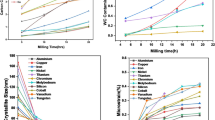
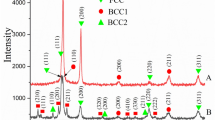
Abstract
The effect of various conditions of mechanical activation of Ti + Zr + Hf + Nb + Ta + 5C mixtures on the microstructure of composite particles, regularities of their ignition, and phase composition of final products was studied. The activation of mixtures was found to decrease the ignition temperature by 600–900°C. It was shown that the intense mechanical activation reduces the activity of the mixture and the subsequent ignition in the thermal explosion mode transforms the mixture into high-entropy compound. Such transformation is not observed in conditions of long-term low-intensity activation.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Akrami, S., Edalati, P., Fuji, M., and Edalati, K., High-entropy ceramics: Review of principles, production and applications, Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep., 2021, vol. 146, p. 100644.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2021.100644
Ye, B., Wen, T., Huang, K., Wang, C.Z., and Chu, Y., First-principles study, fabrication, and characterization of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)C high-entropy ceramic, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2019, vol. 102, pp. 4344–4352. https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.16295
Zhang, Q., Zhang, J., Li, N., and Chen, W., Understanding the electronic structure, mechanical properties, and thermodynamic stability of (TiZrHfNbTa)C combined experiments and first-principles simulation, J. Appl. Phys., 2019, vol. 126, no, 2. p. 025101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5094580
Kochetov, N.A. and Kovalev, I.D., Synthesis and thermal stability of the multielement carbide (TaZrHfNbTi)C5, Inorg. Mater., 2021, vol. 57, no. 1, pp. 8–13. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168520120109
Kovalev, D.Yu., Kochetov, N.A., and Chuev, I.I., Fabrication of high-entropy carbide (TiZrHfTaNb)C by high-energy ball milling, Ceram. Int., 2021, vol. 47, pp. 32626–32633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.08.158
Sarker, P., Harrington, T.J., Gild, J., Sarker, P., Toher, C., Rost, C.M., Dippo, O.F., McElfresh, C., Kaufmann, K., Marin, E., Borowski, L., Hopkins, P.E., Luo, J., Curtarolo, S., Brenner, D.W., and Vecchio, K.S., Phase stability and mechanical properties of novel high entropy transition metal carbides, Acta Mater., 2019, vol. 166, pp. 271–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2018.12.054
Sarker, P., Harrington, T.J., Toher, C., Oses, C., Samiee, M., Maria, J.P., Brenner, D.W., Vecchio, K.S., and Curtarolo, S., High-entropy high-hardness metal carbides discovered by entropy descriptors, Nat. Commun., 2018, vol. 9, p. 4980. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07160-7
Jiang, S., Shao, L., Fan, T., Duan, J.M., Chen, X.T., and Tang, B.Y., Mechanical behavior of high entropy carbide (HfTaZrTi)C and (HfTaZrNb)C under high pressure: ab initio study, Int. J. Quantum Chem., 2020, vol. 121, no. 5, pp. 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/qua.26509
Moskovskikh, D.O., Vorotilo, S., Sedegov, A.S., Kuskov, K.V., Bardasova, K.V., Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, P.V., Zhukovskyi, M., and Mukasyan, A.S., High-entropy (HfTaTiNbZr)C and (HfTaTiNbMo)C carbides fabricated through reactive high-energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering, Ceram. Int., 2020, vol. 46, pp. 19008–19014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.04.230
Wang, F., Zhang, X., Yan, X., Lu, Y., Nastasi, M., Chen, Y., and Cui, B., The effect of submicron grain size on thermal stability and mechanical properties of high-entropy carbide ceramics, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2020, vol. 103, pp. 4463–4472. https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.17103
Feng, L., Fahrenholtz, W.G., and Hilmas, G.E., Low-temperature sintering of single-phase, high-entropy carbide ceramics, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2019, vol. 102, pp. 7217–7224. https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.16672
Chen, H., Xiang, H., Dai, F.Z., Liu, J., Lei, Y., Zhang, J., and Zhou, Y., High porosity and low thermal conductivity high entropy (Zr0.2Hf0.2Ti0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2)C, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2019, vol. 35, pp. 1700–1705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2019.04.006
Ye, B., Wen, T., Liu, D., and Chu, Y., Oxidation behavior of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)C high-entropy ceramics at 1073–1473 K in air, Corros. Sci., 2019, vol. 153, pp. 327–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2019.04.001
Ye, B., Wen, T., and Chu, Y., High-temperature oxidation behavior of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)C high-entropy ceramics in air, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2020, vol. 103, pp. 500–507. https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.16725
Wang, H., Cao, Y., Liu, W., and Wang, Y., Oxidation behavior of (Hf0.2Ta0.2Zr0.2Ti0.2Nb0.2)C–xSiC ceramics at high temperature, Ceram, Int., 2020, vol. 46, pp. 11160–11168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.01.137
Braic, V., Vladescu, A., Balaceanu, M., Luculescu, C.R., and Braic, M., Nanostructured multi-element (TiZrNbHfTa)N and (TiZrNbHfTa)C hard coatings, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2012, vol. 211, pp. 117–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.09.033
Braic, V., Balaceanu, M., Braic, M., Vladescu, A., Panseri, S., Russo, A., Characterization of multiprincipal-element (TiZrNbHfTa)N and (TiZrNbHfTa)C coatings for biomedical applications, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 2012, vol. 10, pp. 197–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2012.02.020
Merzhanov, A.G. and Borovinskaya, I.P., Self-spreading high-temperature synthesis of refractory compounds, Dokl. Chem., 1972, vol. 204, no. 2, pp. 429–431.
Tallarita, G., Licheri, R., Garroni, S., Orrù, R., and Cao, G., Novel processing route for the fabrication of bulk high-entropy metal diborides, Scr. Mater., 2019, vol. 158, pp. 100–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2018.08.039
Vadchenko, S.G., Boyarchenko, O.D., Shkodich, N.F., and Rogachev, A.S., Thermal explosion in various Ni–Al systems: Effect of mechanical activation. Int. J. Self-Propag. High-Temp. Synth., 2013, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 60–64. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1061386213010123
Poluboyarov, V.A., Solonenko, O.P., Zhdanok, A.A., and Pauli, I.A., Comparison of the efficiency of the mills “AGO-2” and “Activator-2SL” at the mechanical activation of titanium powder, J. Sib. Fed. Univ. Eng. Technol., 2017, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 646–656. https://doi.org/10.17516/1999-494X-2017-10-5-646-656
Funding
The research was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 20-13-00277).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by O. Golosova
About this article
Cite this article
Vadchenko, S.G., Kovalev, I.D., Mukhina, N.I. et al. Thermal Explosion in Ti + Zr + Hf + Nb + Ta + 5С System: Effect of Mechanical Activation. Int. J Self-Propag. High-Temp. Synth. 31, 208–214 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1061386222040136
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1061386222040136