Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the lining of the synovial joints and approximately affects 0.5 − 1% of the total population imposing a socioeconomic burden. The current study aimed at investigating the novel possible beneficial effects of using zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) on such devastating disease. The complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA) model was used to mimic RA in rats where ZnO NPs were given orally (2 mg/kg/day) daily for 14 days; and diclofenac Na, the standard drug, was given intraperitoneally (1 mg/kg/day) the day after CFA, daily for 14 days. Our results displayed that ZnO NPs attenuated adjuvant-induced increased production of inflammatory mediators interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-10 (IL-10), and total leukocyte count. Besides, they ameliorated autoimmunity through suppression of anti-citrullinated protein auto antibodies (anti-CCP) levels in rats. In conclusion our results highlight the benefits which could be obtained of nanoparticles either alone or in combination with the known anti-arthritic and/or anti-inflammatory agents, giving rise to new protocols to maximize the control of RA.
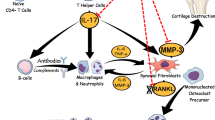
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
A Ali A, S El-Zaitony A, Al-Haleem ENA (2016) Evaluation of therapeutic efficacy of vinpocetine in adjuvant induced arthritis model in rats. J Pain Manag Med 02: https://doi.org/10.35248/2684-1320.16.2.115
Agarwal H, Nakara A, Shanmugam VK (2019) Anti-inflammatory mechanism of various metal and metal oxide nanoparticles synthesized using plant extracts: a review. Biomed Pharmacother 109:2561–2572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.116
Ahmed WMS HO (2015) Effect of atorvastatin and vitamin D on FreundÂ’s adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis in rat. J Bioequiv Availab 07. https://doi.org/10.4172/jbb.1000221
Alivernini S, Tolusso B, Petricca L, et al (2019) Rheumatoid arthritis. In: Mosaic of autoimmunity: the novel factors of autoimmune diseases. Elsevier, pp 501–526
Cascão R, Vidal B, Raquel H et al (2012) Effective treatment of rat adjuvant-induced arthritis by celastrol. Autoimmun Rev 11:856–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2012.02.022
Dai Q, Zhou D, Xu L, Song X (2018) Curcumin alleviates rheumatoid arthritis-induced inflammation and synovial hyperplasia by targeting mTOR pathway in rats. Drug Des Devel Ther 12:4095–4105. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S175763
Goldring SR (2003) Pathogenesis of bone and cartilage destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 42:11–16. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keg327
Guo Q, Wang Y, Xu D, et al (2018) Rheumatoid arthritis: pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41413-018-0016-9
Halloran MM, Szekanecz Z, Barquin N et al (1996) Cellular adhesion molecules in rat adjuvant arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 39:810–819. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780390514
Heidari B (2011) Rheumatoid arthritis: early diagnosis and treatment outcomes. Casp J Intern Med 2:161–170
Isomäki P, Punnonen J (1997) Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Med 29:499–507
Jarosz M, Olbert M, Wyszogrodzka G et al (2017) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of zinc. Zinc-Dependent NF-Κb Signaling Inflammopharmacology 25:11–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0309-4
Jiang J, Pi J, Cai J (2018) The Advancing of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications[1] J. Jiang, J. Pi, and J. Cai, “The Advancing of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications,” vol. 2018, 2018. Bioinorg Chem Appl 2018:18
Kay J, Calabrese L (2004) The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (oxford) 43(Suppl 3):2–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keh201
Kim MH, Jeong HJ (2015) Zinc oxide nanoparticles suppress LPS-Induced NF-κB activation by inducing A20, a negative regulator of NF-κB, in RAW 264.7 Macrophages. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 15:6509–6515. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2015.10319
Kim MH, Seo JH, Kim HM, Jeong HJ (2014) Zinc oxide nanoparticles, a novel candidate for the treatment of allergic inflammatory diseases. Eur J Pharmacol 738:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.05.030
Kinloch AJ, Lundberg KE, Moyes D, Venables PJ (2006) Pathogenic role of antibodies to citrullinated proteins in rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2:365–375. https://doi.org/10.1586/1744666X.2.3.365
Lawrence T (2009) The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a001651
McInnes IB, Schett G (2007) Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol 7:429–442. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2094
Mingomataj E, Bakiri AH (2016) Regulator versus effector paradigm: interleukin-10 as indicator of the switching response. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 50:97–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-015-8514-7
Moreland L (2005) Unmet needs in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 7:2–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar1736
Muravyev Y V. (2018) Extra-articular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Nauchno-Prakticheskaya Revmatol 56:356–362. https://doi.org/10.14412/1995-4484-2018-356-362
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (2018) Rheumatoid arthritis in adults: management NICE guideline
Niewold TB, Harrison MJ, Paget SA (2007) Anti-CCP antibody testing as a diagnostic and prognostic tool in rheumatoid arthritis. QJM 100:193–201. https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/hcm015
Pan T, Cheng T, fang, Jia Y ran, et al (2017) Anti-rheumatoid arthritis effects of traditional Chinese herb couple in adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 205:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2017.04.020
Prasad AS (2014) Zinc is an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent: its role in human health. Front Nutr 1:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2014.00014
Roy R, Parashar V, Chauhan LKS et al (2014) Mechanism of uptake of ZnO nanoparticles and inflammatory responses in macrophages require PI3K mediated MAPKs signaling. Toxicol Vitr 28:457–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2013.12.004
Salem HF, Nafady MM, Kharshoum RM et al (2020) Mitigation of rheumatic arthritis in a rat model via transdermal delivery of dapoxetine HCL amalgamated as a nanoplatform: In vitro and in vivo assessment. Int J Nanomedicine 15:1517–1535. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S238709
Silman AJ, Pearson JE (2002) Epidemiology and genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res 4:S265–S272. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar578
Silverman GJ, Carson DA (2003) Roles of B cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 5:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar1010
Song YW, Kang EH (2010) The pathogenic role of rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Clin Rheumtol 5:651–658. https://doi.org/10.2217/ijr.10.62
Szekanecz Z, Halloran MM, Volin MV et al (2000) Temporal expression of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:1266–1277. https://doi.org/10.1002/1529-0131(200006)43:6%3c1266::AID-ANR9%3e3.0.CO;2-P
Viana MT, Perez MC, Ribas VR et al (2012) Leukocyte, red blood cell and morphological adaptation to moderate physical training in rats undernourished in the neonatal period. Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter 34:285–291. https://doi.org/10.5581/1516-8484.20120073
Funding
No funding sources are available.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AMF and SS conceived and designed research. AMF and MA conducted the experiment. DA, SS and MA analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experimental procedures adopted for in vivo studies were in accordance with the local ethics committee guidelines at Modern Sciences and Arts University (PH1/EC1/2020PD) that comply with the international laws for the care and use of laboratory animals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict.
Additional information
Publisherʼs note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Figure s1
(DOCX 280 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gad, S.S., Fayez, A.M., Abdelaziz, M. et al. Amelioration of autoimmunity and inflammation by zinc oxide nanoparticles in experimental rheumatoid arthritis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 394, 1975–1981 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02105-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02105-2