Abstract
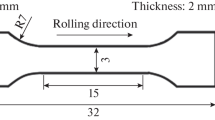
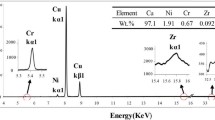
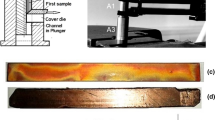
The Cu–Cr system alloys with different Ti contents were prepared and processed by deformation and heat treatment. The microstructures, mechanical, and electrical properties were investigated under as-cast and aged conditions. The results indicate that the Cr precipitates present a dispersed distribution and exhibit a face-centered cubic (fcc) structure rather than equilibrium body-centered cubic (bcc) structure in the initial stage of aging. A certain amount of Ti atoms dissolves in matrix due to the large solid solubility, while the remaining atoms segregate around the interface of the Cr precipitates to form a sandwich structure. Improvement of mechanical properties is achieved with Ti addition and the increasing rolling reduction, which can be ascribed to multiple mechanisms. In addition, Ti has a negative effect on the electrical conductivity, while deformation has a slight effect on conductivity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Raabe, K. Miyake, and H. Takahara: Processing, microstructure, and properties of ternary high-strength Cu–Cr–Ag in situ composites. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 291, 186 (2000).
K. Maki, Y. Ito, H. Matsunaga, and H. Mori: Solid-solution copper alloys with high strength and high electrical conductivity. Scr. Mater. 68, 777 (2013).
N. Takata, S.H. Lee, and N. Tsuji: Ultrafine grained copper alloy sheets having both high strength and high electric conductivity. Mater. Lett. 63, 1757 (2009).
J.H. Su, P. Liu, Q.M. Dong, H.J. Li, and F.Z. Ren: Aging study of rapidly solidified and solid-solution Cu–Cr–Sn–Zn alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 205, 366 (2008).
J.Q. Deng, X.Q. Zhang, S.Z. Shang, F. Liu, Z.X. Zhao, and Y.F. Ye: Effect of Zr addition on the microstructure and properties of Cu–10Cr in situ composites. Mater. Des. 30, 4444 (2009).
C.D. Xia, Y.L. Jia, W. Zhang, K. Zhang, Q.Y. Dong, G.Y. Xu, and M.P. Wang: Study of deformation and aging behaviors of a hot rolled–quenched Cu–Cr–Zr–Mg–Si alloy during thermomechanical treatments. Mater. Des. 39, 404 (2012).
L.P. Deng, K. Han, K.T. Hartwig, T.M. Siegrist, L.Y. Dong, Z.Y. Sun, X.F. Yang, and Q. Liu: Hardness, electrical resistivity, and modeling of in situ Cu–Nb microcomposites. J. Alloys Compd. 602, 331 (2014).
Q. Lei, Z. Li, J. Wang, J.M. Xie, X. Chen, S. Li, Y. Gao, and L. Li: Hot working behavior of a super high strength Cu–Ni–Si alloy. Mater. Des. 51, 1104 (2013).
J.H. Su, P. Liu, H. Li, F.Z. Ren, and Q.M. Dong: Phase transformation in Cu–Cr–Zr–Mg alloy. Mater. Lett. 61, 4963 (2007).
Z.P. Que, J.H. Lee, H.M. Jung, J.H. Shin, S.Z. Han, and K.J. Euh: Microstructure evolution in Cu–1.54wt% Cr alloy during directional solidification. J. Cryst. Growth 362, 58 (2013).
Y. Pang, C.D. Xia, M.P. Wang, Z. Li, Z. Xiao, H.G. Wei, X.F. Sheng, Y.L. Jia, and C. Chen: Effects of Zr and (Ni, Si) additions on properties and microstructure of Cu–Cr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 582, 786 (2014).
C. Watanabe, R. Monzen, and K. Tazaki: Mechanical properties of Cu-Cr system alloys with and without Zr and Ag. J. Mater. Sci. 43, 813 (2008).
J.H. Su, Q.M. Dong, P. Liu, H.J. Li, and B.X. Kang: Research on aging precipitation in a Cu–Cr–Zr–Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 392, 422 (2005).
A. Nagesha, P. Parameswaran, A. Biswas, R. Sandhya, A.K. Asraff, and M.D. Mathew: Microstructural investigations into the low cycle fatigue deformation of a Cu–Cr–Zr–Ti alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 582, 91 (2013).
Y.H. Wang, X.P. Song, Z.B. Sun, X. Zhou, and J. Guo: Effects of Ti addition on microstructures of melt-spun CuCr ribbons. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 17, 72 (2007).
K.X. Wei, W. Wei, F. Wang, Q.B. Du, I.V. Alexandrov, and J. Hu: Microstructure, mechanical properties and electrical conductivity of industrial Cu–0.5%Cr alloy processed by severe plastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 528, 1478 (2011).
C.D. Xia, W. Zhang, Z.Y. Kang, Y.L. Jia, Y.F. Wu, R. Zhang, G.Y. Xu, and M.P. Wang: High strength and high electrical conductivity Cu–Cr system alloys manufactured by hot rolling–quenching process and thermomechanical treatments. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 538, 295 (2012).
N.K. Tewary, S.K. Ghosh, S. Bera, D. Chakrabarti, and S. Chatterjee: Influence of cold rolling on microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of low carbon high Mn TWIP steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 615, 405 (2014).
S.H. Huh, H.K. Kim, J.W. Park, and G.H. Lee: Critical cluster size of metallic Cr and Mo nanoclusters. Phys. Rev. B. 62, 2937 (2000).
M. Hatakeyama, T. Toyama, J. Yang, Y. Nagai, M. Hasegawa, T. Ohkubo, M. Eldrup, and B.N. Singh: 3D-AP and positron annihilation study of precipitation behavior in Cu–Cr–Zr alloy. J. Nucl. Mater. 386–388, 852 (2009).
J.J. Hoyt: On the coarsening of precipitates located on grain boundaries and dislocations. Acta Metall. Mater. 39, 2091 (1991).
J.E. Bailey and P.B. Hirsch: The dislocation distribution, flow stress, and stored energy in cold worked polycrystalline silver. Philos. Mag. 5, 485 (1960).
L. Gao, R.S. Chen, and E.H. Han: Effects of rare-earth elements Gd and Y on the solid solution strengthening of Mg alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 481, 379 (2009).
B. Sun, S. Li, H. Imai, T. Mimoto, J. Umeda, and K. Kondoh: Fabrication of high-strength Ti materials by in-process solid solution strengthening of oxygen via P/M methods. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 563, 95 (2013).
D.L. Ellis and G.M. Michal: Precipitation strengthened high strength, high conductivity Cu-Cr-Nb alloys produced by chill block melt spinning. NASA Contractor Reports Server. 185144, (1989).
R.L. Fleischer: Solution hardening by tetragonal distortions: Application to irradiation hardening in F.C.C. crystals. Acta Metall. 10, 835 (1962).
L. Qu, E.G. Wang, K. Han, X.W. Zuo, L. Zhang, P. Jia, and J.C. He: Studies of electrical resistivity of an annealed Cu-Fe composite. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 173708 (2013).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51134013, 51271042) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (DUT14RC(4)13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Jie, J., Gao, Y. et al. Influence of cold deformation and Ti element on the microstructure and properties of Cu–Cr system alloys. Journal of Materials Research 30, 2073–2080 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.143
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.143