Abstract
Background
Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) is the most common skeletal dysplasia. Two principal methods used in early diagnosis of DDH are clinical examination and ultrasonographic investigation. Dogruel et al. found a low specifcity of clinical examination in patients with DDH. Additionally, Kamath et al. stated that ultrasonography performed by a radiologist in routine clinical practice is more reliable than physical examination performed by the average clinician. In clinical practice, the application and assessment of hip ultrasonography are completed by a single person. This assessment determines the followup of the patient. Thus, hip ultrasonography performed on the same person by different individuals under the same conditions will yield a more accurate assessment of the reliability of ultrasonographic assessment of DDH. Although inter-observer reliability was high in many previous studies of ultrasound image evaluation, reliability rates vary among studies of the application of ultrasonography.
Materials and Methods
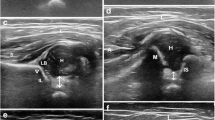
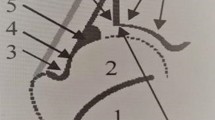
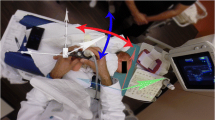
Inter-examiner reliability of hip ultrasonography was analyzed among four investigators who separately evaluated 100 hips (50 infants). The obtained bone structure angles (α), cartilage structure angles (β), and distribution of hip types were compared among the investigators. All infants were brought to the hospital for a healthy child followup examination, according to the country’s health policy. Babies between 0 and 6 months were included in the study. Babies with any neuromuscular disorders, neural tube defects or any type of genetic anomalies were excluded from the study. The study was explained to the families of all infants and written informed consent was obtained.
Results
There was a signifcant difference in the hip type determined by the investigators with respect to a and p angles (P < 0.01, P < 0.01, P = 0.002). The average alpha measurements of the frst orthopedist, second orthopedist, frst radiologist, and second radiologist were 67.38 ± 6.24, 65.60 ± 5.84, 65.44 ± 4.59, and 62.59 ± 4.50, respectively. The average beta measurements of the frst orthopedist, second orthopedist, frst radiologist, and second radiologist were 53.85 ± 8.86, 50.74 ± 7.80, 44.77 ± 6.30, and 44.39 ± 5.81, respectively. Agreement among the results obtained by the clinicians was investigated in dual comparisons. The relative agreement according to the alpha angle ranged from 3.6% to 44.5%, and the relative concordance according to the beta angle ranged from 0.9% to 45.3%. Agreement regarding hip typing was determined to range from 19.1% to 42.6%.
Conclusion
Sonographic evaluation of the hip appears to vary depending on the investigator.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loder RT, Skopelja EN. The epidemiology and demographics of hip dysplasia. ISRN Orthop 2011;2011:238607.
Dogruel H, Atalar H, Yavuz OY, Sayli U. Clinical examination versus ultrasonography in detecting developmental dysplasia of the hip. Int Orthop 2008;32:415–9.
Kamath S, Mehdi A, Wilson N, Duncan R. The lack of evidence of the effect of selective ultrasound screening on the incidence of late developmental dysplasia of the hip in the Greater Glasgow Region. J Pediatr Orthop B 2007;16:189–91.
Graf R. The diagnosis of congenital hip-joint dislocation by the ultrasonic Combound treatment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 1980;97:117–33.
Graf R. Classification of hip joint dysplasia by means of sonography. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 1984;102:248–55.
Bialik GM, Eidelman M, Katzman A, Peled E. Treatment duration of developmental dysplasia of the hip: Age and sonography. J Pediatr Orthop B 2009;18:308–13.
Demirhan M, Dikici F, Eralp L, Onen M, Göksan B. A treatment algorithm for developmental dysplasia of the hip for infants 0 to 18 months of age and its prospective results. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2002;36:42–51.
Eidelman M, Katzman A, Freiman S, Peled E, Bialik V. Treatment of true developmental dysplasia of the hip using Pavlik’s method. J Pediatr Orthop B 2003;12:253–8.
Guille JT, Pizzutillo PD, MacEwen GD. Development dysplasia of the hip from birth to six months. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2000;8:232–42.
Roposch A, Graf R, Wright JG. Determining the reliability of the Graf classification for hip dysplasia. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2006;447:119–24.
Simon EA, Saur F, Buerge M, Glaab R, Roos M, Kohler G. Inter-observer agreement of ultrasonographic measurement of alpha and beta angles and the final type classification based on the Graf method. Swiss Med Wkly 2004;134:671–7.
Omeroglu H, Biçimoglu A, Koparal S, Seber S. Assessment of variations in the measurement of hip ultrasonography by the Graf method in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop B 2001;10:89–95.
Dias JJ, Thomas IH, Lamont AC, Mody BS, Thompson JR. The reliability of ultrasonographic assessment of neonatal hips. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1993;75:479–82.
Bar-On E, Meyer S, Harari G, Porat S. Ultrasonography of the hip in developmental hip dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1998;80:321–4.
Rosendahl K, Aslaksen A, Lie RT, Markestad T. Reliability of ultrasound in the early diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Pediatr Radiol 1995;25:219–24.
Roovers EA, Boere-Boonekamp MM, Geertsma TS, Zielhuis GA, Kerkhoff AH. Ultrasonographic screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip in infants. Reproducibility of assessments made by radiographers. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2003;85:726–30.
Peterlein CD, Schüttler KF, Lakemeier S, Timmesfeld N, Görg C, Fuchs-Winkelmann S, et al. Reproducibility of different screening classifications in ultrasonography of the newborn hip. BMC Pediatr 2010;10:98.
Graf R. The use of ultrasonography in developmental dysplasia of the hip. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2007;41 Suppl 1:6–13.
Keller MS, Nijs EL. The role of radiographs and US in developmental dysplasia of the hip: How good are they? Pediatr Radiol 2009;39 Suppl 2:S211–5.
Harcke HT, Kumar SJ. The role of ultrasound in the diagnosis and management of congenital dislocation and dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1991;73:622–8.
Copuroglu C, Ozcan M, Aykac B, Tuncer B, Saridogan K. Reliability of ultrasonographic measurements in suspected patients of developmental dysplasia of the hip and correlation with the acetabular index. Indian J Orthop 2011;45:553–7.
Hell AK, Becker JC, Rühmann O, Lewinski Gv, Lazovic D. Inter-and intraobserver reliability in Graf’s sonographic hip examination. Z Orthop Unfall 2008;146:624–9.
Wientroub S, Grill F. Ultrasonography in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2000;82-A: 1004-18.
Portinaro NM, Pelillo F, Cerutti P. The role of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop 2007;27:247–50.
Clinical practice guideline: Early detection of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Committee on Quality Improvement, Subcommittee on Developmental Dysplasia of the hip. American Academy of Pediatrics. Pediatrics 2000;105:896–905.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müft Orak, M., Onay, T., Çağırmaz, T. et al. The reliability of ultrasonography in developmental dysplasia of the hip. IJOO 49, 610–614 (2015). https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.168753
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.168753