Abstract
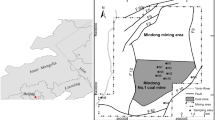
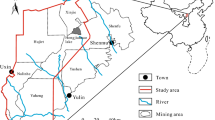
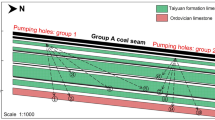
Mine gushing water disaster is one of the important factors affecting the safe production of coal mines, accurate identification of mine gushing water sources, the safe production of coal mines is a significant application. In this paper described, to identify the source of water filling in Tianxin coal mine, using Schukarev classification, Piper trilinear diagram, gray correlation degree, and hydrogen and oxygen isotopes for comprehensive analysis. The analysed results show that the water gushing in the mine of Tianxin coal mine mainly receives the influence of the water of Xiaobaiyang River and Quaternary loose rock pore diving water. However, the reliability of the results is improved by combining the hydrochemical analysis method with the analysis method based on mathematical theory. Identify the source of mine gushing water, and provide guidance for the prevention and control of mine water damage that may occur subsequently.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Li, Y., Xu, Z.M., and Liu, Y., Summary, on methods of distinguishing sources of mine water-invasion, Coal Technol., 2010, vol. 29, no. 11, pp. 87–89.
Hou, E.K., Feng, D., Wen, Q., Che, X.Y., and Gao, T., Logistic regression analysis method for identification of mine inflow water source, Min. Saf. Environ. Prot., 2019, vol. 46, no. 6, pp. 77–83.
Hong, T., Xie, Y.Q., Yu, Q.W., Zhao, Y., Zhao, G.S., and Yang, L.C., Analysis of groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and causes in key areas of Wumeng mountains, Earth Environ., 2016, vol. 44, no. 1, pp. 11–18.
Man, X.Q., Wei, J.C., Xie, D.L., and Xie, C.L., Identification method of water inrush source based on analysis of hydrochemical characteristics, China Sci. Pap., 2021, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 776–781.
Hong, T., Ma, Z.L., Ou, M.M., Qin, X.M., Yang, L.C., and Chen, R.R., Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and the source analysis of the mining water in Yangliu street mine, Ind. Saf. Environ. Prot., 2017, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 83–88.
Hao, B.B., Li, C., and Wang, C.H., Application of grey correlation degree in the identification of sources of mine water bursting, China Coal, 2010, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 20–22. https://doi.org/10.19880/j.cnki.ccm.2010.06.004
Zhang, Y., Hydrochemical analysis method applied to determine mine water inrush sources and verification of tracing method, Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol., 2014, vol. 42, no. 10, pp. 98–100. https://doi.org/10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2014.10.023
Dong, D.L., Zhang, J., Lin, G., Gao, Y.X., and Liu, X., Identification model of the source of water-inrush, Coal Eng., 2020, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 124–127. https://doi.org/10.11799/ce202012026
Wang, Y., Shi, L.Q., Wang, M., and Liu, T.H., Hydrochemical analysis and discrimination of mine water source of the Jiaojia gold mine area, Environ. Earth Sci., 2016, vol. 79, no. 6, pp. 257–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-8856-1
Zhang, S.Y., Hu, Y.B., Ju, Q.D., Distinguishing the sources of water inrush in Zhuji coal mine by hydrochemical characteristics, Min. Saf. Environ. Prot., 2018, vol. 45, no. 6, pp. 53–56.
Liang, J.X., Identification of mine water sources by grey correlation analysis, Coal Geol. Explor., 1993, vol. 21, no. 6, pp. 42–44.
Ju, Q.D. and Hu, Y.B., Source identification of mine water inrush based on principal component analysis and grey situation decision, Environ. Earth Sci., 2021, vol. 157, p. 80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09459-z
Gao, W.D., Application of grey situational decision method in the discrimination of water source for mine water inrush, Min. Saf. Environ. Prot., 2007, vol. 34, no. 6, pp. 47–49.
Chen, S. and Gui, H.R., Isotopic characteristics of D, 18O, 13Cdic, 18Odic, 87Sr/86Sr and their application in coal mine water: A case study, Water Pract. Technol., 2017, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 97–103. https://doi.org/10.2166/wpt.2017.017
Pan, G.Y., Wang, S.N., Sun, X.Y., and Fan, S.K., Application of isotope technology in discerning the source of inrush water in mines, Min. Saf. Environ. Prot., 2009, vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 32–34.
Qu, S., Wang, G.C., Shi, Z.M., Xu, Q.Y., Guo, Y.Y., Ma, L., and Sheng, Y.Z., Using stable isotopes (δD, δ18O, δ34S and 87Sr/86Sr) to identify sources of water in abandoned mines in the Fengfeng coal mining district, Northern China, Hydrogeol. J., 2018, vol. 26, pp. 1443–1553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1803-5
Li, Q., Jia, R.L., Zhou, J.L., and Wang, Y.P., Chemical characteristics of high fluorine groundwater in Aksu area of Xinjiang, J. Arid Land, 2013, vol. 27, no. 12, pp. 87–92. https://doi.org/10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2013.12.031
Zhang, L.Z. and Cao, H.D., Distinguishing the sources of water inrush in Sangshuping coal mine by hydrochemical characteristics, Coal Geol. Explor., 2013, vol. 41, no. 4, pp. 42–45. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2013.04.011
Song, X.F., Liu, J.R., Sun, X.M., Yuan, G.F., Liu, X., Wang, S.Q., and Hou, S.B., China atmospheric precipitation isotope observation network based on CERN, Adv. Earth Sci., 2007, vol. 22, no. 7, pp. 738–747.
Wang, C.X., Zhang, J., Dong, Z.W., Qin, X., and Wang, Y.Z., Analysis of runoff processes in Laohugou glacier region of Qilian mountains based on hydrogen and oxygen isotopes and hydrochemistry, Arid Land Geogr., 2015, vol. 38, no. 5, pp. 927–935. https://doi.org/10.13826/j.cnki.cn651103/x.2015.05.007
FUNDING
The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (project no. 41902254), the Ecological Wisdom Mine Joint Fund of the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei province (project no. D2020402013) and the key R and D project of Hebei Province (project no. 21373901D).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Bian Kai, Hui, S., Shubing, X. et al. Hydrochemical and Hydrogen–Oxygen Isotope-Based Identification of Water Sources in Mine Wells. J. Water Chem. Technol. 45, 290–301 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X23030037
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X23030037