Abstract
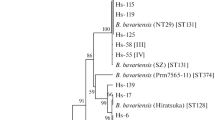
Seventeen isolates of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato with an unclear genetic characteristic isolated in Russia from various species of Ixodes ticks (I. persulcatus, I. ricinus, and I. pavlovskyi) have been studied by multilocus sequencing analysis. According to the results of typing, these isolates were identified as B. bavariensis (n = 7), B. garinii (n = 6), B. finlandensis (n = 3), and B. spielmanii (n = 1), that is, species that can cause ixodid tick-borne borreliosis diseases in human beings. The allelic polymorphism of five genes (rrs, fla, groEL, recA, and ospA) and spacer rrfA–rrlB of B. bavariensis and B. garinii isolates was analyzed in comparison with their diversity in the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pritt, B.S., Respicio-Kingry, L.B., Sloan, L.M., Schriefer, M.E., Replogle, A.J., Bjork, J., et al., Borrelia mayonii sp. nov., a member of the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex, detected in patients and ticks in the upper Midwestern United States, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2016, vol. 66, no. 11, pp. 4878–4880.
Rudenko, N., Golovchenko, M., Vancova, M., Clark, K., Grubhoffer, L., and Oliver, J.H., Isolation of live Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato spirochaetes from patients with undefined disorders and symptoms not typical for Lyme borreliosis, Clin. Microbiol. Infect., 2016, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 267.e9–267.e15. doi 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.11.009
Mongodin, E.F., Casjens, S.R., Bruno, J.F., Xu, Y., Drabek, E.F., Riley, D.R., et al., Inter-and intra-specific pan-genomes of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato: genome stability and adaptive radiation, BMC Genomics, 2013, vol. 14, p.693.
Margos, G., Vollmer, S.A., Ogden, N.H., and Fish, D., Population genetics, taxonomy, phylogeny and evolution of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, Infect., Genet. Evol., 2011, vol. 11, pp. 1545–1563.
Ivanova, L.B., Tomova, A., González-Acuña, D., Murúa, R., Moreno, C.X., and Hernández, C., Borrelia chilensis, a new member of the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex that extends the range of this genospecies in the Southern Hemisphere, Environ. Microbiol., 2014, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 1069–1080.
Margos, G., Chu Chen-Yi, Takano Ai, Jiang Bao-Gui, Liu We, Kurtenbach, K., et al., Borrelia yangtzensis sp. nov., a rodent-associated species in Asia, is related to Borrelia valaisiana, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 65, pp. 3836–3840.
Casjens, S.R., Fraser-Liggett, C.M., Mongodin, E.F., Qiu, W.G., Dunn, J.J., Luft, B.J., and Schutzer, S.E., Whole genome sequence of an unusual Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato isolate, J. Bacteriol., 2011, vol. 193, no. 6, pp. 1489–1490.
Postic, D., Garnier, M., and Baranton, G., Multilocus sequence analysis of atypical Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato isolates-description of Borrelia californiensis sp. nov., and genomospecies 1 and 2, Int. J. Med. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 297, pp. 263–271.
Vysotskii, V.V. and Kotlyarova, G.A., Poly(hetero) morphic forms of pathogenic bacteria in infectious pathology, Zh. Mikrobiol., Epidemiol. Immunobiol., 1999, no. 2, pp. 100–104.
Korenberg, E.I., Nefedova, V.V., Gorelova, N.B., Kovalevskii, Yu.V., Fadeeva, I.A., and Golubova, D.A., Etiological structure of southern taiga combinations of natural foci of ixodic tick-borne borrelioses, Vestn. Ross. Akad. Med. Nauk, 2011, no. 10, pp. 10–15.
Korenberg, E.I. and Nefedova, V.V., Borrelia—pathogens of tick-borne borrelioses and epidemic relapsing fever, in Rukovodstvo po meditsinskoi mikrobiologii. Chastnaya meditsinskaya mikrobiologiya i etiologicheskaya diagnostika infektsii (Guideline on Medical Microbiology. Special Medical Microbiology and Etiological Diagnostics of Infections), Labinskaya, A.S., Kostyukova, N.N., and Ivanova, S.M., Eds., Moscow: BINOM, 2010, pp. 844–866.
Korenberg, E.I., Pomelova, V.G., and Osin, N.S., Prirodnoochagovye infektsii, peredayushchiesya iksodovymi kleshchami (Natural Focal Infections Transmitted by Ixodic Ticks), Moscow: Kommentarii, 2013.
Margos, G., Vollmer, S.A., Cornet, M., Garnier, M., Fingerle, V., Wilske, B., et al., A new Borrelia species defined by Multilocus sequence analysis of housekeeping genes, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2009, vol. 75, no. 16, pp. 5410–5416.
Gorelova, N.B., Korenberg, E.I., Vorob’eva, N.N., Frizen, V.I., Nefedova, V.V., and Teterin, V.Yu., Isolating pathogen of ixodic tick borreliosis from the patients’ blood, Zh. Mikrobiol., Epidemiol. Immunobiol., 2009, no. 1, pp. 63–66.
Nefedova, V.V., Korenberg, E.I., and Gorelova, N.B., Genetic variants of Borrelia garinii, a widespread Eurasian pathogen of ixodic tick borreliosis, Mol. Genet., Microbiol. Virol., 2010, vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 95–100.
Nefedova, V.V., Korenberg, E.I., Fadeeva, I.A., and Gorelova, N.B., Genetic characteristics of pathogenic for humans Borrelia isolated from Ixodes trianguliceps bir. and Ixodes pavlovskyi pom ticks, Med. Parazitol. Parazit. Bolezni, 2005, no. 2, pp. 9–12.
Nefedova, V.V., Korenberg, E.I., and Gorelova, N.B., Genotyping Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato isolates from Ixodes Ricinus ticks in Russia and Ukraine, Mol. Genet., Microbiol. Virol., 2010, vol. 25, no. 1, pp. 25–30.
Korenberg, E.I., Nefedova, V.V., Romanenko, V.N., and Gorelova, N.B., The tick Ixodes pavlovskyi as a host of spirochetes pathogenic for humans and its possible role in the epizootiology and epidemiology of Borrelioses, Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis., 2010, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 453–458.
Mukhacheva, T.A. and Kovalev, S.Y., Multilocus sequence analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi s.1. in Russia, Ticks Tick Borne Dis., 2013, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 275–279.
Richter, D., Schlee, D.B., Allgöwer, R., and Matuschka, F.-R., Relationships of a novel Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia spielmani sp. nov., with its hosts in Central Europe, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 70, no. 11, pp. 6414–6419.
Wang, G., van Dam, A.P., and Dankert, J., Phenotypic and genetic characterization of a novel Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato isolate from a patient with Lyme borreliosis, J. Clin. Microbiol., 1999, vol. 37, no. 9, pp. 3025–3028.
Hao, Q., Hou, X., Geng, Z., and Wan, K., Distribution of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in China, J. Clin. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 647–650.
Gómez-Díaz, E., Boulinier, T., Sertour, N., Cornet, M., Ferquel, E., and McCoy, K.D., Genetic structure of marine Borrelia garinii and population admixture with the terrestrial cycle of Lyme borreliosis, Environ. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 13, no. 9, pp. 2453–2467.
Margos, G., Gatewood, A.G., Aanensen, D.M., Hanincová, K., Terekhova, D., Vollmer, S.A., et al., MLST of housekeeping genes captures geographic population structure and suggests a European origin of Borrelia burgdorferi, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2008, vol. 105, no. 25, pp. 8730–8735.
Marti Ras, N., Postic, D., Foretz, M., and Baranton, G., Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, a bacterial species “made in the U.S.A.”?, Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 1997, vol. 47, no. 4, pp. 1112–1117.
Castillo-Ramírez, S., Fingerle, V., Jungnick, S., Straubinger, R.K., Krebs, S., Blum, H., et al., Trans-Atlantic exchanges have shaped the population structure of the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, Sci. Rep., 2016, vol. 6, p. 22794.
Margos, G., Wilske, B., Sing, A., Hizo-Teufel, C., Cao, W.C., Chu, C., et al., Borrelia bavariensis sp. nov. is widely distributed in Europe and Asia, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2013, vol. 63, pp. 4284–4288.
Huegli, D., Hu, C.M., Humair, P.-F., Wilske, B., and Gern, L., Apodemus species mice are reservoir hosts of Borrelia garinii OspA serotype 4 in Switzerland, J. Clin. Microbiol., 2002, vol. 40, no. 12, pp. 4735–4737.
Takano, A., Nakao, M., Masuzawa, T., Takada, N., Yano, Y., Ishiguro, F., Fujita, H., et al., Multilocus sequence typing implicates rodents as the main reservoir host of human-pathogenic Borrelia garinii in Japan, J. Clin. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 49, no. 5, pp. 2035–2039.
Scholz, H.C., Margos, G., Derschum, H., Speck, S., Tserennorov, D., Erdenebat, N., et al., High prevalence of genetically diverse Borrelia bavariensis-like strains in Ixodes persulcatus from Selenge Aimag, Mongolia, Ticks Tick Borne Dis., 2013, vol. 4, nos. 1–2, pp. 89–92.
Filippova, N.A., Taezhnyy kleshch Ixodes persulcatus Schulze (Acrana, Ixodidae): morfologiya, sistematika, ekologiya, meditsinskoe znachenie (Taiga Tick Ixodes persulcatus Schulze (Acrana, Ixodidae): Morphology, Systematics, Ecology, Medical Significance), Leningrad: Nauka, 1985.
Tveten, A.-K., Exploring diversity among Norwegian Borrelia strains originating from Ixodes ricinus ticks, J. Microbiol., 2014, vol. 2014, Art. ID 397143. http://dx.doi.org/. doi 10.1155/2014/397143
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.V. Nefedova, E.I. Korenberg, N.B. Gorelova, 2017, published in Molekulyarnaya Genetika, Mikrobiologiya i Virusologiya, 2017, No. 4, pp. 145–150.
About this article
Cite this article
Nefedova, V.V., Korenberg, E.I. & Gorelova, N.B. Multilocus Sequence Analysis of “Atypical” Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato Isolated in Russia. Mol. Genet. Microbiol. Virol. 32, 196–203 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0891416817040073
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0891416817040073