Abstract
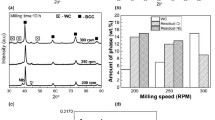
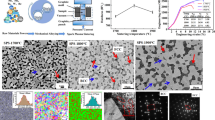
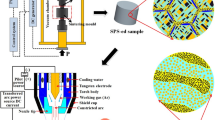
Two different processing routes of mechanical alloying followed by the spark plasma sintering (powder metallurgy) and vacuum arc melting (casting route) were employed to understand the role of processing routes on the phase and microstructural evolution in an equiatomic CrMoNbTiW refractory high-entropy alloy. Besides a major BCC solid solution, a small fraction of carbide, σ phase, nitride, and oxide phases were observed in the alloys prepared by the powder metallurgy route in contrast to a single-phase BCC solid solution in the casting route. The milling atmosphere (dry milling in air and Ar) has significantly influenced the phase and microstructural evolution, illustrating the substantial role of contaminants. Good thermal stability of microstructure at high homologous temperatures was shown based on the long-term heat treatment at 1300 °C for 240 h. The phase evolution predictions via Calphad studies were found to be in reasonable agreement with the experimental observations, albeit with some limitations.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
O.N. Senkov, G.B. Wilks, D.B. Miracle, C.P. Chuang, and P.K. Liaw: Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics18, 1758 (2010).
O.N. Senkov, D.B. Miracle, K.J. Chaput, and J.P. Couzinie: Development and exploration of refractory high entropy alloys—A review. J. Mater. Res.33, 3092 (2018).
S. Praveen and H.S. Kim: High-entropy alloys: Potential candidates for high-temperature applications – An overview. Adv. Eng. Mater.20, 1 (2018).
C. Suryanarayana: Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci.46, 1 (2001).
M. Vaidya, G.M. Muralikrishna, and B.S. Murty: High entropy alloys by mechanical alloying: A review. J. Mater. Res.34, 664 (2019).
M.C. Gao, P.K. Liaw, J.W. Yeh, and Y. Zhang:High-Entropy Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications (Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2016).
S. Uporov, V. Bykov, S. Pryanichnikov, A. Shubin, and N. Uporova: Effect of synthesis route on structure and properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. Intermetallics83, 1 (2017).
S. Syed Ghazi and K.R. Ravi: Phase-evolution in high entropy alloys: Role of synthesis route. Intermetallics73, 40 (2016).
C. Suryanarayana and F.H. Froes: Mechanical alloying of titanium-base alloys. Adv. Mater.5, 96 (1993).
R. John, A. Karati, M.M. Garlapati, M. Vaidya, R. Bhattacharya, D. Fabijanic, and B.S. Murty: Influence of mechanically activated annealing on phase evolution in Al0.3CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. J. Mater. Sci.54, 14588 (2019).
Y. Xie, H. Cheng, Q. Tang, W. Chen, W. Chen, and P. Dai: Effects of N addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy produced by mechanical alloying and vacuum hot pressing sintering. Intermetallics93, 228 (2018).
B. Kang, J. Lee, H.J. Ryu, and S.H. Hong: Ultra high strength WNbMoTaV high-entropy alloys with fine grain structure fabricated by powder metallurgical process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A712, 616 (2018).
J. Pan, T. Dai, T. Lu, X. Ni, J. Dai, and M. Li: Microstructure and mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and Ti8Nb23Mo23Ta23W23 high entropy alloys prepared by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A738, 362 (2018).
S.W. Xin, M. Zhang, T.T. Yang, Y.Y. Zhao, B.R. Sun, and T.D. Shen: Ultra hard bulk nanocrystalline VNbMoTaW high-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd.769, 597 (2018).
G. Wang, Q. Liu, J. Yang, X. Li, X. Sui, Y. Gu, and Y. Liu: Synthesis and thermal stability of a nanocrystalline MoNbTaTiV refractory high-entropy alloy via mechanical alloying. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater.84, 104988 (2019).
J.A. Smeltzer, C.J. Marvel, B.C. Hornbuckle, A.J. Roberts, J.M. Marsico, A.K. Giri, K.A. Darling, J.M. Rickman, H.M. Chan, and M.P. Harmer: Achieving ultra hard refractory multi-principal element alloys via mechanical alloying. Mater. Sci. Eng. A763, 138140 (2019).
V. Soni, B. Gwalani, O.N. Senkov, B. Viswanathan, T. Alam, D.B. Miracle, and R. Banerjee: Phase stability as a function of temperature in a refractory high-entropy alloy. J. Mater. Res.33, 3235 (2018).
L. Raman, K. Guruvidyathri, G. Kumari, S.V.S. Narayana Murty, R.S. Kottada, and B.S. Murty: Phase evolution of refractory high-entropy alloy CrMoNbTiW during mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. J. Mater. Res.34, 756 (2019).
S. Lv, Y. Zu, G. Chen, X. Fu, and W. Zhou: An ultra-high strength CrMoNbWTi-C high entropy alloy co-strengthened by dispersed refractory IM and UHTC phases. J. Alloys Compd.788, 1256 (2019).
S. Praveen, A. Anupam, R. Tilak, and R.S. Kottada: Phase evolution and thermal stability of AlCoCrFe high entropy alloy with carbon as unsolicited addition from milling media. Mater. Chem. Rhys.210, 57 (2018).
P. Sathiyamoorthi, J. Basu, S. Kashyap, K.G. Pradeep, and R.S. Kottada: Thermal stability and grain boundary strengthening in ultrafine-grained CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy composite. Mater. Des.134, 426 (2017).
S. Praveen, J. Basu, S. Kashyap, and R. S. Kottada: Exceptional resistance to grain growth in nanocrystalline CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy at high homologous temperatures. J. Alloys Compd.662, 361 (2016).
H. Conrad: Effect of interstitial solutes on the strength and ductility of titanium. Prog. Mater. Sci.26, 123 (1981).
W. Sun, X. Huang, and A.A. Luo: Phase formations in low density high entropy alloys. Calphad Comput. Coupling Phase Diagrams Thermochem.56, 19 (2017).
R. Raghavan, K.C. Hari Kumar, and B.S. Murty: Analysis of phase formation in multi-component alloys. J. Alloys Compd.544, 152 (2012).
A. Jacob, C. Schmetterer, D. Grüner, E. Wessel, B. Hallstedt, and L. Singheiser: The Cr-Fe-Nb ternary system: Experimental isothermal sections at 700 °C, 1050 °C and 1350 °C. J. Alloys Compd.648, 168 (2015).
J.H. Zhu, P.K. Liaw, and C.T. Liu: Effect of electron concentration on the phase stability of NbCr2-based Laves phase alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A240, 260 (1997).
J.H. Zhu, C.T. Liu, and P.K. Liaw: Phase stability and mechanical behavior of NbCr2-based Laves phases. Intermetallics7, 1011 (1999).
C. Vahlas, B. Drouin Ladouce, P.-Y. Chevalier, C. Bernard, and L. Vandenbulcke: A thermodynamic evaluation of the Ti-N system. Thermochim. Acta180, 23 (1991).
W. Hume-Rothery: Atomic diameters, atomic volumes, and solid solubility relations in alloys. Acta Metall.14, 17 (1966).
Y. Zhang, Y.J. Zhou, J.P. Lin, G.L. Chen, and P.K. Liaw: Solid-solution phase formation rules for multi-component alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater.10, 534 (2008).
N. Yurchenko, N. Stepanov, and G. Salishchev: Laves phase formation criterion for high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol.33, 17 (2016).
M.G. Poletti and L. Battezzati: Electronic and thermodynamic criteria for the occurrence of high entropy alloys in metallic systems. Acta Mater.75, 297 (2014).
M. Tsai, K. Chang, J. Li, and R. Tsai: A second criterion for sigma phase formation in high-entropy alloys. Mater. Res. Lett.4, 90 (2016).
S. Guo, C. Ng, J. Lu, and C.T. Liu: Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys. J. Appl. Phys.109, 103505 (2011).
Y. Long, X. Liang, K. Su, H. Peng, and X. Li: A fine grained NbMoTaWVCr refractory high-entropy alloy with ultra-high strength: Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd.780, 607 (2019).
S. Praveen, A. Anupam, T. Sirasani, B.S. Murty, and R.S. Kottada: Characterization of oxide dispersed AlCoCrFe high entropy alloy synthesized by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Trans Indian Inst Met.66, 369 (2013).
B. Liu, J. Wang, J. Chen, Q. Fang, and Y. Liu: Ultra high strength TiC/Refractory high-entropy-alloy composite prepared by powder metallurgy. JOM69, 651 (2017).
J. Yan, K. Li, and Y.I. Wang: Microstructure and mechanical properties of WMoNbCrTi HEAs sintered from the powders milled for different durations. JOM71, 2489 (2019).
D.E. Huber:Structure and properties of titanium tantalum alloys for biocompatibility. Ph.D. thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, 2016.
L. Zhang, H. Zhang, X. Ren, J. Eckert, Y. Wang, Z. Zhu, T. Gemming, and S. Pauly: Amorphous martensite in β-Ti alloys. Nat. Commun.9, 506 (2018).
Z.J. Yuelan Zhang and H. Liu: Thermodynamic assessment of the Nb-Ti System. Calphad25, 305 (2001).
Z.C. Cordero and C.A. Schuh: Phase strength effects on chemical mixing in extensively deformed alloys. Acta Mater.82, 123 (2015).
W. Guo, S. Martelli, F. Padella, M. Magini, N. Burgio, E. Paradiso, and U. Franzoni: F.C.C. metastable phase induced in the Ti-Al system by mechanical alloying of pure elemental powders. Mater. Sci. Forum88–90, 139 (1992).
D.R. Gaskell:Introduction to the Thermodynamics of Solids, Fourth (Taylor & Francis, Great Britain, 2009).
K. Guruvidyathri, K.C.H. Kumar, and J.W. Yeh: Topologically close-packed phase formation in high entropy alloys: A review of Calphad and experimental results. JOM69, 2113 (2017).
S. Cao and J.C. Zhao: Determination of the Fe-Cr-Mo phase diagram at intermediate temperatures using dual-anneal diffusion multiples. J. Phase Equilib. Diff.37, 25 (2016).
S.G. Seo, C.H. Park, H.Y Kim, W.H. Nam, M. Jeong, Y.N. Choi, Y.S. Lim, W.S. Seo, S.J. Kim, J.Y. Lee, and Y.S. Cho: Preparation and visible-light photocatalysis of hollow rock-salt TiO1−xNxnanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A1, 3639 (2013).
H.O. Pierson: Handbook of refractory carbides and nitrides: Properties, characteristics, processing, and applications. Handb. Refract. Carbides Nitrides362, 287 (1996).
A.D. LeClaire:Diffusion in Solid Metals and Alloys (Springer-Verlag, Berlin/Heidelberg, 1990); pp. 471û472.
M. Cancarevic, M. Zinkevich, and F. Aldinger: Thermodynamic description of the Ti-O system using the associate model for the liquid phase. Calphad Comput. Coupling Phase Diagrams Thermochem.31, 330 (2007).
E.J. Pickering, R. Munoz-Moreno, H.J. Stone, and N.G. Jones: Precipitation in the equiatomic high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi. Scr. Mater.113, 106 (2016).
F. Otto, A. Dlouhy, K.G. Pradeep, M. Kubenova, D. Raabe, G. Eggeler, and E.P. George: Decomposition of the single-phase high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi after prolonged anneals at intermediate temperatures. Acta Mater.112, 40 (2016).
A. Atkinson: Grain-boundary diffusion: An historical perspective. J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans.86, 1307 (1990).
H. Mehrer:Diffusion in Solid Metals and Alloys (Springer-Verlag, Berlin/Heidelberg, 1990).
J.A. Bahena, J. Sebastian Riano, M.R. Chellali, T. Boll, and A.M. Hodge: Thermally activated microstructural evolution of sputtered nanostructured Mo-Au. Materialia4, 157 (2018).
Y. Wang and J. Aktaa: Microstructural evolution, textural evolution and thermal stabilities of W and W–1 wt% La2O3 subjected to high-pressure torsion. Materialia2, 46 (2018).
C.C. Koch, R.O. Scattergood, M. Saber, and H. Kotan: High temperature stabilization of nanocrystalline grain size: Thermodynamic versus kinetic strategies. J. Mater. Res.28(13), 1785 (2013).
N. Saunders and A.P. Miodownik:CALPHAD (Calculation of Phase Diagrams): A Comprehensive Guide (Elsevier Science Inc, New York, USA, 1998).
B. Sundman, B. Jansson, and J.O. Andersson: The Thermo Calc databank system. Calphad9, 153 (1985).
K. Guruvidyathri, B.S. Murty, J.W. Yeh, and K.C. Hari Kumar: Gibbs energy-composition plots as a tool for high-entropy alloy design. J. Alloys Compd.768, 358 (2018).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the NFAPT facility and SAIF-IITM for helping with the EBSD and CHNO analysis, respectively. The authors also thank Dr. Mohammad Khalid Imran (Research Engineer – Additive Manufacturing at the Institute for Frontier Materials, Deakin University) for his assistance in obtaining the cast alloy. Ms. Raman is grateful to Dr. Ajeet Kumar Srivastav, Dr. N.T.B.N. Koundinya, Dr. Niraj Chawake, and Dr. Soumya Sridar for their invaluable suggestions and discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raman, L., Karthick, G., Guruvidyathri, K. et al. Influence of processing route on the alloying behavior, microstructural evolution and thermal stability of CrMoNbTiW refractory high-entropy alloy. Journal of Materials Research 35, 1556–1571 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2020.128
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2020.128