Abstract
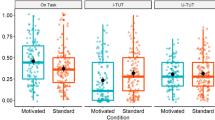
In three experiments, we examined the effects of goal-setting on sustained attention and attention lapses. We measured both behavioral task performance and subjective attentional states during a four -choice reaction time task (Experiments 1 and 2 administered online; Experiment 3 conducted in-person). Experiment 1 compared a vague goal versus a specific goal. The specific goal reduced lapses in the form of long response times (RTs) but did not impact task-unrelated thoughts. Experiment 2 expanded on E1 by making the specific goal progressively harder. Behavioral lapses (i.e., long RTs) were reduced in the harder-over-time goal condition compared to the control condition. Additionally, while RTs increased with time-on-task in the control condition, RTs in the harder-over-time goal condition remained stable with time-on-task. Experiment 3 aimed to replicate the results of E2 in-person and adjusted the difficulty of the harder-over-time goals to be slightly harder. The results largely replicated E2. Overall, setting specific and difficult task goals led to a reduction in lapses of attention and increased sustained attention performance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balota, D. A., & Yap, M. J. (2011). Moving beyond the mean in studies of mental chronometry: The power of response time distributional analyses. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 20(3), 160–166. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963721411408885
Beatty, J. (1982). Task-evoked pupillary responses, processing load, and the structure of processing resources. Psychological Bulletin, 91, 276–292. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.91.2.276
Beatty, J., & Lucero-Wagoner, B. (2000). The pupillary system. In J. T. Cacioppo, L. G. Tassinary, & G. G. Berntson (Eds.), Handbook of psychophysiology (pp. 142–162). New York: Cambridge University Press.
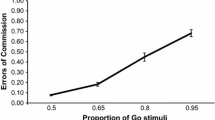
Bedi, A., Russell, P. N., & Helton, W. S. (2023). Go-stimuli probability influences response bias in the sustained attention to response task: A signal detection theory perspective. Psychological Research, 87(2), 509–518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-022-01679-7
Bertelson, P., & Joffe, R. (1963). Blockings in prolonged serial responding. Ergonomics, 6(2), 109–116. https://doi.org/10.1080/00140136308930682
Bills, A. G. (1931). Blocking: a new principle of mental fatigue. The American Journal of Psychology, 43, 230–245. https://doi.org/10.2307/1414771
Bills, A. G. (1935). Fatigue, oscillation and blocks. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 18, 562–573. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0054248
Botvinick, M., & Braver, T. (2015). Motivation and cognitive control: from behavior to neural mechanism. Annual review of psychology, 66, 83–113. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-010814-015044
Broadbent, D. (1958). Perception and communication. Pergamon Press.
Casner, S. M., & Schooler, J. W. (2014). Thoughts in flight: Automation use and pilots’ task-related and task-unrelated thought. Human Factors, 56, 433–442. https://doi.org/10.1177/0018720813501550
Chiew, K. S., & Braver, T. S. (2013). Temporal dynamics of motivation-cognitive control interactions revealed by high-resolution pupillometry. Frontiers in Psychology, 4, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00015
Dinges, D. F., & Powell, J. W. (1985). Microcomputer analyses of performance on a portable, simple visual RT task during sustained operations. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers, 17, 652–655. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03200977
Esterman, M., Noonan, S. K., Rosenberg, M., & Degutis, J. (2013). In the zone or zoning out? Tracking behavioral and neural fluctuations during sustained attention. Cerebral Cortex, 23(11), 2712–2723. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhs261
Esterman, M., Reagan, A., Liu, G., Turner, C., & DeGutis, J. (2014). Reward reveals dissociable aspects of sustained attention. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 143, 2287–2295. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0000019
Giambra, L. M. (1995). A laboratory based method for investigating influences on switching attention to task unrelated imagery and thought. Consciousness and Cognition, 4, 1–21.
Hockey, G. R. J. (1997). Compensatory control in the regulation of human performance under stress and high work-load: A cognitive-energetical framework. Biological Psychology, 45, 73–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/S03010511(96)05223-4
Hull, J. G. (1981). A self-awareness model of the causes and effects of alcohol consumption. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 6, 586–600. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.90.6.586
Jennings, J. R., & van der Molen, M. W. (2005). Preparation for speeded action as a psychophysiological concept. Psychological Bulletin, 131, 434–459. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.131.3.434
Johns, M., Crowley, K., Chapman, R., Tucker, A., & Hocking, C. (2009). The effect of blinks and saccadic eye movements on visual reaction times. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 71, 783–788. https://doi.org/10.3758/APP.71.4.783
Kahneman, D. (1973). Attention and Effort. Prentice-Hall.
Kucyi, A., Esterman, M., Riley, C. S., & Valera, E. M. (2016). Spontaneous default network activity reflects behavioral variability independent of mind-wandering. PNAS Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113(48), 13899–13904. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1611743113
Langner, R., & Eickhoff, S. B. (2013). Sustaining attention to simple tasks: A meta-analytic review of the neural mechanisms of vigilant attention. Psychological Bulletin, 139, 870–900. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0030694
Lindquist, S., & McLean, J. P. (2011). Daydreaming and its correlates in an educational environment. Learning and Individual Differences, 21, 158–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2010.12.006
Locke, E. A., & Latham, G. P. (1990). A theory of goal setting & task performance. Prentice-Hall Inc.
Locke, E. A., & Latham, G. P. (2002). Building a practically useful theory of goal setting and task motivation: A 35-year odyssey. American Psychologist, 57(9), 705–717. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.57.9.705
Mackworth, N. H. (1950). Researches on the measurement of human performance (Medical Research Council Special Report Series No. 268). Her Majesty’s Stationery Office.
Massar, S. A. A., Lim, J., Sasmita, K., & Chee, M. W. L. (2016). Rewards boost sustained attention through higher effort: A value-based decision making approach. Biological Psychology, 120, 21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2016.07.019
McVay, J. C., & Kane, M. J. (2010). Does mind wandering reflect executive function or executive failure? Comment on Smallwood and Schooler (2006) and Watkins (2008). Psychological Bulletin, 136, 188–197. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0018298
Mooneyham, B. W., & Schooler, J. W. (2013). The costs and benefits of mind-wandering: A review. Canadian Journal of Experimental Psychology / Revue canadienne de psychologie expérimentale, 67(1), 11–18. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0031569
Parasuraman, R. (1986). Handbook of perception and human performance Vigilance, monitoring, and search (2nd ed.). Wiley.
Parasuraman, R., & Davies, D. R. (1977). A taxonomic analysis of vigilance performance. In R. Mackie (Ed.), vigilance (pp. 559–574). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-2529-1_26
Peirce, J. W., & MacAskill, M. R. (2018). Building Experiments in PsychoPy. Sage.
Robertson, I. H., & O’Connell, R. G. (2010). Vigilant attention. In A. C. Nobre & J. T. Coull (Eds.), Attention and time (pp. 79–88). Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199563456.003.0006
Robertson, I. H., Manly, T., Andrade, J., Baddeley, B. T., & Yiend, J. (1997). ‘Oops!’: Performance correlates of everyday attentional failures in traumatic brain injured and normal subjects. Neurospsychologia, 35, 747–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0028-3932(97)00015-8
Robison, M. K., & Unsworth, N. (2018). Cognitive and contextual correlates of spontaneous and deliberate mind-wandering. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 44, 85–98. https://doi.org/10.1037/xlm0000444
Robison, M. K., Miller, A. L., & Unsworth, N. (2019). Examining the effects of probe frequency, response options, and framing within the thought-probe method. Behavior Research Methods, 51, 398–408. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-019-01212-6
Robison, M. K., Unsworth, N., & Brewer, G. A. (2021). Examining the effects of goal-setting, feedback, and incentives on sustained attention. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 47(6), 869–891. https://doi.org/10.1037/xhp0000926
Sadaghiani, S., & D’Esposito, M. (2015). Functional characterization of the cingulo-opercular network in the maintenance of tonic alertness. Cerebral Cortex, 25, 2763–2773. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhu072
Schumann, F., Steinborn, M. B., Kürten, J., Cao, L., Händel, B. F., Huestegge, L. (2022). Restoration of attention by rest in a multitasking world: Theory, methodology, and empirical evidence. Frontiers in Psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.867978
See, J. E., Howe, S. R., Warm, J. S., & Dember, W. N. (1995). Meta-analysis of the sensitivity decrement in vigilance. Psychological Bulletin, 117, 230–249. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.117.2.230
Seli, P., Cheyne, J. A., Xu, M., Purdon, C., & Smilek, D. (2015). Motivation, intentionality, and mind wandering: Implications for assessments of task-unrelated thought. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 41(5), 1417–1425. https://doi.org/10.1037/xlm0000116
Smallwood, J., & Schooler, J. W. (2006). The restless mind. Psychological Bulletin, 132(6), 946–958. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.132.6.946
Smallwood, J., & Schooler, J. W. (2015). The science of mind wandering: Empirically navigating the stream of consciousness. Annual Review of Psychology, 66, 487–518. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-010814-015331
Stawarczyk, D., Majerus, S., Maj, M., Van der Linden, M., & D’Argembeau, A. (2011). Mind-wandering: Phenomenology and function as assessed with a novel experience sampling method. Acta Psychologica, 136, 370–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2011.01.002
Steinborn, M. B., & Langner, R. (2012). Arousal modulates temporal preparation under increased time uncertainty: Evidence from higher-order sequential foreperiod effects. Acta Psychologica, 139(1), 65–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2011.10.010
Steinborn, M. B., Langner, R., Flehmig, H. C., & Huestegge, L. (2016). Everyday life cognitive instability predicts simple reaction time variability: Analysis of reaction time distributions and delta plots. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 30, 92–102. https://doi.org/10.1002/acp.3172
Steinborn, M. B., Langner, R., & Huestegge, L. (2017). Mobilizing cognition for speeded action: Try-harder instructions promote motivated readiness in the constant-foreperiod paradigm. Psychological Research, 81, 1135–1151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-016-0810-1
Stuss, D. T., Shallice, T., Alexander, M. P., & Picton, T. W. (1995). A multidisciplinary approach to anterior attentional functions. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 769, 191–211. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb38140.x
Tse, C. S., Balota, D. A., Yap, M. J., Duchek, J. M., & McCabe, D. P. (2010). Effects of healthy aging and early stage dementia of the Alzheimer’s type on components of response time distributions in three attentional tasks. Neuropsychology, 24, 300–315. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0018274
Unsworth, N., & McMillan, B. D. (2014). Similarities and differences between mind-wandering and external distraction: A latent variable analysis of lapses of attention and their relation to cognitive abilities. Acta Psychologica, 150, 14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2014.04.001
Unsworth, N., & McMillan, B. D. (2017). Attentional disengagements in educational contexts: A diary investigation of everyday mind-wandering and distraction. Cognitive Research: Principles and Implications, 2, 32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41235-017-0070-7
Unsworth, N., & Miller, A. L. (2021). Individual differences in the intensity and consistency of attention. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 30, 391–400. https://doi.org/10.1177/09637214211030266
Unsworth, N., & Robison, M. K. (2016). Pupillary correlates of lapses of sustained attention. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 16, 601–615. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-016-0417-4
Unsworth, N., & Robison, M. K. (2018). Tracking arousal state and mind wandering with pupillometry. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 18, 638–664. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-018-0594-4
Unsworth, N., & Robison, M. K. (2020). Working memory capacity and sustained attention: A cognitive-energetic perspective. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 46, 77–103. https://doi.org/10.1037/xlm0000712
Unsworth, N., Redick, T. S., Lakey, C. E., & Young, D. L. (2010). Lapses in sustained attention and their relation to executive and fluid abilities: An individual differences investigation. Intelligence, 38, 111–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2009.08.002
Unsworth, N., Robison, M. K., & Miller, A. L. (2021). Individual differences in lapses of attention: A latent variable analysis. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 150, 1303–1331. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0000998
Unsworth, N., Miller, A. L., & Aghel, S. (2022). Effort mobilization and lapses of sustained attention. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 22, 42–56. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-021-00941-6
van Breukelen, G. J., Roskam, E. E., Eling, P. A., Jansen, R. W., Souren, D. A., & Ickenroth, J. G. (1995). A model and diagnostic measures for response time series on tests of concentration: Historical background, conceptual framework, and some applications. Brain and Cognition, 27, 147–179. https://doi.org/10.1006/brcg.1995.1015
Weissman, D. H., Roberts, K. C., Visscher, K. M., & Woldorff, M. G. (2006). The neural bases of momentary lapses of attention. Nature Neuroscience, 9, 971–978. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1727
Westbrook, A., & Braver, T. S. (2015). Cognitive effort: A neuroeconomic approach. Cognitive, Affective & Behavioral neuroscience, 15(2), 395–415. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-015-0334-y
Williams, H. L., Lubin, A., & Goodnow, J. L. (1959). Impaired performance with acute sleep loss. Psychological Monographs, 73, 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0093749
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Open Practices Statement
This study was not preregistered and the data will be made available on the Open Science Framework.
Author Notes
This research was supported by Office of Naval Research grant N00014-22-1-2083.
Public Significance Statement
Our ability to sustain attention is critical in a number of everyday tasks. In the current study we demonstrate that setting specific and difficult goals leads to a reduction in behavioral lapses of sustained attention and a reduction of time-on-task effects. Theoretically, specific and difficult goals result in participants allocating more attentional effort to the task that helps sustain attention and mitigate lapses. These results further our understanding of lapses of attention and potential ways to curb lapses.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Strayer, D.L., Robison, M.K. & Unsworth, N. Effects of goal-setting on sustained attention and attention lapses. Atten Percept Psychophys (2023). https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-023-02803-4
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-023-02803-4