Abstract
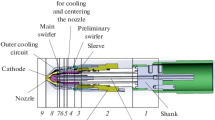
This work studies the structure of cutting seams obtained after cutting steel 09G2S with a new PMVR-5.3 narrow-jet plasma torch which has a number of design features in the gas dynamic stabilization system (GDS) of plasma arc. To increase the efficiency of the GDS in the PMVR-5.3 plasma torch, a symmetrical input of plasma-forming gas (PFG) into the flow division system and a gas-dynamic flow stabilizer using two (forming and stabilizing) swirlers with a variable number of swirl channels were used. It is shown that the achieved advantage in the GDS efficiency makes it possible to obtain a high cutting quality on steel 09G2S with a thickness of 40 mm at high productivity and lower energy costs. Analytical methods have proven a high precision degree of cutting with the new torch—a small cut width, no melting and rounding of the upper edge, as well as a grate in the lower part of the cut and splashes in its upper part, almost zero angular deviation, minimal surface microtopography values and width of the thermal impact zone. A metallographic analysis and a hardness measurement detected three subzones in the thermal impact zone with significant structural changes in two of them. Several factors are noted influencing the revealed structuring changes as well as the changes in the elemental composition of the cutting seam surface layer revealed during the X-ray spectral analysis. Attention is drawn to the surface microtopography after plasma cutting. This topography is commensurate by all quality indicators with the postmilling machining of the surface and corresponds to the second class of surface cleanliness. It is proven that the new narrow-jet plasma torch allows performing a high-quality cutting of plate steel with thicknesses up to 40 mm or more. However, the welding of blanks without pre-machining can be carried out at a cut thickness of no more than 20 mm.










Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Krink, V., Simler, H., and Laurisch, F., Plasmaschneidtechnologie—Erweiterung wirtschaftlicher Anwendungsgebiete, ICCT 2006: Int. Schneidtechnische Tagung; Vorträge der gleichnamigen Konferenz, Hannover, 2006, pp. 18–25.
Mussmann, J., Stand der Bearbeitung von ISO 4063:2009 “Schweissen und verwandte Prozesse—Liste der Prozesse und Ordnungsnummern,” Schweissen Schneiden, 2010, nos. 7–8, pp. 430–433.
Krink, V., Plasmaschneiden – Ein vielseitiges Verfahren zum Schneiden dünner und dicker Bleche, DVS Congress, Nuremberg, 2010, pp. 73–78.
Esibyan, E.M., Air-plasma cutting: State and prospects, Avtom. Svarka, 2000, no. 12, pp. 6–20.
Antipov, N.A. and Medko, V.S., Determination of the defective surface layer during air-plasma cutting of blanks made of carbon low-alloy steel, Elektrofiz. Elektrokhim. Metody Obrab., 2014, no. 2, pp. 25–27.
Vasiliev, A.N., Vnuk, V.V., Zinoviev, V.I., and Kotkina, T.V., Comparative study of air-plasma and plasma-arc cutting, Izv. Mosk. Gos. Tekh. Univ., 2014, no. 2, pp. 13–18.
Gesteigerte Produktivität durch neueste Plasmaschneidtechnologie, Schweissen Schneiden, 2008, no. 9, pp. 458–459.
Nachbargauer, K., Mit Schneidhohmodus beim Plasmaschneiden reproduzierbare Schneidergebnisse erzeilen, DVS Congress, Nuremberg, 2010, pp. 95–96.
Wegmann, H., Gesthuysen, F.-J., and Holthaus, M., Plasma cutting—an economically viable process for mild and low-alloy steels, Weld. Cutting, 2005, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 191–194.
Anakhov, S.V., Printsipy i metody proektirovaniya plazmotronov (Principles and Methods of Plasma Torches Design), Yekaterinburg: Ross. Gos. Profess.-Pedagog. Univ., 2018.
Conrads, H. and Schmidt, M., Plasma generation and plasma sources, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., 2000, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 441–454. https://doi.org/10.1088/0963-0252/9/4/301
Venkatramani, N., Industrial plasma torches and applications, Curr. Sci., 2002, vol. 83, no. 3, pp. 254–262.
Loktionov, A.A., Assessment a cut of quality of sheet materials in the conditions of high-precision plasma cutting, Obrab. Met., 2013, no. 4, pp. 85–89.
Rakhimyanov, H.M., Loktionov, A.A., and Nikitin, Yu.V., Evaluation of geometric precision cut of sheet materials with different high-precision plasma cutting technologies, Obrab. Met., 2013, no. 3, pp. 25–30.
Kirkpatrick, I., High definition plasma—An alternative to laser technology, Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol., 1998, vol. 70, no. 3, pp. 215–217. https://doi.org/10.1108/00022669810370349
Dresvin, S.V. and Zverev, S.G., Plasmotrony. Konstruktsii, parametry, tekhnologii (Plasma Torches: Designs, Parameters, Technologies), St. Petersburg: Izd-vo Politekh. Univ., 2010.
Anakhov, S.V., Pykin, Yu.A., and Matushkin, A.V., Improving the effectiveness of individual gaseous-vortex stabilization in plasma torches for precision cutting of metals, Svar. Proizvod., 2019, no. 4, pp. 27–30.
GOST (State Standard) 14 792–80: Parts and blanks cut by oxygen and plasma arc cutting. Accuracy, quality of the cutting surface, 1980.
Sukhorukov, N.V. and Smolentsev, E.V., Technology of plasma processing in materials separation, Vestn. Voronezh. Gos. Tekh. Univ., 2009, vol. 5, no. 12, pp. 1–3.
Sumets, A.V. and Kassov, V.D., Regularities of structure formation of heat affected zone at metals cutting, Vestn. Kharkov. Nats. Avtomobil.-Dorozhnii Univ., 2017, no. 77, pp. 166–170.
Lyashchenko, G.I., Quality in plasma-arc cutting, Svarshchik, 2012, no. 4, pp. 34–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated by S. Kuznetsov
About this article
Cite this article
Anakhov, S.V., Guzanov, B.N. & Matushkin, A.V. Development of Equipment and Technology for Precision Air-Plasma Cutting of Plate Steel. Steel Transl. 52, 19–26 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3103/S096709122201003X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S096709122201003X