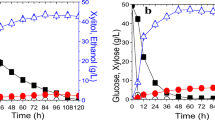
Abstract—In recent years, the demand for technical ethanol has increased due to its use in the transport sector. Xylose is the major five-carbon sugar obtained as a result of lignocellulose hydrolysis; however, the industrial producer of alcohol S. cerevisiae yeast ferments exclusively hexoses. Based on a recombinant strain capable of xylose metabolism, the derivatives with increased expression of the ZNF1 gene and deletion of the SIP4 gene encoding transcription factors were constructed. It was found that overexpression of the ZNF1 gene did not affect the fermentation of glucose or xylose. The deletion of the SIP4 gene did not affect the fermentation of glucose but resulted in a 29% decrease in ethanol production during xylose fermentation in comparison with the parental strain.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Dias De Oliveira, M.E., Burton, E., Vaughan, B.E., and Rykiel, E.J., Ethanol as fuel: energy, carbon dioxide balances, and ecological footprint, BioScience, 2005, vol. 55, no. 7, pp. 593–602. https://doi.org/10.1641/0006-3568(2005)055[0593:EAFECD]2.0.CO;2
Sybirnyi, A., Bio-fuel ethanol of lignocellulose (vegetable biomass): achievements, problems, prospects, Visn. Nats. Akad. Nauk Ukr., 2006, no. 3. ISSN 0372-6436.
Scalcinati, G., Otero, J.M., Van Vleet, J.R., Jeffries, T.W., Olsson, L., and Nielsen, J., Evolutionary engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient aerobic xylose consumption, FEMS Yeast Res., 2012, vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 582–597. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.15671364.2012.00808.x
MacPherson, S., Larochelle, M., and Turcotte, B., A fungal family of transcriptional regulators: the zinc cluster croteins, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2006, vol. 70, no. 3, pp. 583–604. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.00015-06
Tangsombatvichit, P., Semkiv, M.V., Sibirny, A.A., Jensen, L.T., Ratanakhanokchai, K., and Soontorngun, N., Zinc cluster protein Znf1, a novel transcription factor of non-fermentative metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae,FEMS Yeast Res., 2015, vol. 15, no. 2, pii: fou002. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/fou002
Vincent, O. and Carlson, M., Sip4, a Snf1 kinase-dependent transcriptional activator, binds to the carbon source-responsive element of gluconeogenic genes, EMBO J., 1998, vol. 17, no. 23, pp. 7002–7008. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/17.23.7002
Gancedo, J.M., Yeast carbon catabolite repression, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 1998, vol. 62, no. 2, pp. 334–361.
Sambrook, J., Fritsh, E.F., and Maniatis, T., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989.
Gietz, R.D. and Woods, R.A., Transformation of yeast by lithium acetate/single stranded carrier DNA/polyethylene glycol method, Methods Enzymol., 2002, vol. 350, pp. 87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(02)50957-5
Ferreira, R., Teixeira, P.G., Gossing, M., Davi,d, F., Siewers V., and Nielsen, J., Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for overproduction of triacylglycerols, Metab. Eng. Commun., 2018, vol. 6, pp. 22–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meteno.2018.01.002
Wenning, L., Yu, T., David, F., Nielsen, J., and Siewers, V., Establishing very long-chain fatty alcohol and wax ester biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae,Biotechnol. Bioeng., 2017, vol. 114, no. 5, pp. 1025–1035. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26220
Funding
The study was partially supported by the grant of the Polish National Science Center (NCN) DEC- 2012/05/B/ NZ1/01657.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by V. Mittova
About this article
Cite this article
Dzanaeva, L.S., Ruchala, J., Sibirny, A.A. et al. The Impact of Transcriptional Factors Znf1 and Sip4 on Xylose Alcoholic Fermentation in Recombinant Strains of Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae . Cytol. Genet. 54, 386–392 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452720050035
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452720050035