Abstract
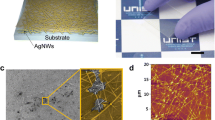
Stretchable transparent conductors are required for flexible and wearable electronics. This study demonstrates biaxially stretchable transparent conductors that use silver nanowire networks. The use of buckled nanowire networks has previously been reported to lend stretchability to the transparent conductor in a single axis. However, a nanowire network that is prestrained and then buckled out-of-plane biaxially shows a deterioration of the electrical conductivity after a single cycle of stretching and releasing the strain uniaxially. This has been attributed to the loss of good electrical contact between the nanowires. By hot pressing the out-of-plane buckled nanowires to obtain an in-plane wavy nanowire network with good wire-to-wire junctions, a biaxially stretchable transparent conductor that maintains good electrical conductivity with stretching up to 10% is demonstrated. The methods of prestraining the nanowire network to achieve out-of-plane buckled nanowires and hot pressing the out-of-plane buckled nanowires to obtain an in-plane wavy nanowire network with fused junctions are expected to be practical for other classes of percolative networks based on one-dimensional (1D) materials used in flexible and stretchable applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
K-Y. Chun, Y. Oh, J. Rho, J-H. Ahn, Y-J. Kim, H.R. Choi, and S. Baik: Highly conductive, printable and stretchable composite films of carbon nanotubes and silver. Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 853 (2010).
K.H. Kim, M. Vural, and M.F. Islam: Single-walled carbon nanotube aerogel-based elastic conductors. Adv. Mater. 23, 2865 (2011).
Y.Y. Huang and E.M. Terentjev: Tailoring the electrical properties of carbon nanotubes-polymer composite. Adv. Funct. Mater. 20, 4062 (2010).
K. Liu, Y. Sun, P. Liu, X. Lin, S. Fan, and K. Jiang: Cross-stacked superaligned carbon nanotube films for transparent and stretchable conductors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 21, 2721 (2011).
M.K. Shin, J. Oh, M. Lima, M.E. Kozlov, S.J. Kim, and R.H. Baughman: Elastomeric conductive composites based on carbon nanotube forests. Adv. Mater. 22, 2663 (2010).
S. Huang, L. Li, Z. Yang, L. Zhang, H. Saiyin, T. Chen, and H. Peng: A new and general fabrication of an aligned carbon nanotube/polymer film for electrode applications. Adv. Mater. 23, 4707 (2011).
T. Sekitani, Y. Noguchi, K. Hata, T. Fukushima, T. Aida, and T. Someya: A rubberlike stretchable active matrix using elastic conductors. Science 321, 1468 (2008).
T. Yamada, Y. Hayamizu, Y. Yamamoto, Y. Yomogida, A. Izadi-Najafabadi, D.N. Futaba, and K. Hata: A stretchable carbon nanotube strain sensor for human-motion detection. Nat. Nanotechnol. 6, 296 (2011).
Y. Zhang, C.J. Sheehan, J. Zhai, G. Zou, H. Luo, J. Xiong, Y.T. Zhu, and Q.X. Jia: Polymer-embedded carbon nanotube ribbons for stretchable conductors. Adv. Mater. 22, 3027 (2010).
Y. Zhu and F. Xu: Buckling of aligned carbon nanotubes as stretchable conductors: A new manufacturing strategy. Adv. Mater. 24, 1073 (2012).
F. Xu, X. Wang, Y. Zhu, and Y. Zhu: Wavy ribbons of carbon nanotubes for stretchable conductors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22, 1279 (2012).
R-H. Kim, M-H. Bae, D.G. Kim, H. Cheng, B.H. Kim, D-H. Kim, M. Li, J. Wu, F. Du, H-S. Kim, S. Kim, D. Estrada, S.W. Hong, Y. Huang, E. Pop, and J.A. Rogers: Stretchable, transparent graphene interconnects for arrays of microscale inorganic light emitting diodes on rubber substrates. Nano Lett. 11, 3881 (2011).
K.S. Kim, Y. Zhao, H. Jang, S.Y. Lee, J.M. Kim, K.S. Kim, J-H. Ahn, P. Kim, J-Y. Choi, and B.H. Hong: Large scale pattern growth of graphene films for stretchable transparent electrodes. Nature 457, 706 (2009).
D.J. Lipomi, B.C-K. Tee, M. Vosgueritchian, and Z. Bao: Stretchable organic solar cells. Adv. Mater. 23, 1771 (2011).
D.J. Lipomi, J.A. Lee, M. Vosgueritchian, B.C-K. Tee, J.A. Bolander, and Z. Bao: Electronic properties of transparent conductive films of PEDOT: PSS on stretchable substrates. Chem. Mater. 24, 373 (2012).
P. Lee, J. Lee, H. Lee, J. Yeo, S. Hong, K.H. Nam, D. Lee, S.S. Lee, and S.H. Ko: Highly stretchable and highly conductive metal electrode by very long metal nanowire percolation network. Adv. Mater. 24, 3326 (2012).
T. Akter and W.S. Kim: Reversible stretchable transparent conductive coatings of spray-deposited silver nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4, 1855 (2012).
J-Y. Lee, S.T. Conner, Y. Cui, and P. Peumans: Solution-processed metal nanowire mesh transparent electrodes. Nano Lett. 8, 689 (2008).
V. Scardaci, R. Coull, P.E. Lyons, D. Rickard, and J.N. Coleman: Spray deposition of highly transparent, low-resistance networks of silver nanowires over large areas. Small 7, 2621 (2011).
S. De, T.M. Higgins, P.E. Lyons, E.M. Doherty, P.N. Nirmalraj, W.J. Blau, J.J. Boland, and J.N. Coleman: Silver nanowire networks as flexible, transparent, conducting films: Extremely high DC to optical conductivity ratios. ACS Nano 3, 1767 (2009).
L. Hu, H.S. Kim, J-Y. Kim, P. Peumans, and Y. Cui: Scalable coating and properties of transparent, flexible, silver nanowire electrodes. ACS Nano 4, 2955 (2010).
X. Ho, J. Tey, W. Liu, C.K. Cheng, and J. Wei: Biaxially stretchable silver nanowire transparent conductors. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 044311 (2013).
M-S. Lee, K. Lee, S-Y. Kim, H. Lee, J. Park, K-H. Choi, H-K. Kim, D-G. Kim, D-Y. Lee, S.W. Nam, and J-U. Park: High-performance, transparent and stretchable electrodes using graphene-metal nanowire hybrid structures. Nano Lett. 13, 2814 (2013).
Y. Zhu, Z. Sun, Z. Yan, Z. Jin, and J.M. Tour: Rational design of hybrid graphene films for high-performance transparent electrodes. ACS Nano 5, 6472 (2011).
L. Hu, H. Wu, and Y. Cui: Metal nanogrids, nanowires and nanofibers for transparent electrodes. MRS Bull. 36, 760 (2011).
P.B. Catrysse and S.H. Fan: Nanopatterned metallic films for use as transparent conductive electrodes in optoelectronic devices. Nano Lett. 10, 2944 (2010).
X. Ho, H. Lu, W. Liu, J. Tey, C.K. Cheng, E. Kok, and J. Wei: Electrical and optical properties of hybrid transparent electrodes that use metal grids and graphene films. J. Mater. Res. 28, 620 (2013).
N. Lu, S. Wang, Z. Suo, and J. Vlassak: Metal films on polymer substrates stretched beyond 50%. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 221909 (2007).
X. Ho and J. Wei: Films of carbon nanomaterials for transparent conductors. Materials 6, 2155 (2013).
Y. Zhu, Q. Qin, F. Xu, F. Fan, Y. Ding, T. Zhang, B.J. Wiley, and Z.L. Wang: Size effects on elasticity, yielding and fracture of silver nanowires: In situ experiments. Phys. Rev. B 85, 045443 (2012).
J.H. Yoo, S.I. Oh, and M.S. Jeong: The enhanced elastic modulus of nanowires associated with multitwins. J. Appl. Phys. 107, 094316 (2010).
R. Gunawidjaja, H. Ko, C. Jiang, and V.V. Tsukruk: Buckling behavior of highly oriented silver nanowire encapsulated within layer-by-layer films. Chem. Mater. 19, 2007 (2007).
J. Wu, J. Zang, A.R. Rathmell, X. Zhao, and B.J. Wiley: Reversible sliding in networks of nanowires. Nano Lett. 13, 2381 (2013).
E.C. Garnett, W. Cai, J.J. Cha, F. Mahmood, S.T. Connor, M.G. Christoforo, Y. Cui, M.D. McGehee, and M.L. Brongersma: Self-limited plasmonic welding of silver nanowire junctions. Nat. Mater. 11, 241 (2012).
J. Lee, I. Lee, T-S. Kim, and J-Y. Lee: Efficient welding of silver nanowire networks without post-processing. Small 9, 2887 (2013).
B. Kang, J. Yun, S-G. Kim, and M. Yang: Adaptive fabrication of a flexible electrode by optically self-selected interfacial adhesion and its application to highly transparent and conductive film. Small 9, 2111 (2013).
T. Tokuno, M. Nogi, M. Karakawa, J. Jiu, T.T. Nge, Y. Aso, and K. Suganuma: Fabrication of silver nanowire transparent electrodes at room temperature. Nano Res. 4, 1215 (2011).
J.A. Rogers, T. Someya, and Y. Huang: Materials and mechanics for stretchable electronics. Science 327, 1603 (2010).
D-H. Kim, J. Xiao, J. Song, Y. Huang, and J.A. Rogers: Stretchable, curvilinear electronics based on inorganic materials. Adv. Mater. 22, 2108 (2010).
Y. Zhang, S. Xu, H. Fu, J. Lee, J. Su, K-C. Hwang, J.A. Rogers, and Y. Huang: Buckling in serpentine microstructures and applications in elastomer-supported ultra-stretchable electronics with high areal coverage. Soft Matter. 9, 8062 (2013).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors acknowledge Vuong Ngoc Dung at Singapore Institute of Manufacturing Technology for help with designing and printing the fixture for prestraining the PDMS equibiaxially. This work was supported by the Agency of Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), Singapore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ho, X., Cheng, C.K., Tey, J.N. et al. Biaxially stretchable transparent conductors that use nanowire networks. Journal of Materials Research 29, 2965–2972 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.338
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.338