Abstract
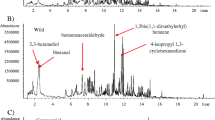
To explore the volatile profiles and the contents of ten bioactive components (polyphenols and caffeine) of sun-dried Pu-erh tea leaves from ancient tea plants on Bulang Mountain, 17 samples of three tea varieties were analyzed by headspace-solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). A total of 75 volatile components were tentatively identified. Laomaner (LME), Laobanzhang (LBZ), and other teas on Bulang Mountain (BL) contained 70, 53, and 71 volatile compounds, respectively. Among the volatile compounds, alcohols (30.2%–45.8%), hydrocarbons (13.7%–17.5%), and ketones (12.4%–23.4%) were qualitatively the most dominant volatile compounds in the different tea varieties. The average content of polyphenol was highest in LME (102.1 mg/g), followed by BL (98.7 mg/g) and LBZ (88.0 mg/g), while caffeine showed the opposite trend, 27.3 mg/g in LME, 33.5 mg/g in BL, and 38.1 mg/g in LBZ. Principal component analysis applied to both the volatile compounds and ten bioactive components showed a poor separation of samples according to varieties, while partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) showed satisfactory discrimination. Thirty-four volatile components and five bioactive compounds were selected as major discriminators (variable importance in projection (VIP) >1) among the tea varieties. These results suggest that chromatographic data combined with multivariate analysis could provide a useful technique to characterize and distinguish the sun-dried Pu-erh tea leaves from ancient tea varieties on Bulang Mountain.
中文概要
目的: 为布朗山不同品种古树普洱晒青茶香气物质和活性成分(多酚类和咖啡碱)深入研究提供理论依据。
创新点: 首次采用气质联用技术(GC-MS)和高效液相色谱(HPLC)结合化学计量学对布朗山不同品种的古树普洱晒青茶进行研究,探究不同品种古树晒青茶成分之间的差异性。
方法: 采用顶空固相微萃取法(HS-SPME)结合GC-MS对香气成分进行鉴定;采用70%甲醇溶液对活性成分进行富集,使用HPLC 进行分析;结合主成分分析(PCA)和偏最小二乘判别分析(PLS-DA)对不同品种的古树普洱晒青茶进行区分并对区分起主要作用的物质进行筛选。
结论: 三个品种的古树普洱晒青茶(老曼峨、老班章和布朗)香气成分组成及含量差异较大,但主要成分均为醇类、碳氢类和酮类化合物。老曼峨中多酚类化合物含量较高,其次为布朗和老班章,相比于多酚类,咖啡碱含量表现出了相反的趋势。相比于PCA 分析,PLS-DA 分析对三个品种的古树普洱晒青茶均显示出了较好的区分效果。变量投影重要性准则(VIP)分析结果显示34 种香气和5 种生物活性成分对不同品种的古树普洱晒青茶区分贡献较大。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alasalvar C, Topal B, Serpen A, et al., 2012. Flavor characteristics of seven grades of black tea produced in Turkey. J Agric Food Chem, 60(25):6323–6332. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf301498p
Burdock GA, 2010. Fenaroli’s Handbook of Flavor Ingredients, 6th Ed. CRC Press, Florida, USA.
Byju K, Anuradha V, Rosmine E, et al., 2013. Chemical characterization of the lipophilic extract of Hydrilla verticillata: a widely spread aquatic weed. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol, 22(3):304–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-012-0159-5
Cai L, Liang MZ, Xia LF, et al., 2014. Analysis of fingerprint for local old-plant tea variety “Laobanzhang” by HPLC. Hunan Agric Sci, (8):10–11, 14 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-060X.2014.08.003
Du LP, Li JX, Li W, et al., 2014. Characterization of volatile compounds of Pu-erh tea using solid-phase microextraction and simultaneous distillation-extraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Res Int, 57: 61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.01.008
Du LP, Ma LJ, Qiao Y, et al., 2016. Determination of phthalate esters in teas and tea infusions by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Chem, 197:1200–1206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.11.082
Fan DM, Fan K, Yu CP, et al., 2017. Tea polyphenols dominate the short-term tea (Camellia sinensis) leaf litter decomposition. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 18(2):99–108. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600044
Gulati A, Ravindranath SD, 1996. Seasonal variations in quality of Kangra tea (Camellia sinensis (L) O Kuntze) in Himachal Pradesh. J Sci Food Agric, 71(2):231–236. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0010(199606)71:2<231::AID-JSFA573>3.0.CO;2-Y
He CJ, Guo XM, Yang YM, et al., 2016. Characterization of the aromatic profile in “Zijuan” and “Pu-erh” green teas by headspace solid-phase microextraction coupled with GC-O and GC-MS. Anal Methods, 8(23):4727–4735. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6AY00700G
Kawakami M, Kobayashi A, Kator K, 1993. Volatile constituents of Rooibos tea (Aspalathus linearis) as affected by extraction process. J Agric Food Chem, 41(4):633–636. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00028a023
Kawakami M, Ganguly SN, Banerjee J, et al., 1995. Aroma composition of oolong tea and black tea by brewed extraction method and characterizing compounds of Darjeeling tea aroma. J Agric Food Chem, 43(1):200–207. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00049a037
Kumazawa K, Masuda H, 2002. Identification of potent odorants in different green tea varieties using flavor dilution technique. J Agric Food Chem, 50(20):5660–5663. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf020498j
Lin J, Dai Y, Guo YN, et al., 2012. Volatile profile analysis and quality prediction of Longjing tea (Camellia sinensis) by HS-SPME/GC-MS. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 13(12):972–980. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1200086
Lin J, Zhang P, Pan ZQ, et al., 2013. Discrimination of oolong tea (Camellia sinensis) varieties based on feature extraction and selection from aromatic profiles analysed by HS-SPME/GC-MS. Food Chem, 141(1):259–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.02.128
Lv HP, Zhong QS, Lin Z, et al., 2012. Aroma characterisation of Pu-erh tea using headspace-solid phase microextraction combined with GC/MS and GC-olfactometry. Food Chem, 130(4):1074–1081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.07.135
Lv SD, Wu YS, Li CW, et al., 2014. Comparative analysis of Pu-erh and Fuzhuan teas by fully automatic headspace solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and chemometric methods. J Agric Food Chem, 62(8):1810–1818. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf405237u
Lv SD, Wu YS, Song YZ, et al., 2015. Multivariate analysis based on GC-MS fingerprint and volatile composition for the quality evaluation of Pu-erh green tea. Food Anal Methods, 8(2):321–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-014-9900-0
Pripdeevech P, Machan T, 2011. Fingerprint of volatile flavour constituents and antioxidant activities of teas from Thailand. Food Chem, 125(2):797–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.09.074
Schuh C, Schieberle P, 2006. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in the beverage prepared from Darjeeling black tea: quantitative differences between tea leaves and infusion. J Agric Food Chem, 54(3):916–924. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf052495n
Shi J, Wang L, Ma CY, et al., 2014. Aroma changes of black tea prepared from methyl jasmonate treated tea plants. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 15(4):313–321. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1300238
Stevens KL, Merrill GB, 1981. Dihydroactinidiolide—a potent growth inhibitor from Eleocharis coloradoensis (Spikerush). Experientia, 37(11):1133. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01989879
Tao H, Li ZR, Li F, 2013. Development plan and countermeasures of tea industry of Bulang Mountain. Agric Technol, (7):231 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-962X.2013.07.193
Wang C, Zhang CX, Shao CF, et al., 2016a. Chemical fingerprint analysis for the quality evaluation of Deepure instant Pu-erh tea by HPLC combined with chemometrics. Food Anal Methods, 9(12):3298–3309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0524-4
Wang C, Lv SD, Wu YS, et al., 2016b. Study of aroma formation and transformation during the manufacturing process of Biluochun green tea in Yunnan Province by HS-SPME and GC-MS. J Sci Food Agric, 96(13):4492–4498. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7663
Wang C, Zhang CX, Kong YW, et al., 2017. A comparative study of volatile components in Dianhong teas from fresh leaves of four tea cultivars by using chromatography-mass spectrometry, multivariate data analysis, and descriptive sensory analysis. Food Res Int, 100:267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2017.07.013
Wang LF, Lee JY, Chung JO, et al., 2008. Discrimination of teas with different degrees of fermentation by SPME-GC analysis of the characteristic volatile flavour compounds. Food Chem, 109(1):196–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.12.054
Wu YS, Lv SD, Wang C, et al., 2016. Comparative analysis of volatiles difference of Yunnan sun-dried Pu-erh green tea from different tea mountains: Jingmai and Wuliang mountain by chemical fingerprint similarity combined with principal component analysis and cluster analysis. Chem Cent J, 10:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-016-0159-y
Xia LF, Liang MZ, Wang L, et al., 2012. Studying on the quality of Menghai’s sunny dried tea. Chin Agric Sci Bull, 28(16):239–244 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2012.16.043
Xu YQ, Wang C, Li CW, et al., 2015. Characterization of aroma-active compounds of Pu-erh tea by headspace solid-phase microextraction (HS-SPME) and simultaneous distillation-extraction (SDE) coupled with GC-olfactometry and GC-MS. Food Anal Methods, 9(5):1188–1198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161
Yao SS, Guo WF, Lu Y, et al., 2005. Flavor characteristics of lapsang souchong and smoked lapsang souchong, a special Chinese black tea with pine smoking process. J Agric Food Chem, 53(22):8688–8693. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf058059i
Zhu M, Li E, He H, 2008. Determination of volatile chemical constitutes in tea by simultaneous distillation extraction, vacuum hydrodistillation and thermal desorption. Chromatographia, 68(7-8):603–610. https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-008-0732-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Electronic Supplementary Material
Electronic supplementary materials: The online version of this article (https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1800183) contains supplementary materials, which are available to authorized users
Electronic supplementary material
11585_2019_11_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Comparison of volatile profiles and bioactive components of sun-dried Pu-erh tea leaves from ancient tea plants on Bulang Mountain measured by GC-MS and HPLC
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Wj., Liu, C., Yang, Rj. et al. Comparison of volatile profiles and bioactive components of sun-dried Pu-erh tea leaves from ancient tea plants on Bulang Mountain measured by GC-MS and HPLC. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 20, 563–575 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1800183
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1800183