Abstract
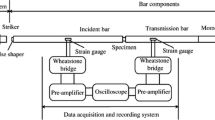
Microstructural and property evolution of 1050 commercial pure aluminum subjected to high-strain-rate deformation (1.2–2.3 × 103 s−1) by split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) and subsequent annealing treatment were investigated. The as-deformed and their annealed samples at 373–523 K were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and microhardness tests. TEM observations reveal that the as-deformed sample is mainly composed of a lamellar structure, whose transverse/longitudinal average subgrain/cell sizes are 293 and 694 nm, respectively. The initial coarse grains are refined significantly. The initial lamellar grain structures are subdivided into pancake-shaped subgrains due to a gradual transition by triple junction motion at 473 K, and then a dramatic microstructural coarsening is observed at 523 K. It is suggested that annealing behavior of this dynamic loading structure is better considered as a continuous process of grain coarsening or continuous recovery.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Sabirov, M.Y. Murashkin, and R.Z. Valiev: Nanostructured aluminum alloys produced by severe plastic deformation: New horizons in development. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 560, 1 (2013).
M.A. Meyers: Dynamic Behavior of Materials (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 1994); pp. 405–408.
Y. Yang, F. Ma, and H.B. Hu: Microstructure evolution of 2195 Al-Li alloy subjected to high-strain-rate deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 606, 299 (2014).
D. Hull and D.J. Bacon: Introduction to Dislocations, 3rd ed. (Pergamon Press, Oxford, England, 1984); p. 257.
Y.J. Chen, Y.J. Li, J.C. Walmsley, S. Dumoulin, S.S. Gireesh, S. Armada, P.C. Skaret, and H.J. Roven: Quantitative analysis of grain refinement in titanium during equal channel angular pressing. Scr. Mater. 64, 904 (2011).
F. Huang, N.R. Tao, and K. Lu: Effects of strain rate and deformation temperature on microstructures and hardness in plastically deformed pure aluminum. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 27, 1 (2011).
Y.S. Li, N.R. Tao, and K. Lu: Microstructural evolution and nanostructure formation in copper during dynamic plastic deformation at cryogenic temperature. Acta Mater. 56, 230 (2008).
P.N. Rao, D. Singh, and R. Jayaganthan: Mechanical properties and microstructural evolution of Al 6061 alloy processed by multidirectional forging at liquid nitrogen temperature. Mater. Des. 56, 97 (2014).
C.C. Koch: Optimization of strength and ductility in nanocrystalline and ultrafine grained metals. Scr. Mater. 49, 657 (2003).
P.C. Millett, R.P. Selvam, and A. Saxena: Stabilizing nanocrystalline materials with dopants. Acta Mater. 55, 2329 (2007).
M.R. Shankar, S. Chandrasekar, A.H. King, and W.D. Compton: Microstructure and stability of nanocrystalline aluminum 6061 created by large strain machining. Acta Mater. 53, 4781 (2005).
H. Kolsky: An investigation of the mechanical properties of materials at very high rates of loading. Proc. Phys. Soc., Sect. B 62, 676 (1949).
Q. Liu, D. Juul, and N. Hansen: Effect of grain orientation on deformation structure in cold-rolled polycrystalline aluminum. Acta Mater. 46, 5819 (1998).
Z.P. Luo, H.W. Zhang, N. Hansen, and K. Lu: Quantification of the microstructures of high purity nickel subjected to dynamic plastic deformation. Acta Mater. 60, 1322 (2012).
R. Kapoor, A. Sarkar, R. Yogi, S.K. Shekhawat, I. Samajdar, and J.K. Chakravartty: Softening of Al during multi-axial forging in a channel die. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 560, 404 (2013).
N. Tsuji, Y. Ito, Y. Saito, and Y. Minamino: Strength and ductility of ultrafine grained aluminum and iron produced by ARB and annealing. Scr. Mater. 47, 893 (2002).
N. Kamikawa, X. Huang, N. Tsuji, and N. Hansen: Strengthening mechanisms in nanostructured high-purity aluminum deformed to high strain and annealed. Acta Mater. 57, 4198 (2009).
E.A. El-Danaf, M.S. Soliman, A.A. Almajid, and M.M. El-Rayes: Enhancement of mechanical properties and grain size refinement of commercial purity aluminum 1050 processed by ECAP. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 458, 226 (2007).
R.W. Cahn and P. Haasen: Physical Metallurgy, 4th ed., Vol. III (North-Holland, The Netherlands, 1996); p. 1869.
C.Y. Yu, P.Y. Sun, P.W. Kao, and C.P. Chang: Evolution of microstructure during annealing of a severely deformed aluminum. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 366, 310 (2004).
N. Rangaraju, T. Raghuram, B.V. Krishna, K.P. Rao, and P. Venugopal: Effect of cryo-rolling and annealing on microstructure and properties of commercial pure aluminum. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 398, 246 (2005).
O.V. Mishin, A. Godfrey, D. Juul Jensen, and N. Hansen: Recovery and recrystallization in commercial purity aluminum cold rolled to an ultrahigh strain. Acta Mater. 61, 5354 (2013).
N. Hansen, X. Huang, M.G. Moller, and A. Godfrey: Thermal stability of aluminum cold rolled to large strain. J. Mater. Sci. 43, 6254 (2008).
T.B. Yu, N. Hansen, and X.X. Huang: Linking recovery and recrystallization through triple junction motion in aluminum cold rolled to a large strain. Acta Mater. 61, 6577 (2013).
T. Fur, R. Oresund, and E. Nest: Subgrain growth in heavily deformed aluminum-experimental investigation and modelling treatment. Acta Metall. Mater. 43, 2209 (1995).
F.X. Zhao, X.C. Xu, H.Q. Liu, and Y.L. Wang: Effect of annealing treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine-grained aluminum. Mater. Des. 53, 262 (2014).
R.A. Vandermeer and N. Hansen: Recovery kinetics of nanostructured aluminum: Model and experiment. Acta Mater. 56, 5719 (2008).
A. Godfrey, W.Q. Cao, N. Hansen, and Q. Liu: Stored energy, microstructure, and flow stress of deformed metals. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36, 2371 (2005).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51274245), NSAF (No. U1330126), the Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (No. 20120162130006), the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 14JJ2011), and the key project of State Key Laboratory of Explosion Science and Technology (No. KFJJ11-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Chen, Y.D., Hu, H.B. et al. Microstructural evolution and thermal stability of 1050 commercial pure aluminum processed by high-strain-rate deformation. Journal of Materials Research 30, 3502–3509 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.341
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.341