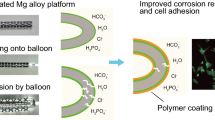
Abstract
Magnesium is a biodegradable material that has potential application in cardiovascular stent development: its excellent mechanical properties and blood compatibility make it highly useful in interventional therapy. Nevertheless, the following shortcomings restrict its further application: antihyperplasia function and promoting surface endothelialization. In this study, we immobilized a specific link peptide of endothelial cells, Arg-Glu-Asp-Val (REDV), onto polydopamine (PDA)-deposited Mg–Zn–Y–Nd alloy surface via covalent reaction to improve the growth of the endothelial cells. The PDA/REDV coating with optimized parameters maintained the good blood compatibility of the Mg–Zn–Y–Nd alloy at the biomimetic speed of the blood flow and significantly inhibited the growth of the vascular smooth muscle cells and macrophage attachment/activation, which indicated its better functions in antihyperplasia and anti-inflammation. In particular, the PDA/REDV coating not only showed consistent results in promoting the attachment of endothelial cells as reported elsewhere, but also displayed the ability of enhancing the viability of endothelial cells (or inhibiting apoptosis), suggesting its pro-endothelialized function through different pathways. In summary, this PDA/REDV coating addressed the above-mentioned shortcomings of the magnesium alloy, which may promise its wider application.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.Z. Sheng, X. Liu, L.L. Min, H.L. Wang, W. Liu, M. Wang, L.Z. Huang, F. Wu, and X. Hou: Bioinspired approaches for medical devices. Chin. Chem. Lett. 28, 1131–1134 (2017).
S. Ramcharitar and P.W. Serruys: Fully biodegradable coronary stents. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 8, 305–314 (2008).
P.W. Serruys, M.J.B. Kutryk, and A.T.L. Ong: Coronary-artery stents. N. Engl. J. Med. 354, 483–495 (2006).
S.H. Im, Y. Jung, and S.H. Kim: Current status and future direction of biodegradable metallic and polymeric vascular scaffolds for next-generation stents. Acta Biomater. 60, 3–22 (2017).
Y.F. Zheng and H.T. Yang: Research progress in biodegradable metals for stent application. Acta Metall. Sin. 53, 1227–1237 (2017).
W.E.C. Wacker and B.L. Vallee: Magnesium metabolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 259, 431–438 (1958).
P. Lu, H.N. Fan, Y. Liu, L. Cao, X.F. Wu, and X.H. Xu: Controllable biodegradability, drug release behavior and hemocompatibility of PTX-eluting magnesium stents. Colloids Surf., B 83, 23–28 (2011).
E. Galvin, C. Cummins, S. Yoshihara, B.J. Mac Donald, and C. Lally: Plastic strains during stent deployment have a critical influence on the rate of corrosion in absorbable magnesium stents. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 55, 1261–1275 (2017).
N. Li and Y.F. Zheng: Novel magnesium alloys developed for biomedical application: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 29, 489–502 (2013).
J. Wang, Y. Jang, G.J. Wan, V. Giridharan, G.L. Song, Z.G. Xu, Y. Koo, P.K. Qi, J. Sankar, N. Huang, and Y. Yun: Flow-induced corrosion of absorbable magnesium alloy: In-situ and real-time electrochemical study. Corros. Sci. 104, 277–289 (2016).
Q. Wu, S.J. Zhu, L.G. Wang, Q. Liu, G.C. Yue, J. Wang, and S.K. Guan: The microstructure and properties of cyclic extrusion compression treated Mg–Zn–Y–Nd alloy for vascular stent application. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 8, 1–7 (2012).
Y.J. Shi, L. Zhang, J.H. Chen, J. Zhang, F. Yuan, L. Shen, C.X. Chen, J. Pei, Z.H. Li, J.Y. Tan, and G.Y. Yuan: In vitro and in vivo degradation of rapamycin-eluting Mg–Nd–Zn–Zr alloy stents in porcine coronary arteries. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 80, 1–6 (2017).
E. Lukyanova, N. Anisimova, N. Martynenko, M. Kiselevsky, S. Dobatkin, and Y. Estrin: Features of in vitro and in vivo behaviour of magnesium alloy WE43. Mater. Lett. 215, 308–311 (2018).
I. Adekanmbi, C.Z. Mosher, H.H. Lu, M. Riehle, H. Kubba, and K.E. Tanner: Mechanical behaviour of biodegradable AZ31 magnesium alloy after long term in vitro degradation. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 77, 1135–1144 (2017).
H. Feng, H.P. Liu, H. Cao, Y. Yang, Y.C. Xu, and J.Y. Guan: Effect of precipitates on mechanical and damping properties of Mg–Zn–Y–Nd alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 639, 1–7 (2015).
S.S. Hou, R.R. Zhang, S.K. Guan, C.X. Ren, J.H. Gao, Q.B. Lu, and X.Z. Cui: In vitro corrosion behavior of Ti–O film deposited on fluoride-treated Mg–Zn–Y–Nd alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 3571–3577 (2012).
J. Liu, P. Wang, C.C. Chu, and T.F. Xi: Arginine-leucine based poly(ester urea urethane) coating for Mg–Zn–Y–Nd alloy in cardiovascular stent applications. Colloids Surf., B 159, 78–88 (2017).
A. Strohbach and R. Busch: Polymers for cardiovascular stent coatings. Int. J. Polym. Sci., 2015, 782653 (2015).
J.A. Li, K. Zhang, and N. Huang: Engineering cardiovascular implant surfaces to create a vascular endothelial growth microenvironment. Biotechnol. J. 12, 1600401 (2017).
J.A. Li: Constructing a spatially ordered composite system on cardiovascular biomaterials surface to create preferable endothelial microenvironment. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 123, S18–S19 (2018).
K. Zhang, Y.X. Bai, X.F. Wang, Q. Li, F.X. Guan, and J.A. Li: Surface modification of esophageal stent materials by a polyethylenimine layer aiming at anti-cancer function. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 28, 125 (2017).
H. Su, G.N. Xue, C.R. Ye, Y. Wang, A.S. Zhao, N. Huang, and J.A. Li: The effect of anti-CD133/fucoidan bio-coatings on hemocompatibility and EPC capture. J. Biomater. Sci., Polym. Ed. 28, 2066–2081 (2017).
Y. Wei, Y. Ji, L.L. Xiao, Q.K. Lin, and J. Ji: Different complex surfaces of polyethyleneglycol (PEG) and REDV ligand to enhance the endothelial cells selectivity over smooth muscle cells. Colloids Surf., B 84, 369–378 (2011).
K. Zhang, J.A. Li, J. Wang, T. Liu, X. Wang, J.Y. Chen, N. Huang, and F.X. Guan: Combined REDV polypeptide and heparin onto titanium surface for the hemocompatibility and selectively endothelialization. J. Cell Sci. Ther. 6, 198 (2015).
Y.X. Bai, K. Zhang, R. Xu, H.T. Liu, F.X. Guan, H.W. Liu, Y. Chen, and J.A. Li: Surface modification of esophageal stent materials by a drug-eluting layer for better anti-restenosis function. Coatings 8, 215 (2018).
J.A. Li, F. Wu, K. Zhang, Z.K. He, D. Zou, X. Luo, Y.H. Fan, P. Yang, A.S. Zhao, and N. Huang: Controlling molecular weight of hyaluronic acid conjugated on amine-rich surface: Towards better multifunctional biomaterials for cardiovascular implants. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 30343–30358 (2017).
K. Zhang, X.F. Wang, F.X. Guan, Q. Li, and J.A. Li: Immobilization of Ophiopogonin D on stainless steel surfaces for improving surface endothelialization. RSC Adv. 6, 113893–113898 (2016).
Z.K. He, J.A. Li, X. Luo, D. Zou, P. Yang, A.S. Zhao, and N. Huang: Mechanical property of TiO2 nano-tubes surface based on the investigation of residual stress, tensile force and fluid flow shear stress: For potential application of cardiovascular devices. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 18, 798–804 (2018).
F. Wu, J.A. Li, K. Zhang, Z.K. He, P. Yang, D. Zou, and N. Huang: Multi-functional coating based on hyaluronic acid and dopamine conjugate for potential application on surface modification of cardiovascular implanted devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 109–121 (2016).
L. Chen, J.A. Li, J.W. Chang, S.B. Jin, D. Wu, H.H. Yan, X.F. Wang, and S.K. Guan: Mg–Zn–Y–Nd coated with citric acid and dopamine by layer-by-layer self-assembly to improve surface biocompatibility. Sci. China: Technol. Sci. 61, 1228–1237 (2018).
J.A. Li, K. Zhang, Y. Xu, J. Chen, P. Yang, Y.C. Zhao, A.S. Zhao, and N. Huang: A novel co-culture models of human vascular endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells by hyaluronic acid micro-pattern on titanium surface. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part A 102, 1950–1960 (2014).
G.C. Li, P. Yang, W. Qin, M.F. Maitz, S. Zhou, and N. Huang: The effect of coimmobilizing heparin and fibronectin on titanium on hemocompatibility and endothelialization. Biomaterials 32, 4691–4703 (2011).
J.A. Li, K. Zhang, J.J. Wu, L.J. Zhang, P. Yang, Q.F. Tu, and N. Huang: Tailoring of the titanium surface by preparing cardiovascular endothelial extracellular matrix layer on the hyaluronic acid micro-pattern for improving biocompatibility. Colloids Surf., B 128, 201–210 (2015).
J.A. Li, K. Zhang, H.Q. Chen, T. Liu, P. Yang, Y.C. Zhao, and N. Huang: A novel coating of type IV collagen and hyaluronic acid on stent material-titanium for promoting smooth muscle cells contractile phenotype. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 38, 235–243 (2014).
L.J. Xiang, J.A. Li, Z.K. He, J.J. Wu, P. Yang, and N. Huang: Design and construction of TiO2 nanotubes in microarray using two-step anodic oxidation for application of cardiovascular implanted devices. Micro Nano Lett. 10, 287–291 (2015).
J.A. Li, G.C. Li, K. Zhang, Y.Z. Liao, P. Yang, M.F. Maitz, and N. Huang: Co-culture of vascular endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells by hyaluronic acid micro-pattern on titanium surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 273, 24–31 (2013).
J.A. Li, W. Qin, K. Zhang, F. Wu, P. Yang, Z.K. He, A.S. Zhao, and N. Huang: Controlling mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into contractile smooth muscle cells on a TiO2 micro/nano interface: Towards benign pericytes environment for endothelialization. Colloids Surf., B 145, 410–419 (2016).
L.H. Li, Y. Xu, Z. Zhou, J. Chen, P. Yang, Y.H. Yang, J.A. Li, and N. Huang: The effects of Cu-doped TiO2 thin films on hyperplasia, inflammation and bacteria infection. Appl. Sci. 5, 1016–1032 (2015).
J.A. Li, K. Zhang, W.Y. Ma, F. Wu, P. Yang, Z.K. He, and N. Huang: Investigation of enhanced hemocompatibility and tissue compatibility associated with multi-functional coating based on hyaluronic acid and type IV collagen. Regener. Biomater. 3, 149–157 (2016).
H. Yao, J.A. Li, N. Li, K.B. Wang, X. Li, and J. Wang: Surface modification of cardiovascular stent material-316L SS with estradiol loaded poly(trimethylene carbonate) film for better biocompatibility. Polymers 9, 598 (2017).
Y.S. Feng, S.J. Zhu, L.G. Wang, L. Chang, B.B. Yan, X.Z. Song, and S.K. Guan: Characterization and corrosion property of nano-rod-like HA on fluoride coating supported on Mg–Zn–Ca alloy. Bioact. Mater. 2, 63–70 (2017).
Y. Xu, J.A. Li, L.F. Yao, L.H. Li, P. Yang, and N. Huang: Preparation and characterization of Cu-doped TiO2 thin films and effects on platelet adhesion. Surf. Coat. Technol. 261, 436–441 (2015).
Y. Wei, Y. Ji, L.L. Xiao, Q.K. Lin, J.P. Xu, K.F. Ren, and J. Ji: Surface engineering of cardiovascular stent with endothelial cell selectivity for in vivo re-endothelialisation. Biomaterials 34, 2588–2599 (2013).
J.A. Li, K. Zhang, P. Yang, L.L. Wu, J.L. Chen, A.S. Zhao, G.C. Li, and N. Huang: Research of smooth muscle cells response to fluid flow shear stress by hyaluronic acid micro-pattern on a titanium surface. Exp. Cell Res. 319, 2663–2672 (2013).
J.A. Li, D. Zou, K. Zhang, X. Luo, P. Yang, Y.Y. Jing, Y.X. Zhang, G.L. Cui, and N. Huang: Strong multi-functions based on conjugating chondroitin sulfate on amine-rich surface direct vascular cells fate for cardiovascular implanted devices. J. Mater. Chem. B 5, 8299–8313 (2017).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant Nos. 2017YFGX090043-04 and 2016YFC1102403), Fostering Talents of National Natural Science Foundation of China and Henan Province (No. U1504310), Key Scientific Research Projects of Higher Education Institutions in Henan Province (No. 16A430030), Key Project and Special Foundation of Research, Development and Promotion in Henan Province (No. 182102310076), Young Teachers Foundation of Zhengzhou University (No. 32210475), and the Joint Fund for Fostering Talents of NCIR-MMT & HNKL-MMT (No. MMT2017-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Li, J., Wang, S. et al. Surface modification of the biodegradable cardiovascular stent material Mg–Zn–Y–Nd alloy via conjugating REDV peptide for better endothelialization. Journal of Materials Research 33, 4123–4133 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.410
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.410