Abstract
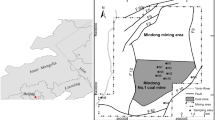
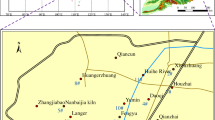
Water gushing in mines is one of the most threatening geological disasters in the process of coal mine production, so the key to preventing water-gushing disasters in mines is to identify the water-gushing sources (WGS) quickly and effectively. Given the problem that it is difficult to effectively identify the WGS from adjacent limestone aquifers by conventional technical approaches, a typical coal mine in Huainan coalfield, the Group A coal seams in the Panji-2 coal mine, was selected as the object of investigation in this study. A total of 60 water samples were collected from the Taiyuan Formation limestone aquifer and the Ordovician limestone aquifer five times by using underground hydrological long-observation holes. The conventional ion hydrogeochemical analysis of Taiyuan Formation limestone water (TLW) and Ordovician limestone water (OLW) samples, in conjunction with the Sr concentration of rocks and limestone water with their isotope test results, indicated that there is a difference between Taiyuan limestone water and Ordovician limestone water through comprehensive analyses. On the basis of five algorithms, principal component analysis (PCA), Fisher identification analysis model (Sr-F), Distance discriminant analysis model (Sr-D), BP neural network analysis model (Sr-B) and Grey relational analysis model (Sr-G), four identification models are constructed for the training dataset by combining the Sr isotope values. The prediction results showed that Sr-B had the highest prediction accuracy of 95% compared to the other three models. A comparative study was carried out on the prediction dataset to further explore the accuracy and stability of the four models. The results revealed that the Sr-B model has the highest prediction accuracy and good stability, and can be used to identify the TLW and OLW. However, the Sr-D model shows better stability but lacks accuracy and needs to be used with caution in practical applications.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakari S S, Aagaard P, Vogt R D, Ruden F, Johansen I and Vuai S A 2013 Strontium isotopes as tracers for quantifying mixing of groundwater in the alluvial plain of a coastal watershed south-eastern Tanzania; J. Geochem. Explor. 130 1–14, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.02.008.
Barnes J D and Sharp Z D 2017 Chlorine isotope geochemistry; Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 82(1) 345–378, https://doi.org/10.2138/rmg.2017.82.9.
Bing W, Zhou J, Zhou A, Liu C and Xie L 2016 Sources migration and transformation of antimony contamination in the water environment of Xikuangshan China: Evidence from geochemical and stable isotope (S, Sr) signatures; Sci. Total Environ. 569–570 114–122, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.124.
Brand U and Veizer J 1980 Chemical diagenesis of a component carbonate system-1: Trace elements; J. Sedim. Petrol. 50 1219–1236, https://doi.org/10.1306/212F7BB7-2B24-11D7-8648000102C1865D.
Bullen T D, Krabbenhoft D P and Kendall C 1996 Kinetc and mineralogic controls on the evolution of ground hydrochemistry and 87Sr/86Sr in a sandy silicate aquifer northern Wisconsin USA; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 60(10) 1807–1821, https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(96)00052-X.
Cartwright I, Weaver T and Petrides B 2007 Controls on 87Sr/86Sr ratios of groundwater in silicate-dominated aquifers: SE Murray Basin Australia; Chem. Geol. 246 107–123, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.09.006.
Denison R E, Koepnick R B, Fletcher A, Howell M W and Callaway W S 1994 Criteria for the retention original seawater 87Sr/86Sr in ancient shelf limestones; Chem. Geol. 112 131–143, https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(94)90110-4.
Dong D, Chen Z, Lin G, Li X, Zhang R and Ji Y 2019 Combining the Fisher feature extraction and support vector machine methods to identify the water-gushing sources: A case study of the Wuhai Mining Area; Mine Water Environ. 38 855–862, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-019-00637-x.
Favara R, Grassa F and Valenza M 2000 Hydrochemical evolution and environmental features of Salso River catchment central Sicily (Italy); Environ. Geol. 39(11) 1205–1215, https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540000116.
Hao Q, Wu X, Mu W and Yu F 2022 Groundwater source identification based on principal component analysis and improved extreme learning machine algorithm using the genetic algorithm: A case study from the Dagushan iron mine Liaoning Province China; Arab. J. Geosci. 15 536, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09100-0.
Huang W W 2020 Groundwater hydrogeochemistry and environmental isotope characteristics in Xinji Mining Area; Anhui University.
Huang P and Wang X 2018 Groundwater-mixing mechanism in a multiaquifer system based on isotopic tracing theory: A case study in a coal mine district China; Geofluids 2018 1–10, https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9549141.
Huang P, Yang Z, Wang X and Ding F 2019 Research on Piper-PCA-Bayes-LOOCV identification model of water inrush source in mines; Arab. J. Geosci. 12 334, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4500-3.
Jiang C, An Y, Zheng L and Huang W 2021 Water source identification in a multiaquifer mine using a comprehensive stepwise discriminant method; Mine Water Environ. 40 442–455, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-020-00742-2.
Li S, Jin F and Wang D 1995 Geochemical characteristics of carbonate rock diagenesis; Petrol. Geol. Exp. 01 55–62, https://doi.org/10.11781/sysydz199501055.
Liu Q, Sun Y, Xu Z and Xu G 2018 Application of the comprehensive identification model in analyzing the source of water gushing; Arab. J. Geosci. 11 189, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3550-2.
Lu T, Liu S, Wang B, Wu R and Hu X 2017 A review of geophysical exploration technology for mine water disaster in China: Applications and trends; Mine Water Environ. 36 331–340, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0467-z.
Miller E K, Blum J D and Friedland A J 1993 Determination of soil exchangeable-cation loss and weathering rate using Sr isotope; Nature 362 438–441, https://doi.org/10.1038/362438a0.
Montgomery J, Evans J and Wildman G 2006 87Sr/86Sr isotope composition of bottled British mineral waters for environmental and forensic purposes; Appl. Geochem. 21(10) 1626–1634, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2006.07.002.
Pearce C R, Parkinson I J, Gaillardet J, Charlier B L A, Mokadem F and Burton K W 2015 Reassessing the stable (δ88/86Sr) and radiogenic (87Sr/86Sr) strontium isotopic composition of marine inputs; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 157 125–146, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2015.02.029.
Qu S, Wang G, Shi Z, Xu Q, Guo Y, Ma L and Sheng Y 2018 Using stable isotopes (δD, δ18O, δ34S and 87Sr/86Sr) to identify sources of water in abandoned mines in the Fengfeng coal mining district northern China; Hydrogeol. J. 26 1443–1453, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1803-5.
Scanlon B, Reedy R and Tachovsky J 2007 Semiarid unsaturated zone chloride profiles: Archives of past land use change impacts on water resources in the southern High Plains United States; Water Resour. Res. 43 W06423, https://doi.org/10.1029/2006WR005769.
Sikdar P K, Sarkar S S and Palchoudhury S 2011 Geochemical evolution of groundwater in the Quaternary aquifer of Calcutta and Howrah, India; J. Asian Earth Sci. 19(5) 579–594, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1367-9120(00)00056-0.
Wang X, Ji H, Wang Q, Liu X, Huang D, Yao X and Chen G 2016 Divisions based on groundwater chemical characteristics and identification of water-gushing sources in the Pingdingshan coalfield; Environ. Earth Sci. 75 872, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5616-3.
Wang Y, Shi L, Wang M and Liu T 2020 Hydrochemical analysis and identification of mine water source of the Jiaojia gold mine area China; Environ. Earth Sci. 79 123, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-8856-1.
Warren J 2000 Dolomite: Occurrence, evolution and economically important associations; Earth-Sci. Rev. 52 1–81, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-8252(00)00022-2.
Xu J, Zhou R, Song D, Li N, Zhang K and Xi D 2017 Deformation and damage dynamic characteristics of coal–rock materials in deep coal mines; Int. J. Damage Mech. 28(1) 58–78, https://doi.org/10.1177/1056789517741950.
Yan Z, Han J, Yu J and Yang Y 2018 Water inrush sources monitoring and identification based on mine IoT; Concurr. Comp.-Pract. E. 31 e4843, https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.4843.
Yan P, Shang S, Zhang C, Yin N, Zhang X, Yang G, Zhang Z and Sun Q 2021 Research on the processing of coal mine water source data by optimizing BP neural network algorithm with sparrow search algorithm; IEEE Access 9 108,718–108,730, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3102020.
Yuan L G, Li X L, Li X, Yu Y L, Chen L G, Xu X P and Wang X 2021 A failure case study of tunnel water inrush source identified by statistical analysis model; Arab. J. Geosci. 14 1809, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08200-1.
Zhang L and Cao H 2013 Distinguishing the sources of water inrush in Sangshuping coal mine by hydrochemical characteristics; Coal Geol. Expl. 41(04) 42–45, https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2013.04.011.
Zhang H and Yao D 2020 The Bayes recognition model for mine water inrush source based on multiple logistic regression analysis; Mine Water Environ. 39 888–901, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-020-00699-2.
Zhang H, Xing H, Yao D, Liu L, Xue D and Guo F 2019 The multiple logistic regression recognition model for water gushing in mine source based on cluster analysis; Environ. Earth Sci. 78 612, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8624-2.
Zhou M R, Lai W H, Wang Y, Hu F, Li D T and Wang R 2018 Application of CNN in LIF Fluorescence Spectrum Image Recognition of Mine Water Inrush; Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 38(07) 2262–2266, https://doi.org/10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2018)07-2262-05.
Zhou A, Hu J and Wang K 2020 Carbon emission assessment and control measures for coal mining in China; Environ. Earth Sci. 79 461, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09189-8.
Zhu T, Bian W, Zhang S, Di P and Nie B 2017 An Improved Approach to Estimate Methane Emissions from Coal Mining in China; Environ. Sci. Technol. 51 12,072–12,080, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b01857.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Annual Open Fund 2021 (2021SKMS06) of Shaanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Coal Mine Water Disaster Prevention and Control Technology and the Anhui Provincial Central Leading Local Science and Technology Development Special Project (201907d07050007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JW, CW and XG conceived the experiments. DW, BL and JL conducted the experiments and performed statistical analysis and figure generation. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Ramananda Chakrabarti
Corresponding editor: Ramananda Chakrabarti
Supplementary material pertaining to this article is available on the Journal of Earth System Science website (http://www.ias.ac.in/Journals/Journal_of_Earth_System_Science).
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dun, W., Jian, W., Chao, W. et al. Identification and prediction of mixed water sources in adjacent limestone aquifers based on conventional hydrochemistry and strontium isotopes. J Earth Syst Sci 133, 44 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-023-02248-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-023-02248-1