Abstract
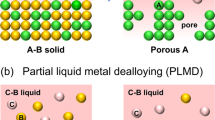
A specialized dealloying technique called thermal dealloying was developed over 10 years ago for certain biomedical materials. This method is not widely used for synthesizing nanoporous metals. However, it offers advantages over conventional dealloying processes for fabrication of nanoporous structures, and is highly suitable for refractory metals that may be susceptible to oxidation during chemical/electrochemical dealloying and liquid metal dealloying. In this study, nanoporous structures were successfully fabricated from magnesium-based precursor alloys via sublimation of magnesium at elevated temperature under vacuum conditions. Different refractory metal diffusion rates affect the resulting density and amount of retained magnesium in each nanoporous material.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Wang, Z. Wang, D. Zhao, and C. Xu: Facile fabrication of nanoporous PdFe alloy for nonenzymatic electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Anal. Chim. Acta 832, 34–43 (2014).
J. Weissmüller and K. Sieradzki: Dealloyed nanoporous materials with interface-controlled behavior. MRS Bull. 43, 14–19 (2018).
M.J. Detisch, T.J. Balk, and D. Bh attacharyya: Synthesis of catalytic nanoporous metallic thin films on polymer membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 57, 4420–1429 (2018).
W. Lucand F. Jiao: Nanoporous metals as electrocatalysts: state-of-the-art, opportunities, and challenges. ACS Catal. 7, 5856–5861 (2017).
X. Zhang and Y. Ding: Unsupported nanoporous gold for heterogeneous catalysis. Catal. Sci. Techno! 3, 2862–2868 (2013).
E. Seker, Y. Berdichevsky, K.J. Staley, and M.L. Yarmush: Microfabrication-compatible nanoporous gold foams as biomaterials for drug delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 1, 172–176 (2012).
C. Xu, Y. Liu, F. Su, A. Liu, and H. Qiu: Nanoporous PtAg and PtCu alloys with hollow ligaments for enhanced electrocatalysis and glucose biosens-ing. Biosens. Bloelectron. 27, 160–166 (2011).
J.B. Cook, E. Detsi, Y. Liu, Y.-L. Liang, H.-S. Kim, X. Petrissans, B. Dunn, and S.H. Tolbert: Nanoporous tin with a granular hierarchical ligament morphology as a highly stable Li-ion battery anode. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 293–303 (2017).
I. McCue, E. Benn, B. Gaskey, and J. Erlebacher: Dealloying and dealloyed materials.. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 46, 263–286 (2016).
J. Erlebacher: An atomistic description of dealloying porosity evolution, the critical potential, and rate-limiting behavior. J. Electrochem. Soc. 151, 10 (2004).
K. Sieradzki, N. Dimitrov, D. Movrin, C. McCall, N. Vasiljevic, and J. Erlebacher: The dealloying critical potential. J. Electrochem. Soc. 149, B370–B377 (2002).
J. Erlebacher, M.J. Aziz, A. Karma, N. Dimitrov, and K. Sieradzki: Evolution of nanoporosity in dealloying. Nature 410, 450–453 (2001).
T. Wada, K. Yubuta, A. Inoue, and H. Kato: Dealloying by metallic melt. Mater. Lett. 65, 1076–1078 (2011).
T. Wada, A.D. Setyawan, K. Yubuta, and H. Kato: Nano- to submicro-porous β-Ti alloy prepared from dealloying in a metallic melt. Scripta Mater. 65, 532–535 (2011).
I. McCue, B. Gaskey, P.-A. Geslin, A. Karma, and J. Erlebacher: Kinetics and morphological evolution of liquid metal dealloying. Acta Mater. 115, 10–23 (2016).
I. McCue, A. Karma, and J. Erlebacher: Pattern formation during electrochemical and liquid metal dealloying. MRS Bull. 43, 27–34 (2018).
Q. Zhang, X. Wang, Z. Qi, Y. Wang, and Z. Zhang: A benign route to fabricate nanoporous gold through electrochemical dealloying of Al-Au alloys in a neutral solution. Electrochim. Acta 54, 6190–6198 (2009).
J. Erlebacher: Mechanism of coarsening and bubble formation in high-genus nanoporous metals. Phys. Rev. Lett., 106, 225504 1–4, (2011).
Z. Lu, C. Li, J. Han, F. Zhang, P. Liu, H. Wang, Z. Wang, C. Cheng, L. Chen, A. Hirata, T. Fujita, J. Erlebacher, and M. Chen: Three-dimensional bicontinuous nanoporous materials by vapor phase dealloying. Nat. Commun. 9, 276 (2018).
J. Spradlin, W.-K. Lye, M. Reed, and M.S. Hudson: Nanoporous layers using thermal dealloying. Patent: US 2006/0193889 A1, (2006).
Z. Esen and S. Bor: Processing of titanium foams using magnesium spacer particles. Scr. Mater. 56, 341–344 (2007).
G. Adamek: Tantalum foams prepared by the thermal dealloying process. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater 65, 88–93 (2017).
C. Zhao, Z. Qi, X. Wang, and Z. Zhang: Fabrication and characterization of monolithic nanoporous copper through chemical dealloying of Mg-Cu alloys. Corros. Sci. 51, 2120–2125 (2009).
L. Wang, N. Briot, P. Swartzentruber, and T.J. Balk: Magnesium alloy precursor thin films for efficient, practical fabrication of nanoporous metals. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 1–5 (2014).
J.N.J. Ong: Oxidation of refractory metals as afunction of pressure, temperature, and time: tungsten in oxygen. J. Electrochem. Soc. 109, 284–288 (1962).
W.P. Gilbreath: The vapor pressure of Mg (223 °C-385 °C). National Aeronautics and Space Administration - NASA Technical Note (1965).
Y. Sun and T.J. Balk: Evolution of structure, composition, and stress in nanoporous gold thin films with grain-boundary cracks. Metall Mater Trans A 39, 2656–2665 (2008).
G.-R. Xu, Y. Wen, X.-P. Min, W.-H. Dong, A.-P. Tang, and H.-S. Song: Construction of Mn02/3-dimensional porous crack Ni for high-performance supercapacitors. Electrochlm. Acta 186, 133–141 (2015).
E. Seker, M. Reed, and M. Begley: A thermal treatment approach to reduce microscale void formation in blanket nanoporous gold films. Scr. Mater. 60, 435–438 (2009).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge support from the Electron Microscopy Center at the University of Kentucky, with special thanks to Nicolas J. Briot for help with FIB preparation of cross sections and EDS analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kosmidou, M., Detisch, M.J., Maxwell, T.L. et al. Vacuum thermal dealloying of magnesium-based alloys for fabrication of nanoporous refractory metals. MRS Communications 9, 144–149 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2019.15
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2019.15