Abstract
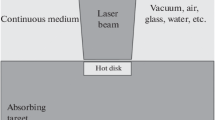
A mathematical model of ablation of tissue by an incident laser beam is formulated in terms of a series of layers in which laser power is absorbed and water and tissue vaporized. Thermal energy is also deposited and removed by conduction. Time dependent mathematical equations are set up for these processes; they are solved numerically. The model assumes that absorption is dominant over scattering, so that it is possible to calculate the thickness of the vacuolated zone. The evolution of the ablating surface is found.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Welch AJ, Valvano JW, Pearce JA et al. Effects of laser radiation on tissue during laser angioplasty.Lasers Surg Med 1985,5:251–64
Cross FW, Wright JK, Bowker TJ, Bown SG. The role of pulse length in limiting distant damage to vascular tissue caused by the Nd-YAG laser.Lasers Med Sci 1987,2:175–81
McKenzie AL. How far does thermal damage extend beneath the surface of CO2 laser incisions?Phys Med Biol 1983,28:905–12
Bowker TJ, Cross FW, Rumsby PT et al. Excimer laser angioplasty: qualitative comparison in vitro of three ultra-violet wavelengths on tissue ablation and haemolysis.Lasers Med Sci 1986,1:91–9
Dabby FW, Paek V. High intensity laser induced vaporization and explosion of solid material.IEEE J Quant Elec 1972,8:106–11
McKenzie AL. A three-zone model of soft-tissue damage by a CO2 laser.Phys Med Biol 1986,31:967–83
Dowden JM, Davis M, Kapadia P, Matthewson K. Heat flow in laser treatment by local laser hyperthermia.Lasers Med Sci 1987,2:211–21
Whiting P, Dowden JM, Kapadia P. A mathematical analysis of the results of experiments in rats' livers by local laser hyperthermia.Lasers Med Sci 1989,4:55–64
Davis MP,Fluid dynamical models of laser welding. PhD thesis, University of Essex, UK, 1983
Davis MP, Kapadia P, Dowden JM. Solution of a Stefan problem in the theory of laser welding by the Method of Lines.J Comp Phys 1985,60:543–8
Davis MP, Kapadia P, Whiting P, Dowden JM. Solution of a problem in the theory of laser medicine by the Method of Lines.J Comp Phys 1989,81:406–20
Rastegar S, Motamedi M, Welch AJ, Hayes LJ. A theoretical study of the effect of optical properties in laser ablation of tissue.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 1989,36:1180–7
Dowden JM, Jordan T, Kapadia P. Temperature distribution produced by a cylindrical etched fibre tip in laser treatment of tumours by local hyperthermia.Lasers Med Sci 1988,3:47–54
Selten F One-dimensional laser ablation of biological tissue and gels. MSc Thesis. Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Faculteit der Technische Natuurkunde en Lasercentrum, Academisch Medisch Centrum, Amsterdam, 1989
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whiting, P., Dowden, J.M., Kapadia, P.D. et al. A one-dimensional mathematical model of laser induced thermal ablation of biological tissue. Laser Med Sci 7, 357–368 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02594073
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02594073