Abstract
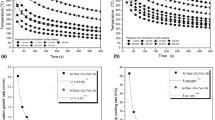
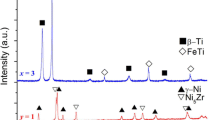
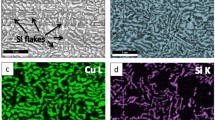
The effect of cooling rate on the microstructure evolution and the mechanical properties of ingots and rods of 2–5 mm diameter of (Ni0.92Zr0.08)100−xAlx (0 ≤ x ≤ 4 at.%) ultrafine eutectic composites have been investigated. The microstructure of the composites is comprised of micrometer size γ-Ni dendrites embedded in a nano/-ultrafine lamellar fcc γ-Ni and Ni5Zr matrix. The evolution of the microstructure at a wide range of cooling rates (10–104 K/s) has been analyzed in respect of volume fraction of the phases, lamellar spacing, and secondary dendritic arm spacing. All these composites exhibit high hardness up to 4.6 GPa and yield strength up to 1.6 GPa with large compressive plasticity up to 22% at room temperature. The effect of cooling rates on the strength and hardness, and the plasticity of the nanolamellar composites with wide range of alloy composition have been correlated.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Elliott: Eutectic solidification. Mater. Sci. Eng. 65, 85 (1984).
J.M. Park, K.B. Kim, W.T. Kim, M.H. Lee, J. Eckert, and D.H. Kim: High strength ultrafine eutectic Fe–Nb–Al composites with enhanced plasticity. Intermetallics 16, 642 (2008).
J.M. Park, T.E. Kim, S.W. Sohn, D.H. Kim, K.B. Kim, W.T. Kim, and J. Eckert: High strength Ni–Zr binary ultrafine eutectic-dendrite composite with large plastic deformability. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 031913 (2008).
J. Das, R. Theissmann, W. Löser, and J. Eckert: Effect of Sn on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti–Fe–(Sn) ultrafine eutectic composites. J. Mater. Res. 25, 943 (2010).
L.C. Zhang, J. Das, H.B. Lu, C. Duhamel, M. Calin, and J. Eckert: High strength Ti–Fe–Sn ultrafine composites with large plasticity. Scr. Mater. 57, 101 (2007).
T. Maity, B. Roy, and J. Das: Mechanism of lamellae deformation and phase rearrangement in ultrafine β-Ti/FeTi eutectic composites. Acta Mater. 97, 170 (2015).
D. Barbier, M.X. Huang, and O. Bouaziz: A novel eutectic Fe–15 wt% Ti alloy with an ultrafine lamellar structure for high temperature applications. Intermetallics 35, 41 (2013).
G. He, J. Eckert, W. Löser, and L. Schultz: Novel Ti-base nanostructure-dendrite composite with enhanced plasticity. Nat. Mater. 2, 33 (2003).
D.V. Louzguine, H. Kato, L.V. Louzguina, and A. Inoue: High-strength binary Ti–Fe bulk alloys with enhanced ductility. J. Mater. Res. 19, 3600 (2004).
J. Eckert, J. Das, S. Pauly, and C. Duhamel: Mechanical properties of bulk metallic glasses and composites. J. Mater. Res. 22, 285 (2007).
B.A. Pint, J.R. DiStefano, and I.G. Wright: Oxidation resistance: One barrier to moving beyond Ni-base superalloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 415, 255 (2006).
T. Maity and J. Das: High strength Ni–Zr–(Al) nanoeutectic composites with large plasticity. Intermetallics 63, 51 (2015).
T. Maity, A. Singh, A. Dutta, and J. Das: Microscopic mechanism on the evolution of plasticity in nanolamellar γ-Ni/Ni5Zr eutectic composites. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 666, 72 (2016).
J.T. Kim, S.H. Hong, H.J. Park, Y.S. Kim, G.H. Park, J-Y. Park, N. Lee, Y. Seo, J.M. Park, and K.B. Kim: Improving the plasticity and strength of Fe–Nb–B ultrafine eutectic composite. Mater. Des. 76, 190 (2015).
J.T. Kim, S.W. Lee, S.H. Hong, H.J. Park, J-Y. Park, N. Lee, Y. Seo, W-M. Wang, J.M. Park, and K.B. Kim: Understanding the relationship between microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–Cu–Si ultrafine eutectic composites. Mater. Des. 92, 1038 (2016).
J.T. Kim, S.H. Hong, H.J. Park, Y.S. Kim, J.Y. Suh, J.K. Lee, J.M. Park, T. Maity, J. Eckert, and K.B. Kim: Deformation mechanisms to ameliorate the mechanical properties of novel TRIP/TWIP Co–Cr–Mo–(Cu) ultrafine eutectic alloys. Sci. Rep. 7, 39959 (2017).
S.W. Lee, J.T. Kim, S.H. Hong, H.J. Park, J-Y. Park, N.S. Lee, Y. Seo, J.Y. Suh, J. Eckert, D.H. Kim, J.M. Park, and K.B. Kim: Micro-to-nano-scale deformation mechanisms of a bimodal ultrafine eutectic composite. Sci. Rep. 4, 6500 (2014).
J. Das, A. Güth, H.J. Klauß, C. Mickel, W. Löser, J. Eckert, S.K. Roy, and L. Schultz: Effect of casting conditions on microstructure and mechanical properties of high-strength Zr73.5Nb9Cu7Ni1Al9.5 in situ composites. Scr. Mater. 49, 1189 (2003).
J. Das, S. Pauly, C. Duhamel, B.C. Wei, and J. Eckert: Microstructure and mechanical properties of slowly cooled Cu47.5Zr47.5Al5. J. Mater. Res. 22, 326 (2007).
J. Das, S.K. Roy, W. Löser, J. Eckert, and L. Schultz: Novel in situ nanostructure-dendrite composites in Zr-base multicomponent alloy system. Mater. Manuf. Processes 19, 423 (2004).
W. Löser, J. Das, A. Güth, H-J. Klauß, C. Mickel, U. Kühn, J. Eckert, S. Roy, and L. Schultz: Effect of casting conditions on dendrite-amorphous/nanocrystalline Zr–Nb–Cu–Ni–Al in situ composites. Intermetallics 12, 1153 (2004).
G.A. Chadwick: Yield poixt analyses in eutectic alloys. Acta Metall. 24, 1137 (1976).
G. Ghosh: Thermodynamics and kinetics of stable and metastable phases in the Ni–Zr system. J. Mater. Res. 9, 598 (1994).
S. Miura, H. Unno, T. Yamazaki, S. Takizawa, and T. Mohri: Reinvestigation of Ni-solid solution/liquid equilibria in Ni–Al binary and Ni–Al–Zr ternary systems. J. Phase Equilib. 22, 457 (2001).
Y.R. Luo: Comprehensive Handbook of Chemical Bond Energies, 1st ed. (CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Florida, 2007); pp. 903–906.
D. Bouchard and J.S. Kirkaldy: Prediction of dendrite arm spacings in unsteady- and steady-state heat flow of unidirectionally solidified binary alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 28, 651 (1997).
W.R. Osorio, P.R. Goulart, G.A. Santos, C.M. Neto, and A. Garcia: Effect of dendritic arm spacing on mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Al 9 wt% Si and Zn 27 wt% Al alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 37, 2525 (2006).
W. Kurz and D.J. Fisher: Fundamental of Solidification, 3rd ed. (Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland, 1989); pp. 108–111.
K.A. Jackson and J.D. Hunt: Lamellar and rod eutectic growth. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 236, 1129 (1966).
R.M. Srivastava, J. Eckert, W. Löser, B.K. Dhindaw, and L. Schultz: Cooling rate evaluation for bulk amorphous alloys from eutectic microstructures in casting processes. Mater. Trans. 43, 1670 (2002).
R. Caram and S. Milenkovic: Microstructure of Ni–Ni3Si eutectic alloy produced by directional solidification. J. Cryst. Growth 198–199, 844 (1999).
H. Kaya, U. Boyuk, E. Cadirli, and N. Marasli: Unidirectional solidification of aluminium–nickel eutectic alloy. Met. Mater. 48, 291 (2010).
D.R. Stull and G.C. Sinke: Thermodynamic properties of the elements. R.F. Gould (Ed.) In Advances in Chemistry (American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, 1956); pp. 37–225.
D.R. Gaskell: Introduction to the Thermodynamics of Materials, 4th ed. (Taylor & Francis Group, New York, 2003); pp. 705–706.
H.G. Lee: Materials Thermodynamics with Emphasis on Chemical Approach (World Scientific Publishing Co., Pte., Ltd., Singapore, Malaysia, 2012); p. 433.
D.A. Porter, K.E. Easterling, and M.Y. Sherif: Phase Transformation in Metals and Alloys, 3rd ed. (CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Florida, 2009); pp. 212–220.
S.H. Zhou, Y. Wang, L-Q. Chen, Z-K. Liu, and R.E. Napolitano: Solution-based thermodynamic modelling of the Ni–Al–Mo system using first-principles calculations. Calphad 46, 124 (2014).
J. Bratberg, H. Mao, L. Kjellqvist, A. Engström, P. Mason, and Q. Chen: The development and validation of a new thermodynamic database for Ni-based alloys. Superalloys 2012, 803 (2012).
W.D. Callister and D.G. Rethwisch, Jr.: Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction, 2nd ed. (Wiley India Pvt., Ltd., New Delhi, India, 2014).
A.M. Glezer, E.V. Kozlov, N.A. Koneva, N.A. Popova, and I.A. Kurzina: Plastic Deformation of Nanostructured Materials (CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, Florida, 2017); p. 83.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank M. Das, S. Maity, and R. Kundu at the CRF at IIT Kharagpur for technical assistance. The financial support provided by Naval Research Board (NRB/4003/PG/357), Government of India, and SRIC (SGIRG), IIT Kharagpur are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dutta, A., Jana, P.P. & Das, J. Effect of cooling rate and composition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of (Ni0.92Zr0.08)100−xAlx (0 ≤ x ≤ 4 at.%) ultrafine eutectic composites. Journal of Materials Research 34, 1704–1713 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.49
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.49