Abstract
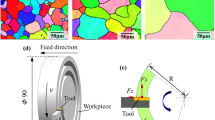
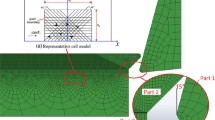
Subsurface microstructure alteration has been a major concern to implement micromachining of titanium alloy in the high-tech industry. To quantitatively promulgate the underlying mechanisms of this alteration, a discrete dislocation dynamics-based model is proposed and used to simulate the subsurface defects and their evolution under different cutting conditions. The model considers the subsurface dislocation configuration and inner stress distribution during the orthogonal cutting of titanium alloy. The results show that subsurface defect structure consists of plenty of dislocation dipoles, twining dislocation bands, and refined grains after cutting. In the primary shear zone, two different characteristics of subsurface damage layers can be found, the near-surface damage layer and deep-surface damage layer, which have different structural natures and distribution features. Moreover, it is found that high cutting speed and small depth of the cut can suppress the formation and propagation of subsurface defects. A powerful inner stress state would promote the distortion of the lattice and result in a microcrack within the subsurface matrix. The simulation results have been compared with experimental findings on the machined surface and subsurface of similar materials, and strong similarities were revealed and discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Tan, D.H. Zhang, C.F. Yao, D.X. Wu, and J.Y. Zhang: Evolution and empirical modeling of compressive residual stress profile after milling, polishing and shot peening for TC17 alloy. J. Manuf. Process 26, 155–165 (2017).
R.M. Saoubi, J.C. Outeiro, H. Chandrasekaran, O.W. Dillon, and I.S. Jawahir: A review of surface integrity in machining and its impact on functional performance and life of machined products. Int. J. Sustainable Manuf. 1, 203–236 (2008).
D. Ulutan and T. Ozel: Machining induced surface integrity in titanium and nickel alloys: A review. Int. J. Mach. Tool Manufact. 51, 250–280 (2011).
T.H. Tan and J.W. Yan: Atomic-scale characterization of subsurface damage and structural changes of single-crystal silicon carbide subjected to electrical discharge machining. Acta Mater. 123, 362–372 (2017).
C.H. Che-Haron: Tool life and surface integrity in turning titanium alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 118, 231–237 (2001).
A.R.C. Sharman, J.J. Hughes, and K. Ridgway: Workpiece surface integrity and tool life issues when turning Inconel 718 nickel based superalloy. Mach. Sci. Technol. 8, 399–414 (2004).
V. Bushlya, J.M. Zhou, and J.E. Stahl: Modeling and experimentation on multistage work-hardening mechanism in machining with nose-radiused tools and its influence on machined subsurface quality and tool wear. Int. J. Adv. Des. Manuf. Technol. 73, 545–555 (2014).
I.S. Jawahir, E. Brinksmeier, R.M. Saoubi, D.K. Aspinwall, J.C. Outeiro, D. Meyer, D. Umbrello, and A.D. Jayal: Surface integrity in material removal processes: Recent advances. CIRP Ann. 60, 603–626 (2011).
A. Ginting and M. Nouari: Surface integrity of dry machined titanium alloys. Int. J. Mach. Tool Manufact. 49, 325–332 (2009).
M. Thomas, S. Turnerb, and M. Jackson: Microstructural damage during high-speed milling of titanium alloys. Scr. Mater. 62, 250–253 (2010).
J. Kwong, D.A. Axinte, and P.J. Withers: The sensitivity of Ni-based superalloy to hole making operations: Influence of process parameters on subsurface damage and residual stress. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209, 3968–3977 (2009).
D. Jin and Z.Q. Liu: Damage of the machined surface and subsurface in orthogonal milling of FGH95 superalloy. Int. J. Adv. Des. Manuf. Technol. 68, 1573–1581 (2013).
D.X. Lv, H.X. Wang, W.W. Zhang, and Z.Q. Yin: Subsurface damage depth and distribution in rotary ultrasonic machining and conventional grinding of glass BK7. Int. J. Adv. Des. Manuf. Technol. 86, 2361–2371 (2016).
S.J. Zhang, S. To, C.F. Cheung, and Y. Zhu: Micro-structural changes of Zn–Al alloy influencing micro-topographical surface in micro-cutting. Int. J. Adv. Des. Manuf. Technol. 72, 9–15 (2014).
J.X. Bai, Q.S. Bai, Z. Tong, C. Hu, and X. He: Evolution of surface grain structure and mechanical properties in orthogonal cutting of titanium alloy. J. Mater. Res. 31, 1–11 (2016).
Y.B. Guo, W. Li, and I.S. Jawahir: Surface integrity characterization and prediction in machining of hardened and difficult-to-machine alloys: A state-of-the-art research review and analysis. Mach. Sci. Technol. 13, 437–470 (2009).
M.M. Gurusamy and B.C. Rao: On the performance of modified Zerilli–Armstrong constitutive model in simulating the metal-cutting process. J. Manuf. Process 28, 253–265 (2017).
H.T. Ding and Y.C. Shin: Multi-physics modeling and simulations of surface microstructure alteration in hard turning. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 213, 877–886 (2013).
S. Hore, S.K. Das, S. Banerjee, and S. Mukherjee: Computational modelling of static recrystallization and two dimensional microstructure evolution during hot strip rolling of advanced high strength steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 17, 78–87 (2015).
Q.L. Wang, Q.S. Bai, J.X. Chen, Y.B. Guo, and W.K. Xie: Stress-induced formation mechanism of stacking fault tetrahedra in nano-cutting of single crystal copper. Appl. Surf. Sci. 355, 1153–1160 (2015).
J. Li, Q.H. Fang, Y.W. Liu, and L.C. Zhang: A molecular dynamics investigation into the mechanisms of subsurface damage and material removal of monocrystalline copper subjected to nanoscale high speed grinding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 303, 331–343 (2014).
S.S. Shishvan and E. Van der Giessen: Mode I crack analysis in single crystals with anisotropic discrete dislocation plasticity: I. Formation and crack growth. Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 21, 065006 (2013).
S.S. Shishvan and E. Van der Giessen: Mode I crack analysis in single crystals with anisotropic discrete dislocation plasticity: II. Stationary crack-tip fields. Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 21, 065007 (2013).
E. Tarleton, D.S. Balint, J. Gong, and A.K. Wilkinson: A discrete dislocation plasticity study of the micro-cantilever size effect. Acta Mater. 88, 271–282 (2015).
C.H. Che-Haron and A. Jawaid: The effect of machining on surface integrity of titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 166, 188–192 (2005).
P. Crawforth, B. Wynne, S. Turnerb, and M. Jackson: Subsurface deformation during precision turning of a near-alpha titanium alloy. Scr. Mater. 67, 842–845 (2012).
M.J. Bermingham, S.D. McDonald, M.S. Dargusch, and D.H. StJohn: Grain-refinement mechanisms in titanium alloys. J. Mater. Res. 23, 97–104 (2008).
Q.Q. Wang, Z.Q. Liu, B. Wang, Q.H. Song, and Y. Wan: Evolutions of grain size and micro-hardness during chip formation and machined surface generation for Ti–6Al–4V in high-speed machining. Int. J. Adv. Des. Manuf. Technol. 82, 1725–1736 (2016).
C.J. Ouyang, Z.H. Li, M.S. Huang, and C.T. Hou: Discrete dislocation analyses of circular nanoindentation and its size dependence in polycrystals. Acta Mater. 56, 2706–2717 (2008).
N. Ahmed and A. Hartmaier: A two-dimensional dislocation dynamics model of the plastic deformation of polycrystalline metals. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 58, 2054–2064 (2010).
A.A. Benzerga, Y. Brechet, A. Needleman, and E. Van der Giessen: Incorporating three-dimensional mechanisms into two-dimension dislocation dynamics. Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 12, 159–196 (2004).
K.M. Davoudi, L. Nicola, and J.J. Vlassak: Dislocation climb in two-dimensional discrete dislocation dynamics. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 103522 (2012).
K. Danas and V.S. Deshpande: Plane-strain discrete dislocation plasticity with climb-assisted glide motion of dislocations. Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 21, 45008–45033 (2013).
Y.C. Zhang, T. Mabrouki, D. Nelias, and Y.D. Gong: Chip formation in orthogonal cutting considering interface limiting shear stress and damage evolution based on fracture energy approach. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 47, 850–863 (2011).
M.S. Huang and Z.H. Li: Coupled DDD–FEM modeling on the mechanical behavior of microlayered metallic multilayer film at elevated temperature. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 85, 74–97 (2015).
J. Sun and Y.B. Guo: A comprehensive experimental study on surface integrity by end milling Ti–6Al–4V. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209, 4036–4042 (2009).
D.H. Shin, I. Kim, J. Kim, Y.S. Kim, and S.L. Semiatin: Microstructure development during equal-channel angular pressing of titanium. Acta Mater. 51, 83–996 (2003).
B. Jiang, T.T. He, Y.P. Gu, Q.L. Wang, and G.L. Cao: Method for recognizing wave dynamics damage in high-speed milling cutter. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 92, 139–150 (2017).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research work was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51575138) and the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51535003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, J., Bai, Q., Tong, Z. et al. The influence of cutting parameters on the defect structure of subsurface in orthogonal cutting of titanium alloy. Journal of Materials Research 33, 720–732 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.397
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.397