Abstract
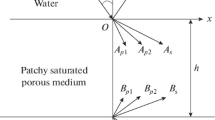
This paper reports a study on plane waves in a fluid incident on an infinitely long fluid-saturated porous cylinder. With consideration of both the fluid dynamic viscosity and the inelastic loss of the frame of the porous media, as well as the application-wide frequency of the Biot-Stoll model, the theoretical calculation of acoustic scattering of an acoustic wave at oblique incidence is carried out. The acoustic backscattering spectrum is calculated and used to investigate the influence of the incident angle and the boundary conditions on the scattering characteristics. The results show that the position of the peak on the horizontal coordinate moves to higher frequency as the incident angle is increased. In the soft porous cylinder, whose shear wave velocity is lower than the velocity of the fluid, the change in the backscattering spectrum under the open-pore boundary condition is more obvious than that in the sealed-pore boundary condition. The influence of the incident angle is more obvious in a hard porous cylinder whose shear wave velocity is larger than the velocity of the fluid than it is in a soft porous cylinder.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Beattie, R. C. Chivers and L. W. Anson, J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 94, 3421 (1993).
S. M. Hasheminejad and H. Hossseini, Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 22, 441 (2002).
S. M. Hasheminejad and M. Maleki, Ultrasonics 45, 165 (2006).
S. M. Hasheminejad and M. Rajabi, Ultrasonics 47, 32 (2007).
P. Lu and Y. Wang, Acta Phys. Sin. 50, 697 (2001).
G. Ding, C. Xu and P. Wang, J. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 30, 31 (2010).
A. Taher and F. Honarvar, Ultrasonics 64, 69 (2016).
Y. Zhou, Y. Wang, L. Ma and T. Gao, Acta Phys. Sin. 49, 480 (2000).
R. D. Stoll, J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 70, 149 (1981).
Z. Cui, K. Wang, H. Hu and J. Sun, Chin. Phys. 16, 746 (2007).
M. A. Biot and D. G. Willis, J. Appl. Mech. 24, 594 (1957).
H. Hu and K. Wang, Chin. J. Geophys. 44, 135 (2001).
Z. Cui and K. Wang, Int. J. Eng. Sci. 41, 2179 (2003).
M. Kimura, Acoust. Sci. Technol. 28, 230 (2007).
K. Wu, Q. Xue and L. Adler, J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 87, 2349 (1990).
C. Wang, Z. Cui, J. Liu and K. Wang, Tech. Acoust. 27, 260 (2008).
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province of China (Grant No. 20180101282JC) and by Science and Technology Research Planning Project of the Education Department of Jilin Province, China (Grant No. JJKH20190182KJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Liu, J. & Cui, Z. Acoustic Waves Scattering from a Fluid-Saturated Porous Cylinder. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 77, 565–571 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.77.565
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.77.565