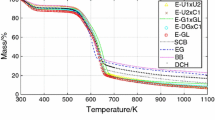
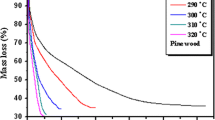
Abstract
Pyrolysis kinetics of a hardwood representative, beech (Fagus sylvatica), was investigated by two different kinetic approaches: model-free isoconversional method and model-fitting method. The model-free isoconversional method was used for the determination of apparent kinetic parameters, i.e. the activation energy and pre-exponential factor. The model fitting method was used for the optimization of kinetic parameters of the reaction pathways of three selected reaction mechanisms: one-step, two-step, and three-step one. In both approaches, thermo-gravimetric data were used at five heating rates: 2°C min−1, 5°C min−1, 10°C min−1, 15°C min−1 and 20°C min−1. As the most suitable mechanism, the three-step mechanism containing the intermediate degradation step was chosen. This selection was supported by experimental results from the 13C NMR analysis of solid residues prepared at the key temperatures within the range of 230–500°C. The progress of mass fraction values of each component in this mechanism was simulated. Conclusions from the simulation were confronted with experimental results from the 13C NMR.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antal, M. J., Jr., & Várhegyi, G. (1995). Cellulose pyrolysis kinetics: The current state of knowledge. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 34, 703–717. DOI: 10.1021/ie00042a001.
Antal, M. J., Jr., Várhegyi, G., & Jakab, E. (1998). Cellulose pyrolysis kinetics: Revisited. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 37, 1267–1275. DOI: 10.1021/ie970144v.
Arseneau, D. F. (1971). Competitive reactions in the thermal decomposition of cellulose. Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 49, 632–638. DOI: 10.1139/v71-101.
Banyasz, J. L., Li, S., Lyons-Hart, J., & Shafer, K. H. (2001a). Cellulose pyrolysis: The kinetics of hydroxyacetaldehyde evolution. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 57, 223–248. DOI: 10.1016/s0165-2370(00)00135-2.
Banyasz, J. L., Li, S., Lyons-Hart, J., & Shafer, K. H. (2001b). Gas evolution and the mechanism of cellulose pyrolysis. Fuel, 80, 1757–1763. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-2361(01)00060-6.
Bardet, M., Emsley, L., & Vincendon, M. (1997). Twodimensional spin-exchange solid-state NMR studies of 13Cenriched wood. Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 8, 25–32. DOI: 10.1016/s0926-2040(96)01273-8.
Bradburry, A. G. W., Sakai, Y., & Shafizadeh, F. (1979). A kinetic model for pyrolysis of cellulose. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 23, 3271–3280. DOI: 10.1002/app.1979.070231112.
Brewer, C. E., Schmidt-Rohr, K., Satrio, J. A., & Brown, R. C. (2009). Characterization of biochar from fast pyrolysis and gasification systems. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 28, 386–396. DOI: 10.1002/ep.10378.
Broido, A., & Weinstein, M. (1972). Low temperature isothermal pyrolysis of cellulose. In Thermal analysis (pp. 285–296). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-0348-5775-825.
Brown, M. E., Maciejewski, M., Vyazovkin, S., Nomen, R., Sempere, J., Burnham, A., Opfermann, J., Strey, R., Anderson, H. L., Kemmler, A., Keuleers, R., Janssens, J., Desseyn, H. O., Li, C. R., Tang, T. B., Roduit, B., Málek, J., & Mitsuhashi, T. (2000). Computational aspects of kinetic analysis: Part A: The ICTAC kinetics project-data, methods and results. Thermochimica Acta, 355, 125–143. DOI: 10.1016/s0040-6031(00)00443-3.
Budrugeac, P. (2002). Differential non-linear isoconversional procedure for evaluating the activation energy of nonisothermal reactions. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 68, 131–139. DOI: 10.1023/a:1014932903582.
Burnham, A. K., & Dinh, L. N. (2007). A comparison of isoconversional and model-fitting approaches to kinetic parameter estimation and application predictions. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 89, 479–490. DOI: 10.1007/s10973-006-8486-1.
Di Blasi, C. (2008). Modeling chemical and physical processes of wood and biomass pyrolysis. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 34, 47–90. DOI: 10.1016/j.pecs.2006.12.001.
Fisher, T., Hajaligol, M., Waymack, B., & Kellogg, D. (2002). Pyrolysis behavior and kinetics of biomass derived materials. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 62, 331–349. DOI: 10.1016/s0165-2370(01)00129-2.
Flynn, J. H. (1997). The ‘temperature integral’ — its use and abuse. Thermochimica Acta, 300, 83–92. DOI: 10.1016/s0040-6031(97)00046-4.
Friedman, H. L. (1964). Kinetics of thermal degradation of char-forming plastics from thermogravimetry. Application to a phenolic plastic. Journal of Polymer Science Part C: Polymer Symposia, 6, 183–195. DOI: 10.1002/polc.5070060121.
Gašparovič, L., Koreňová, Z., & Jelemenský, Ľ. (2010). Kinetic study of wood chips decomposition by TGA. Chemical Papers, 64, 174–181. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-009-0109-4.
Geng, Z. F., Zhang, M. H., & Yu, Y. Z. (2011). Theoretical investigation on pyrolysis mechanism of glycerol. Fuel, 93, 92–98. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.08.021.
Gil, A. M., & Neto, C. P. (1999). Solid-state NMR studies of wood and other lignocellulosic materials. Annual Reports on NMR Spectroscopy, 37, 75–117. DOI: 10.1016/s0066-4103(08)60014-9.
Haydary, J., & Susa, D. (2013). Kinetics of thermal decomposition of aseptic packages. Chemical Papers, 67, 1514–1520. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-013-0319-7.
Hoekstra, E., Van Swaaij, W. P. M., Kersten, S. R. A., & Hogendoorn, K. J. A. (2012). Fast pyrolysis in a novel wiremesh reactor: Decomposition of pine wood and model compounds. Chemical Engineering Journal, 187, 172–184. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.118.
Hosoya, T., Kawamoto, H., & Saka, S. (2008). Different pyrolytic pathways of levoglucosan in vapor- and liquid/solidphases. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 83, 64–70. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2008.06.008.
Howell, B. A. (2006). Utility of kinetic analysis in the determination of reaction mechanism. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 85, 165–167. DOI: 10.1007/s10973-005-7484-z.
Kilzer, F. J., & Broido, A. (1965). Speculation on the nature of cellulose pyrolysis. Pyrodynamics, 2, 151–163.
Koufopanos, C. A., Lucchesi, A., & Maschio, G. (1989). Kinetic modelling of the pyrolysis of biomass and biomass components. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 67, 75–84. DOI: 10.1002/cjce.5450670111.
Lédé, J. (2012). Cellulose pyrolysis kinetics: An historical review on the existence and role of intermediate active cellulose. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 94, 17–32. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2011.12.019.
Li, S., Lyons-Hart, J., Banyasz, J. L., & Shafer, K. H. (2001). Real-time evolved gas analysis by FTIR method: An experimental study of cellulose pyrolysis. Fuel, 80, 1809–1817. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-2361(01)00064-3.
Mamleev, V., Bourbigot, S., & Yvon, J. (2007). Kinetic analysis of the thermal decomposition of cellulose: The change of the rate limitation. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 80, 141–150. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2007.01.012.
Maunu, S. L. (2002). NMR studies of wood and wood products. Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, 40, 151–174. DOI: 10.1016/s0079-6565(01)00041-3.
Melkior, T., Jacob, S., Gerbaud, G., Hediger, S., Le Pape, L., Bonnefois, L., & Bardet, M. (2012). NMR analysis of the transformation of wood constituents by torrefaction. Fuel, 92, 271–280. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.06.042.
Miyanami, K, Fan, L. S., Fan, L. T., & Walawender, W. P. (1977). A mathematical model for pyrolysis of a solid particle — effects of the heat of reaction. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 55, 317–325. DOI: 10.1002/cjce.5450550314.
Opfermann, J. (2000). Kinetic analysis using multivariate nonlinear regression. I. Basic concepts. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 60, 641–658. DOI: 10.1023/a:1010167 626551.
Paine, J. B., Pithawalla, Y. B., Naworal, J. D., & Thomas, C. E., Jr. (2007). Carbohydrate pyrolysis mechanisms from isotopic labeling: Part 1: The pyrolysis of glycerin: Discovery of competing fragmentation mechanisms affording acetaldehyde and formaldehyde and the implications for carbohydrate pyrolysis. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 80, 297–311. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2007.03.007.
Prakash, N., & Karunanithi, T. (2008). Kinetic modeling in biomass pyrolysis. A review. Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 4, 1627–1636.
Sánchez-Jiménez, P. E., Pérez-Maqueda, L. A., Perejón, A., & Criado, J. M. (2010). A new model for the kinetic analysis of thermal degradation of polymers driven by random scission. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 95, 733–739. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2010.02.017.
Shafizadeh, F., & Chin, P. P. S. (1977). Thermal deterioration of wood. ACS Symposium Series, 43, 57–81. DOI: 10.1021/bk-1977-0043.ch005.
Shafizadeh, F. (1982). Introduction to pyrolysis of biomass. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 3, 283–305. DOI: 10.1016/0165-2370(82)80017-x.
Shen, D. K., & Gu, S. (2010). Corrigendum to “The mechanism for thermal decomposition of cellulose and its main products” [Biores. Technol. 100 (2009) 6496–6504]. Bioresource Technology, 101, 6879. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.04.002.
Thurner, F., & Mann, U. (1981). Kinetic investigation of wood pyrolysis. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Process Design and Development, 20, 482–488. DOI: 10.1021/i200014a015.
Várhegyi, G., Jakab, E., & Antal, M. J., Jr. (1994). Is the Broido-Shafizadeh model for cellulose pyrolysis true? Energy & Fuels, 8, 1345–1352. DOI: 10.1021/ef00048a025.
Várhegyi, G., Antal, M. J., Jr., Jakab, E., & Szabó, P. (1997). Kinetic modeling of biomass pyrolysis. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 42, 73–87. DOI: 10.1016/s0165-2370(96)00971-0.
Vyazovkin, S., & Dollimore, D. (1996). Linear and nonlinear procedures in isoconversional computations of the activation energy of nonisothermal reactions in solids. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 36, 42–45. DOI: 10.1021/ci950062m.
Vyazovkin, S., Burnham, A. K., Criado, J. M., Pérez-Maqueda, L. A., Popescu, C., & Sbirrazzuoli, N. (2011). ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data. Thermochimica Acta, 520, 1–19. DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2011.03.034.
White, J. E., Catallo, W. J., & Legendre, B. L. (2011). Biomass pyrolysis kinetics: A comparative critical review with relevant agricultural residue case studies. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 91, 1–33. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2011.01.004.
Wichman, I. S., & Atreya, A. (1987). A simplified model for the pyrolysis of charring materials. Combustion and Flame, 68, 231–247. DOI: 10.1016/0010-2180(87)90002-2.
Wu, S. L., Shen, D. K., Hu, J., Xiao, R., & Zhang, H. Y. (2013). TG-FTIR and Py-GC-MS analysis of a model compound of cellulose — glyceraldehyde. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 101, 79–85. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2013.02.009.
Yoon, H. C., Pozivil, P., & Steinfeld, A. (2012). Thermogravimetric pyrolysis and gasification of lignocellulosic biomass and kinetic summative law for parallel reactions with cellulose, xylan and lignin. Energy & Fuels, 26, 357–364. DOI: 10.1021/ef201281n.
Zheng, A. Q., Zhao, Z. L., Chang, S., Huang, Z., Wang, X. B., He, F., & Li, H. B. (2013). Effect of torrefaction on structure and fast pyrolysis behavior of corncobs. Bioresource Technology, 128, 370–377. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.10.067.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to the memory of professor Elemír Kossaczký
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hrablay, I., Jelemenský, Ľ. Kinetics of thermal degradation of wood biomass. Chem. Pap. 68, 1725–1738 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-014-0622-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-014-0622-y