenas E, Lindvall O, Kokaia M (2011) Functional integration of grafted neural stem cell-derived dopaminergic neurons monitored by optogenetics in an in vitro Parkinson model. PLoS One 6:e17560
Wang DD, Krueger DD, Bordey A (2003) GABA depolarizes neuronal progenitors of the postnatal subventricular zone via GABAA receptor activation. J Physiol 550:785–800
Weick JP, Johnson MA, Skroch SP, Williams JC, Deisseroth K, Zhang SC (2010) Functional control of transplantable human ESC-derived neurons via optogenetic targeting. Stem Cells 28:2008–2016
Woods D, Parry D, Cherwinski H, Bosch E, Lees E, McMahon M (1997) Raf-induced proliferation or cell cycle arrest is determined by the level of Raf activity with arrest mediated by p21Cip1. Mol Cell Biol 17:5598–5611
Yawo H, Asano T, Sakai S, Ishizuka T (2013) Optogenetic manipulation of neural and non-neural functions. Dev Growth Differ 55:474–490
Zhang F, Wang LP, Boyden ES, Deisseroth K (2006) Channelrhodopsin-2 and optical control of excitable cells. Nat Methods 3:785–792
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 8113001) and (973 Project 2013CB967002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S.J., Weng, C.H., Xu, H.W. et al. Effect of Optogenetic Stimulus on the Proliferation and Cell Cycle Progression of Neural Stem Cells. J Membrane Biol 247, 493–500 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9659-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9659-7