Abstract
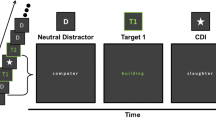
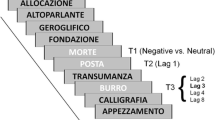
Reporting the second of two targets within a stream of distracting words during rapid serial visual presentation (RSVP) is impaired when the targets are separated by a single distractor word, a deficit in temporal attention that has been referred to as the attentional blink (AB). Recent conceptual and empirical work has pointed to pre-target brain states as potential mediators of the AB effect. The current study examined differences in pre-target electrophysiology between correctly and incorrectly reported trials, considering amplitude and phase measures of alpha oscillations as well as the steady-state visual evoked potential (ssVEP) evoked by the RSVP stream. For incorrectly reported trials, relatively lower alpha-band power and greater ssVEP inter-trial phase locking were observed during extended time periods preceding presentation of the first target. These results suggest that facilitated processing of the pre-target distracter stream indexed by reduced alpha and heightened phase locking characterizes a dynamic brain state that predicts lower accuracy in terms of reporting the second target under strict temporal constraints. Findings align with hypotheses in which the AB effect is attributed to neurocognitive factors such as fluctuations in pre-target attention or to cognitive strategies applied at the trial level.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian ED, Matthews BHC (1934) The Berger rhythm: potential changes from the occipital lobes in man. Brain 57(4):355–385. doi:10.1093/brain/57.4.355
Asplund CL, Fougnie D, Zughni S, Martin JW, Marois R (2014) The attentional blink reveals the probabilistic nature of discrete conscious perception. Psychol Sci 25(3):824–831. doi:10.1177/0956797613513810
Bollimunta A, Mo J, Schroeder CE, Ding M (2011) Neuronal mechanisms and attentional modulation of corticothalamic alpha oscillations. J Neurosci 31(13):4935–4943
Bradley MM, Lang PJ (1999) Affective norms for English words (ANEW): instruction manual and affective ratings. University of Florida, Center for the Study of Emotion and Attention, Gainesville
Brainard DH (1997) The psychophysics toolbox. Spat Vis 10(4):433–436
Busch NA, Dubois J, VanRullen R (2009) The phase of ongoing EEG oscillations predicts visual perception. J Neurosci 29(24):7869–7876. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0113-09.2009
Chun MM, Potter MC (1995) A two-stage model for multiple target detection in rapid serial visual presentation. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 21(1):109–127
Dell’Acqua R, Dux PE, Wyble B, Jolicoeur P (2012) Sparing from the attentional blink is not spared from structural limitations. Psychon Bull Rev 19(2):232–238. doi:10.3758/s13423-011-0209-3
Di Lollo V, Kawahara J, Shahab Ghorashi SM, Enns JT (2005) The attentional blink: resource depletion or temporary loss of control? Psychol Res 69(3):191–200
Ding J, Sperling G, Srinivasan R (2006) Attentional modulation of SSVEP power depends on the network tagged by the flicker frequency. Cereb Cortex 16(7):1016–1029
Ergenoglu T, Demiralp T, Bayraktaroglu Z, Ergen M, Beydagi H, Uresin Y (2004) Alpha rhythm of the EEG modulates visual detection performance in humans. Cogn Brain Res 20(3):376–383. doi:10.1016/j.cogbrainres.2004.03.009
Fisher NI (1995) Statistical analysis of circular data. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Foxe JJ, Snyder AC (2011) The role of alpha-band brain oscillations as a sensory suppression mechanism during selective attention. Front Psychol 2:154. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00154
Glennon M, Keane MA, Elliott MA, Sauseng P (2015) Distributed cortical phase synchronization in the EEG reveals parallel attention and working memory processes involved in the attentional blink. Cereb Cortex. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhv023
Gross J, Schmitz F, Schnitzler I, Kessler K, Shapiro K, Hommel B, Schnitzler A (2004) Long-range neural synchrony predicts temporal limitations of visual attention in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13050–13055
Hommel B, Kessler K, Schmitz F, Gross J, Akyurek E, Shapiro K, Schnitzler A (2006) How the brain blinks: towards a neurocognitive model of the attentional blink. Psychol Res 70(6):425–435
Jensen O, Mazaheri A (2010) Shaping functional architecture by oscillatory alpha activity: gating by inhibition. Front Human Neurosci 4:186. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2010.00186
Jensen O, Gelfand J, Kounios J, Lisman JE (2002) Oscillations in the alpha band (9–12 Hz) increase with memory load during retention in a short-term memory task. Cereb Cortex 12(8):877–882
Keil A, Heim S (2009) Prolonged reduction of electrocortical activity predicts correct performance during rapid serial visual processing. Psychophysiology 46:718–725
Keil A, Gruber T, Muller MM (2001) Functional correlates of macroscopic high-frequency brain activity in the human visual system. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 25(6):527–534
Keil A, Ihssen N, Heim S (2006) Early cortical facilitation for emotionally arousing targets during the attentional blink. BMC Biol 4:23
Klimesch W, Doppelmayr M, Hanslmayr S (2006) Upper alpha ERD and absolute power: their meaning for memory performance. In: Neuper C, Klimesch W (eds) Progress in brain research, vol 159. Elsevier, pp 151–165. Retrieved from http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0079612306590107
Kranczioch C, Debener S, Maye A, Engel AK (2007) Temporal dynamics of access to consciousness in the attentional blink. NeuroImage 37(3):947–955
Lachaux JP, Rodriguez E, Martinerie J, Varela FJ (1999) Measuring phase synchrony in brain signals. Hum Brain Mapp 8(4):194–208
Ling S, Carrasco M (2006) When sustained attention impairs perception. Nat Neurosci 9(10):1243–1245
MacLean MH, Arnell KM (2011) Greater attentional blink magnitude is associated with higher levels of anticipatory attention as measured by alpha event-related desynchronization (ERD). Brain Res 1387:99–107. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.02.069
Marois R, Chun MM, Gore JC (2000) Neural correlates of the attentional blink. Neuron 28:299–308
Marois R, Yi D-J, Chun MM (2004) The neural fate of consciously perceived and missed events in the attentional blink. Neuron 41:465–472
Martens S, Wyble B (2010) The attentional blink: past, present, and future of a blind spot in perceptual awareness. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 34(6):947–957. doi:10.1016/J.Neubiorev.2009.12.005
Marti S, Sigman M, Dehaene S (2012) A shared cortical bottleneck underlying attentional blink and psychological refractory period. NeuroImage 59(3):2883–2898. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.063
Mathewson KE, Gratton G, Fabiani M, Beck DM, Ro T (2009) To see or not to see: prestimulus α phase predicts visual awareness. J Neurosci 29(9):2725–2732. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3963-08.2009
Mathewson KE, Lleras A, Beck DM, Fabiani M, Ro T, Gratton G (2011) Pulsed out of awareness: EEG alpha oscillations represent a pulsed-inhibition of ongoing cortical processing. Front Psychol. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00099
Muller MM, Hillyard S (2000) Concurrent recording of steady-state and transient event-related potentials as indices of visual-spatial selective attention. Clin Neurophysiol 111(9):1544–1552
Müller MM, Malinowski P, Gruber T, Hillyard SA (2003) Sustained division of the attentional spotlight. Nature 424(6946):309–312
Neuper C, Scherer R, Reiner M, Pfurtscheller G (2005) Imagery of motor actions: differential effects of kinesthetic and visual-motor mode of imagery in single-trial EEG. Cogn Brain Res 25(3):668–677
Nieuwenstein MR, Potter MC, Theeuwes J (2009) Unmasking the attentional blink. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 35(1):159–169. doi:10.1037/0096-1523.35.1.159
Olivers CNL, Meeter M (2008) A boost and bounce theory of temporal attention. Psychol Rev 115(4):836–863. doi:10.1037/a0013395
Olivers CNL, Nieuwenhuis S (2005) The beneficial effect of concurrent task-irrelevant mental activity on temporal attention. Psychol Sci 16(4):265–269. doi:10.1111/j.0956-7976.2005.01526.x
Olivers CN, van der Stigchel S, Hulleman J (2007) Spreading the sparing: against a limited-capacity account of the attentional blink. Psychol Res 71:126–139
Pfurtscheller G, Berghold A (1989) Patterns of cortical activation during planning of voluntary movement. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 72(3):250–258
Porcu E, Keitel C, Müller MM (2013) Concurrent visual and tactile steady-state evoked potentials index allocation of inter-modal attention: a frequency-tagging study. Neurosci Lett 556:113–117
Potter MC, Staub A, O’Connor DH (2002) The time course of competition for attention: attention is initially labile. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 28(5):1149–1162
Rajagovindan R, Ding M (2011) From prestimulus alpha oscillation to visual-evoked response: an inverted-U function and its attentional modulation. J Cogn Neurosci 23(6):1379–1394. doi:10.1162/jocn.2010.21478
Ray WJ, Cole HW (1985) EEG alpha activity reflects attentional demands, and beta activity reflects emotional and cognitive processes. Science 228(4700):750–752. doi:10.1126/science.3992243
Raymond JE, Shapiro KL, Arnell KM (1992) Temporary suppression of visual processing in an RSVP task: an attentional blink? J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 18(3):849–860. doi:10.1037/0096-1523.18.3.849
Regan D (1989) Human brain electrophysiology: evoked potentials and evoked magnetic fields in science and medicine. Elsevier, New York
Romei V, Gross J, Thut G (2010) On the role of prestimulus alpha rhythms over occipito-parietal areas in visual input regulation: correlation or causation? J Neurosci 30(25):8692–8697. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0160-10.2010
Shapiro K, Schmitz F, Martens S, Hommel B, Schnitzler A (2006) Resource sharing in the attentional blink. NeuroReport 17(2):163–166
Steriade M, Llinás RR (1988) The functional states of the thalamus and the associated neuronal interplay. Physiol Rev 68(3):649–742
Taatgen NA, Juvina I, Schipper M, Borst JP, Martens S (2009) Too much control can hurt: a threaded cognition model of the attentional blink. Cogn Psychol 59(1):1–29. doi:10.1016/j.cogpsych.2008.12.002
Tallon-Baudry C, Bertrand O (1999) Oscillatory gamma activity in humans and its role in object representation. Trends Cogn Sci 3(4):151–162. doi:10.1016/S1364-6613(99)01299-1
Tallon-Baudry C, Bertrand O, Peronnet F, Pernier J (1998) Induced γ-band activity during the delay of a visual short-term memory task in humans. J Neurosci 18(11):4244–4254
Vul E, Nieuwenstein M, Kanwisher N (2008) Temporal selection is suppressed, delayed, and diffused during the attentional blink. Psychol Sci 19(1):55–61. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02046.x
Weisz N, Wühle A, Monittola G, Demarchi G, Frey J, Popov T, Braun C (2014) Prestimulus oscillatory power and connectivity patterns predispose conscious somatosensory perception. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(4):E417–E425. doi:10.1073/pnas.1317267111
Wieser MJ, Keil A (2011) Temporal trade-off effects in sustained attention: dynamics in visual cortex predict the target detection performance during distraction. J Neurosci 31(21):7784–7790. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5632-10.2011
Wyble B, Potter MC, Bowman H, Nieuwenstein M (2011) Attentional episodes in visual perception. J Exp Psychol Gen 140(3):488
Zauner A, Fellinger R, Gross J, Hanslmayr S, Shapiro K, Gruber W, Klimesch W (2012) Alpha entrainment is responsible for the attentional blink phenomenon. NeuroImage 63(2):674–686. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.06.075
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Nadia Cacodcar for her assistance during data collection. This research was funded by a Grant from the NIH (R01 MH097320).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petro, N.M., Keil, A. Pre-target oscillatory brain activity and the attentional blink. Exp Brain Res 233, 3583–3595 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-015-4418-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-015-4418-2