Abstract
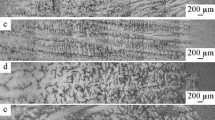
Ti-47Al-1.0W-0.5Si (at.%) alloy was directionally solidified in the range of growth rate (V) (V = 3–100 μm/s) at a constant temperature gradient (G = 18 K/mm). It was found that α phase was the primary phase of the alloy. Both primary dendritic arm spacing (λ) and interlamellar spacing (λs) decreased with increase of the growth rate (V) according to the relationship of λ ∝ V−0.356 and λs ∝ V−0.49, respectively. The Solidification segregation occurred since the enrichment of the solute element W in primary α phase during solidification. The degree of the segregation increased with the increase of the growth rate (V). The results also revealed that the lamellar orientation was not always perpendicular to the growth direction (GD) because the GD of primary α dendritic deviated from the preferred <0001> direction. The microhardness increased with increasing growth rate (V) according to HV ∝ 289.5 V0.12 because of the microstructure refinement.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Kim, J.K. Hong, Y. Na, J. Yeom, and S.E. Kim: Development of TiAl alloys with excellent mechanical properties and oxidation resistance. Mater. Des. 54, 814–819 (2014).
H. Clemens and S. Mayer: Design, processing, microstructure, properties, and applications of advanced intermetallic TiAl alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 15, 191–215 (2013).
D.R. Johnson, H. Inui, S. Muto, Y. Omiya, and T. Yamanaka: Microstructural development during directional solidification of α-seeded TiAl alloys. Acta Mater. 54, 1077–1085 (2006).
H. Inui, M.H. Oh, A. Nakamura, M. Yamaguchi: Room-temperature tensile deformation of polysynthetically twinned (PST) crystals of TiAl. Acta Mater. 40, 3095–3140 (1992).
D.R. Johnson, H. Inui and M. Yamaguch: Directional solidification and microstructural control of the TiAl/Ti3Al lamellar microstructure in TiAl-Si alloys. Acta Mater. 44, 2523–2535 (1996).
D.R. Johnson, Y. Masuda, H. Inui, M. Yamaguchi: Alignment of the TiAl/Ti3Al lamellar microstructure in TiAl alloys by growth from a seed material. Acta Mater. 45, 2523–2533 (1997).
S.E. Kim, Y.T. Lee, M.H. Oh, H. Inui, and M. Yamaguchi: Directional solidification of TiAl base alloys using a polycrystalline seed. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 329, 25–30 (2002).
H.N. Lee, D.R. Johnson, H. Inui, M.H. Oh, D.M. Wee, and M. Yamaguchi: A composition window in the TiAl–Mo–Si system suitable for lamellar structure control through seeding and directional solidification. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 329, 19–24 (2002).
I.S. Jung, H.S. Jang, M.H. Oh, J.H. Lee, and D.M. Wee: Microstructure control of TiAl alloys containing β stabilizers by directional solidification. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 329–331, 13–18 (2002).
I. Jung, M. Oh, N. Park, K.S. Kumar, and D. Wee: Lamellar boundary alignment of DS-processed TiAl–W alloys by a solidification procedure. Met. Mater. Int. 13, 455 (2007).
S. Dong, R. Chen, J. Guo, H. Ding, Y. Su, and H. Fu: Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of cast and directionally solidified high-Nb contained TiAl-based alloys. J. Mater. Res. 30, 1–12 (2015).
J. Lapin, L. Ondrú, and M. Nazmy: Directional solidification of intermetallic Ti–46Al–2W–0.5Si alloy in alumina moulds. Intermetallics 10, 1019–1031 (2002).
C. Kenel and C. Leinenbach: Influence of Nb and Mo on microstructure formation of rapidly solidified ternary Ti–Al–(Nb, Mo) alloys. Intermetallics 69, 82–89 (2016).
D. Hu: Role of boron in TiAl alloy development: A review. Rare Met. 35, 1–14 (2015).
R.M. Imayev, V.M. Imayev, M. Oehring, and F. Appel: Alloy design concepts for refined gamma titanium aluminide based alloys. Intermetallics 15, 451–460 (2007).
A. Brotzu, F. Felli, and D. Pilone: Effect of alloying elements on the behaviour of TiAl-based alloys. Intermetallics 54, 176–180 (2014).
W.M. Yin, V. Lupinc, and L. Battezzati: Microstructure study of a γ-TiAl based alloy containing W and Si. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 239–240, 713–721 (1997).
A.M. Hodge, L.M. Hsiung, and T.G. Nieh: Creep of nearly lamellar TiAl alloy containing W. Scr. Mater. 51, 411–415 (2004).
R. Yu, L.L. He, Z.X. Jin, J.T. Guo, H.Q. Ye, and V. Lupinc: On the orientation relationship between Ti5Si3 precipitates and B2 phase in a Ti–47Al–2W–0.5Si alloy. Scr. Mater. 44, 911–916 (2001).
J. Fan, X. Li, Y. Su, R. Chen, J. Guo, and H. Fu: Dependency of microstructure parameters and microhardness on the temperature gradient for directionally solidified Ti–49Al alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 130, 1232–1238 (2011).
J. Fan, X. Li, Y. Su, J. Guo, and H. Fu: The microstructure parameters and microhardness of directionally solidified Ti–43Al–3Si alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 506, 593–599 (2010).
H. Kaya, E. Çadırlı, and M. Gündüz: Directional cellular growth of Al-2 wt% Li bulk samples. Appl. Phys. A 94, 155–165 (2009).
H. Kaya, M. Gündüz, E. Çadırlı, and N. Maraşlı: Dependency of microindentation hardness on solidification processing parameters and cellular spacing in the directionally solidified Al based alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 478, 281–286 (2009).
U. Böyük and N. Maraşlı: The microstructure parameters and microhardness of directionally solidified Sn–Ag–Cu eutectic alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 485, 264–269 (2009).
E. Çadırlı, H. Kaya, and M. Gündüz: Effect of growth rates and temperature gradients on the lamellar spacing and the undercooling in the directionally solidified Pb–Cd eutectic alloy. Mater. Res. Bull. 38, 1457–1476 (2003).
U. Böyük, N. Maraşlı, H. Kaya, E. Çadırlı, and K. Keşlioğlu: Directional solidification of Al–Cu–Ag alloy. Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process. 95, 923–932 (2009).
H. Zhong, S. Li, H. Kou, and J. Li: The solidification path related columnar-to-equiaxed transition in Ti–Al alloys. Intermetallics 59, 81–86 (2015).
M. Yamaguchia, D.R. Johnson, H.N. Lee, and H. Inui: Directional solidification of TiAl-base alloys. Intermetallics 8, 511–517 (2000).
J. Lapin and Z. Gabalcová: Solidification behaviour of TiAl-based alloys studied by directional solidification technique. Intermetallics 19, 797–804 (2011).
J. Fan, X. Li, Y. Su, J. Guo, and H. Fu: Effect of growth rate on microstructure parameters and microhardness in directionally solidified Ti–49Al alloy. Mater. Des. 34, 552–558 (2012).
X.F. Ding, J.P. Lin, H. Qi, L.Q. Zhang, X.P. Song, and G.L. Chen: Microstructure evolution of directionally solidified Ti–45Al–8.5Nb–(W, B, Y) alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 4041–4046 (2011).
G.L. Chen, X.J. Xu, Z.K. Teng, Y.L. Wang, and J.P. Lin: Microsegregation in high Nb containing TiAl alloy ingots beyond laboratory scale. Intermetallics 15, 625–631 (2007).
J. Fan, X. Li, Y. Su, R. Chen, J. Guo, and H. Fu: Directional solidification of Ti–49 at.%Al alloy. Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process. 105, 239–248 (2011).
M.C. Kim, M.H. Oh, J.H. Lee, H. Inui, M. Yamaguchi, and D.M. Wee: Composition and growth rate effects in directionally solidified TiAl alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 239, 570–576 (1997).
T. Haxhimali, A. Karma, F. Gonzales, and M. Rappaz: Orientation selection in dendritic evolution. Nat. Mater. 5, 660–664 (2006).
J. Lapin: Effect of lamellar structure on microhardness and yield stress of directionally solidified intermetallic Ti–46Al–2W–0.5Si alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 22, 747–749 (2003).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51425402, 51331005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Luo, L., Su, Y. et al. Effect of growth rate on microstructures and microhardness in directionally solidified Ti-47Al-1.0W-0.5Si alloy. Journal of Materials Research 31, 618–626 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.48
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.48