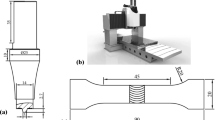
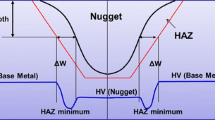
Abstract
Friction stir welding is one of the promising techniques to join dissimilar aluminum alloys. In this study, the friction stir welding technique is implemented to enable a sound butt-joint between aluminum alloy AA5052 and AA6061. The study investigates the influence of conventional heat treatment and newly-devised cyclic treatment on the properties of the friction stir weldment. The results indicate that the newly-devised cyclic heat treatment increases the microhardness by ~22%, tensile strength by ~22%, and ductility by 20% than the conventionally heat-treated specimens. The mechanism of property enhancement in the weldment is comprehensively correlated with the microstructural evolution.












Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ramalingam, V.V., Ramasamy, P., Kovukkal, M.D., and Myilsamy, G., Research and development in magnesium alloys for industrial and biomedical applications: A review, Met. Mater. Int., 2019, pp. 1–22. Ramalingam, V.V., Ramasamy, P., Kovukkal, M.D., and Myilsamy, G., Research and development in magnesium alloys for industrial and biomedical applications: a review, Met. Mater. Int., 2020, vol. 26, pp. 409–430.
Paidar, M., Vignesh, R.V., Khorram, A., Oladimeji Ojo, O.O., Rasoulpouraghdam, A., and Pustokhina, I., Dissimilar modified friction stir clinching of AA2024-AA6061 aluminum alloys: Effects of materials positioning, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2020, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 6037–6047.
Raghav, A.K., Vignesh, R.V., Kalyan, K.P., and M. Govindaraju, Friction welding of cast iron and phosphor bronze, J. Inst. Eng. (India): Ser. C, 2020, vol. 101, pp. 347–354.
Padmanaban, R., Balusamy, V., and Vaira Vignesh, R., Effect of friction stir welding process parameters on the tensile strength of dissimilar aluminum alloy AA2024-T3 and AA7075-T6 joints, Materialwiss. Werkstofftech., 2020, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 17–27.
Karlsson, L., Berqvist, E.-L., and Larsson, H., Application of friction stir welding to dissimilar welding, Weld. World, 2002, vol. 46, nos. 1–2, pp. 10–14.
Amancio-Filho, S., Sheikhi, S., Dos Santos, J., and Bolfarini, C., Preliminary study on the microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar friction stir welds in aircraft aluminium alloys 2024-T351 and 6056-T4, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, vol. 206, nos. 1–3, pp. 132–142.
Khodir, S.A. and Shibayanagi, T., Friction stir welding of dissimilar AA2024 and AA7075 aluminum alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng., B, 2008, vol. 148, nos. 1–3, pp. 82–87.
Bahemmat, P., Haghpanahi, M., Besharati, M., Ahsanizadeh, S., and Rezaei, H., Study on mechanical, micro-, and macrostructural characteristics of dissimilar friction stir welding of AA6061-T6 and AA7075-T6, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part B, 2010, vol. 224, no. 12, pp. 1854–1864.
Dinaharan, I., Kalaiselvan, K., Vijay, S., and Raja, P., Effect of material location and tool rotational speed on microstructure and tensile strength of dissimilar friction stir welded aluminum alloys, Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng., 2012, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 446–454.
Devaiah, D., Kishore, K., and Laxminarayana, P., Effect of material location and tool rotational speed on the mechanical properties of dissimilar friction stir welded aluminum alloys (5083-H321 to 6061-T6), Bonfring Int. J. Ind. Eng. Manage. Sci., 2016, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 186–190.
Selamat, N.F.M., Baghdadi, A., Sajuri, Z., and Kokabi, A., Friction stir welding of similar and dissimilar aluminium alloys for automotive applications, Int. J. Automot. Mech. Eng., 2016, vol. 13, p. 3401.
Park, S.-K., Hong, S.-T., Park, J.-H., Park, K.-Y., Kwon, Y.-J., and Son, H.-J., Effect of material locations on properties of friction stir welding joints of dissimilar aluminium alloys, Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining, 2010, vol. 15, no. 4, pp. 331–336.
Kumbhar, N. and Bhanumurthy, K., Friction stir welding of Al 5052 with Al 6061 alloys, J. Metall., 2012, vol. 2012, article no. 303756.
RajKumar, V., VenkateshKannan, M., Sadeesh, P., Arivazhagan, N. and Ramkumar, K.D., Studies on effect of tool design and welding parameters on the friction stir welding of dissimilar aluminium alloys AA 5052–AA 6061, Procedia Eng., 2014, vol. 75, pp. 93–97.
Elangovan, K. and Balasubramanian, V., Influences of post-weld heat treatment on tensile properties of friction stir-welded AA6061 aluminum alloy joints, Mater. Charact., 2008, vol. 59, no. 9, pp. 1168–1177.
Priya, R., Effect of post weld heat treatment on the microstructure and tensile properties of dissimilar friction stir welded AA 2219 and AA 6061 alloys, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2009, vol. 62, no. 1, pp. 11–19.
Sivaraj, P., Kanagarajan, D., and Balasubramanian, V., Effect of post weld heat treatment on tensile properties and microstructure characteristics of friction stir welded armour grade AA7075-T651 aluminium alloy, Def. Technol., 2014, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 1–8.
Bayazid, S.M., Farhangi, H., Asgharzadeh, H., Radan, L., Ghahramani, A., and Mirhaji, A., Effect of cyclic solution treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded 7075 Al alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2016, vol. 649, pp. 293–300.
Fathy, N., Ramadan, M., Hafez, K., Alghamdi, A., and Halim, K.A., Microstructure and induced defects of 6061 Al alloy after short times cyclic semi-solid heat treatment, MATEC Web Conf., 2016, vol. 67, p. 05012.
Khludkova, A. and Savitskii, K., Effect of quenching temperature on pore formation during the cyclic heat treatment of aluminum, Sov. Phys. J., 1965, vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 19–22.
Mahmood, N.Y., Zainulabdeen, A.A., Mohmmed, J.H., and Abd Oun, H., Effect of cyclic heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of AA 6061-T6 aluminum alloy, Al-Nahrain J. Eng. Sci., 2020, vol. 23, no. 4, pp. 383–387.
Mishra, S., Mishra, A., Show, B.K., and Maity, J., Simultaneous enhancement of ductility and strength in AISI 1080 steel through a typical cyclic heat treatment, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2017, vol. 688, pp. 262–271.
Omori, T., et al., Abnormal grain growth induced by cyclic heat treatment, Science, 2013, vol. 341, no. 6153, pp. 1500–1502.
Sui, S.-H., Song, T.-G., and Zhao, H.-Y., Cyclic heating treatment for microstructures evolution of LC9 aluminum alloy (J), Foundry, 2007, vol. 56, no. 2, pp. 10–13.
Vignesh, R.V., Padmanaban, R., Govindaraju, M., and Priyadharshini, G.S., Mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of AZ91D-HAP surface composites fabricated by friction stir processing, Mater. Res. Express, 2019, vol. 6, no. 8, p. 085401.
Funding
The authors confirm that the authors did not receive research grants or honorarium to carry out any part of the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Availability of Data and Material
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
The Author transfers to Springer (respective to owner if other than Springer and for U.S. government employees: to the extent transferable) the non-exclusive publication rights and he warrants that his/her contribution is original and that he/she has full power to make this grant. The author signs for and accepts responsibility for releasing this material on behalf of any and all co-authors. This transfer of publication rights covers the non-exclusive right to reproduce and distribute the article, including reprints, translations, photographic reproductions, microform, electronic form (offline, online), or any other reproductions of similar nature.
About this article
Cite this article
Srikanth, C., Vignesh, R.V. & Padmanaban, R. Investigations on the Effect of Cyclic Heat Treatment on the Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded Aluminum Alloys (AA5052 & AA6061). Russ. J. Non-ferrous Metals 62, 692–707 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821221060079
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821221060079