Abstract
Toxoplasma gondii is a worldwide parasite that can infect almost all kinds of mammals and cause fatal toxoplasmosis in immunocompromised patients. Apoptosis is one of the principal strategies of host cells to clear pathogens and maintain organismal homeostasis, but the mechanism of cell apoptosis induced by T. gondii remains obscure. To explore the apoptosis influenced by T. gondii, Vero cells infected or uninfected with the parasite were subjected to apoptosis detection and subsequent dual RNA sequencing (RNA-seq). Using high-throughput Illumina sequencing and bioinformatics analysis, we found that pro-apoptosis genes such as DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 (DDIT3), growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible α (GADD45A), caspase-3 (CASP3), and high-temperature requirement protease A2 (HtrA2) were upregulated, and anti-apoptosis genes such as poly(adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribose) polymerase family member 3 (PARP3), B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), and baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) repeat containing 5 (BIRC5) were downregulated. Besides, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor 1 (TRAF1), TRAF2, TNF receptor superfamily member 10b (TNFRSF10b), disabled homolog 2 (DAB2)-interacting protein (DAB2IP), and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 3 (ITPR3) were enriched in the upstream of TNF, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress pathways, and TRAIL-receptor 2 (TRAIL-R2) was regarded as an important membrane receptor influenced by T. gondii that had not been previously considered. In conclusion, the T. gondii RH strain could promote and mediate apoptosis through multiple pathways mentioned above in Vero cells. Our findings improve the understanding of the T. gondii infection process through providing new insights into the related cellular apoptosis mechanisms.
摘要
目的
研究并阐明弓形虫感染宿主细胞后影响细胞凋亡及相关信号通路。
创新点
通过转录组研究发现弓形虫感染促进了细胞凋亡, 并发现了包括DDIT3、GADD45A、CASP3及HtrA2在内的多个关键上调基因。
方法
首先通过流式细胞仪对感染及未感染弓形虫的细胞进行凋亡检测, 提取RNA后进行转录组测序, 通过转录组基因上调、下调分析, GO和KEGG通路、关键基因富集、基因网络关系图、RT-PCR验证等手段进行分析。
结论
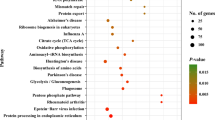
流式细胞仪检测发现弓形虫感染后能显著诱导细胞发生凋亡, 进一步的转录组分析发现, 与对照组相比, 感染组有1579个基因表达有显著变化, 其中有918个基因上调, 661个基因下调;在富集的54条通路中, 凋亡通路有16个关键基因上调, 11个基因下调, 其中caspase-3是我们发现的关键网络基因。细胞凋亡与细胞周期密切、与免疫及多种疾病有关, 进一步深入研究和探索弓形虫与宿主细胞之间的凋亡机制可为寻找理想药物靶点提供理论基础。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angeloni MB, Guirelli PM, Franco PS, et al., 2013. Differential apoptosis in BeWo cells after infection with highly (RH) or moderately (ME49) virulent strains of Toxoplasma gondii is related to the cytokine profile secreted, the death receptor fas expression and phosphorylated ERK1/2 expression. Placenta, 34(11):973–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2013.09.005
Ariyasu D, Yoshida H, Hasegawa Y, 2017. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and endocrine disorders. Int J Mol Sci, 18(2):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020382
Bader GD, Hogue CWV, 2003. An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics, 4:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-4-2
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, et al., 2014. CytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol, 8(S4):S11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-8-S4-S11
Cong W, Dottorini T, Khan F, et al., 2018. Acute Toxoplasma gondii infection in cats induced tissue-specific transcriptional response dominated by immune signatures. Front Immunol, 9:2403. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02403
Cui JM, Shen B, 2020. Transcriptomic analyses reveal distinct response of porcine macrophages to Toxoplasma gondii infection. Parasitol Res, 119(6):1819–1828. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06677-5
Delavallée L, Mathiah N, Cabon L, et al., 2020. Mitochondrial AIF loss causes metabolic reprogramming, caspase-independent cell death blockade, embryonic lethality, and perinatal hydrocephalus. Mol Metab, 40:101027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101027
Enari M, Sakahira H, Yokoyama H, et al., 1998. A caspase-activated DNase that degrades DNA during apoptosis, and its inhibitor ICAD. Nature, 391(6662):43–50. https://doi.org/10.1038/34112
Estaquier J, Vallette F, Vayssiere JL, et al., 2012. The mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis. In: Scatena R, Bottoni P, Giardina B (Eds.), Advances in Mitochondrial Medicine. Springer, Dordrecht, p.157–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-2869-1_7
Fox BA, Bzik DJ, 2015. Nonreplicating, cyst-defective type II Toxoplasma gondii vaccine strains stimulate protective immunity against acute and chronic infection. Infect Immun, 83(5):2148–2155. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.02756-14
Gao M, Guo N, Huang CS, et al., 2009. Diverse roles of GADD45α in stress signaling. Curr Protein Pept Sci, 10(4): 388–394. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920309788922216
Hill RD, Gouffon JS, Saxton AM, et al., 2012. Differential gene expression in mice infected with distinct Toxoplasma strains. Infect Immun, 80(3):968–974. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.05421-11
Hu YY, Bi Y, Yao DH, et al., 2019. Omi/HtrA2 protease associated cell apoptosis participates in blood-brain barrier dysfunction. Front Mol Neurosci, 12:48. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2019.00048
Ihara F, Fereig RM, Himori Y, et al., 2020. Toxoplasma gondii dense granule proteins 7, 14, and 15 are involved in modification and control of the immune response mediated via Nf-κB pathway. Front Immunol, 11:1709. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01709
Kim CM, Park HH, 2020. Comparison of target recognition by TRAF1 and TRAF2. Int J Mol Sci, 21(8):2895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082895
Lima TS, Lodoen MB, 2019. Mechanisms of human innate immune evasion by Toxoplasma gondii. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 9:103. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2019.00103
Lin YC, Shen ZR, Song XH, et al., 2018. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals adriamycin-induced apoptosis via p53 signaling pathway in retinal pigment epithelial cells. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 19(12):895–909. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1800408
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD, 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the \({2^{- \Delta \Delta {C_{\rm{T}}}}}\) method. Methods, 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lossi L, Castagna C, Merighi A, 2018. Caspase-3 mediated cell death in the normal development of the mammalian cerebellum. Int J Mol Sci, 19(12):3999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123999
Lu G, Zhou J, Zhao YH, et al., 2019. Transcriptome sequencing investigated the tumor-related factors changes after T. Gondii infection. Front Microbiol, 10:181. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00181
Mammari N, Halabi MA, Yaacoub S, et al., 2019. Toxoplasma gondii modulates the host cell responses: an overview of apoptosis pathways. Biomed Res Int, 2019:6152489. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6152489
Mangla A, Guerra MT, Nathanson MH, 2020. Type 3 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor: a calcium channel for all seasons. Cell Calcium, 85:102132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2019.102132
Parlog A, Schlüter D, Dunay IR, 2015. Toxoplasma gondii-induced neuronal alterations. Parasite Immunol, 37(3): 159–170. https://doi.org/10.1111/pim.12157
Quan JH, Cha GH, Zhou W, et al., 2013. Involvement of PI 3 kinase/Akt-dependent Bad phosphorylation in Toxoplasma gondii-mediated inhibition of host cell apoptosis. Exp Parasitol, 133(4):462–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2013.01.005
Rajedadram A, Pin KY, Ling SK, et al., 2021. Hydroxychavicol, a polyphenol from Piper betle leaf extract, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in TP53-resistant HT-29 colon cancer cells. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 22(2):112–122. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000446
Ranjan A, Iwakuma T, 2016. Non-canonical cell death induced by p53. Int J Mol Sci, 17(12):2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122068
Rosowski EE, Saeij JPJ, 2012. Toxoplasma gondii clonal strains all inhibit STAT1 transcriptional activity but polymorphic effectors differentially modulate IFNγ induced gene expression and STAT1 phosphorylation. PLoS ONE, 7(12):e51448. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0051448
Rosowski EE, Lu D, Julien L, et al., 2011. Strain-specific activation of the NF-κB pathway by GRA15, a novel Toxoplasma gondii dense granule protein. J Exp Med, 208(1): 195–212. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20100717
Sajjad N, Mir MM, Khan J, et al., 2019. Recognition of TRAIP with TRAFs: current understanding and associated diseases. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 115:105589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2019.105589
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, et al., 2015. STRING v10: Protein—protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res, 43(D1):D447–D452. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1003
Tantral L, Malathi K, Kohyama S, et al., 2004. Intracellular calcium release is required for caspase-3 and -9 activation. Cell Biochem Funct, 22(1):35–40. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.1050
Venugopal K, Marion S, 2018. Secretory organelle trafficking in Toxoplasma gondii: a long story for a short travel. Int J Med Microbiol, 308(7):751–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2018.07.007
Wan LJ, Gong LL, Wang W, et al., 2015. T. Gondii rhoptry protein ROP18 induces apoptosis of neural cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Parasit Vectors, 8:554. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-015-1103-z
Wang T, Zhou J, Gan XF, et al., 2014. Toxoplasma gondii induce apoptosis of neural stem cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Parasitology, 141(7):988–995. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182014000183
Wei W, Zhang FF, Chen H, et al., 2018. Toxoplasma gondii dense granule protein 15 induces apoptosis in choriocarcinoma JEG-3 cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress. Parasit Vectors, 11(1):251. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-2835-3
Yang ZS, Hou YH, Hao TF, et al., 2017. A human proteome array approach to identifying key host proteins targeted by Toxoplasma kinase ROP18. Mol Cell Proteomics, 16(3): 469–484. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M116.063602
Yuan X, Gajan A, Chu Q, et al., 2018. Developing TRAIL/TRAIL death receptor-based cancer therapies. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 37(4):733–748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-018-9728-y
Zhou CX, Elsheikha HM, Zhou DH, et al., 2016. Dual identification and analysis of differentially expressed transcripts of porcine PK-15 cells and Toxoplasma gondii during in vitro infection. Front Microbiol, 7:721. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00721
Zhou LJ, Chen M, Puthiyakunnon S, et al., 2019. Toxoplasma gondii ROP18 inhibits human glioblastoma cell apoptosis through a mitochondrial pathway by targeting host cell P2X1. Parasit Vectors, 12:284. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-019-3529-1
Zhuo XH, Sun HC, Huang B, et al., 2017. Evaluation of potential anti-toxoplasmosis efficiency of combined traditional herbs in a mouse model. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 18(6):453–461. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600316
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81802037 and 81871684), the Qingshan Lake United Fund of Zhejiang Province (No. LQY19H190002), the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. LY22H190003), the Zhejiang Provincial Program for the Cultivation of High-level Innovative Health Talents, and the Basic Scientific Research Funds of Department of Education of Zhejiang Province (Nos. KYZD202104 and KYYB202101), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Data availability statement
The datasets supporting the results of this article are available in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Sequence Read Archive (SRA) repository with the accession number PRJNA791458.
Author contributions
Kaige DU, Fei LU, and Xunhui ZHUO performed the experimental research and data analysis. Chengzuo XIE, Haojie DING, Yu SHEN, and Yafan GAO analyzed the data. Kaige DU and Xunhui ZHUO wrote and edited the manuscript. Shaohong LU contributed to the study design and editing of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript, and therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Compliance with ethics guidelines
Kaige DU, Fei LU, Chengzuo XIE, Haojie DING, Yu SHEN, Yafan GAO, Shaohong LU, and Xunhui ZHUO declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, K., Lu, F., Xie, C. et al. Toxoplasma gondii infection induces cell apoptosis via multiple pathways revealed by transcriptome analysis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 23, 315–327 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2100877
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2100877