Abstract
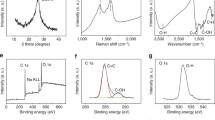
Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) are zero-dimensional material with characteristics derived from functionalized graphene precursors are graphene sheets a few nanometers in the lateral dimension having a several-layer thickness. Combining the structure of graphene with the quantum confinement and edge effects, GQDs possess unique chemical behavior and physical properties. Intense research activity in GQDs is attributed to their novel phenomena of charge transport and light absorption and photoluminescence excitation. The optical transitions are known to be available up to 6 eV in GQDs, applicable for ultraviolet photonics and optoelectronics devices, biomedical imaging capabilities and technologies. We present facile hydrothermal and solvothermal methods for synthesizing homogenous dispersed and uniform sized GQDs with a strong greenish and violet blue emission peaks at ∼10-14% yield. This approach enabled a large-scale production of aqueous GQD dispersions without the need for chemical stabilizers. The structure and emission mechanism of the GQDs have been studied by combining extensive characterization techniques and rigorous control experiments. We further demonstrate the distinctive advantages of such GQDs as high-performance photodetectors (PDs). Here we also report high-efficient photocurrent (PC) behaviors consisting of multilayer GQDs sandwiched between monolayer graphene sheets. It is conceivable that the observed unique PD characteristics proved to be dominated by tunneling of charge carriers which occurs through the multiple energy states within the bandgap of GQDs, based on bias-dependent variation of the band profiles. This results in novel dark current and PC behaviors. The external quantum efficiency (η) is predicted to be 47% at applied potential 2 V. These findings highlight rich photophysics and comparable performance of graphene/graphene oxide hybrids opening up potential applications as optoelectronic devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Geim and K. Novoselov, Nature Mater. 6, 183 (2007).
S. Gupta and S. B. Carrizosa, J. Electron. Materials 44, 4492 (2015).
S. Gupta, M. vanMeveren and J. Jasinski, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 10, 10272 (2015).
S. Bai, K. Zhang, L. Wang, J. Sun, R. Luo, D. Li and A. Chen, J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 7927 (2014).
G. Wang L. Zhang and J. Zhang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 797 (2012).
A. Geim and K. S. Novoselov, Nat. Mater. 6, 652 (2007).
R. Raccichini, A. Varzi, S. Passerini and B. Scrosati, Nat. Mater. 14, 271 (2015).
Q. Zhang, J. Jie, S. Diao, Z. Shao, Q. Zhang, L. Wang, W. Deng, W. Hu, H. Xia, X. Yuan and S.-T. Lee, ACS Nano 9, 1561 (2015).
G. Konstantatos, M. Badioli, L. Gaudreau, J. Osmond, M. Bernechea, F. Pelayo G. de Arquer, F. Gatti and F. H. L. Koppens, Nat. Nanotechnol. 7, 363 (2012).
Y. Li, Y. Hu, Y. Zhao, G. Shi, L. Deng, Y. Hou and L. Qu, Adv. Mater. 23, 776 (2011).
X. Yan, X. Cui and L. S. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 5944 (2010).
G. Konstantatos and E. H. Sargent, Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 391 (2010).
Y. Sun, S. Wang, C. Li, P. Luo, L. Tao, Y. Wei and G. Shi, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 9907 (2013).
L. E. Brus, Appl. Phys. 53, 465 (1991).
A. L. Efros and M. Rosen, Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci. 30, 475 (2000).
C. O. Kim, S. W. Hwang, S. Kim, D. H. Shin, S. S. Kang, J. M. Kim, C. W. Jang, J. H. Kim, K. W. Lee, S.-H. Choi and E. Hwang, Sci. Rep. 4: 5603 (2014).
K. Byrappa, M. Yoshimura, in Handbook of Hydrothermal Technology (Noyes Publications, New Jersey, USA, 2001).
R. Roy, J. Sol. Stat. Chem. 111, s11–17 (1994).
G. Eda and M. Chowalla, Adv. Mater. 22, 2392 (2010).
D. Pan, J. Zhang, Z. Li and M. Wu, Adv. Mater. 22, 734 (2010).
S. Gupta, T. Smith, A. Banaszak and J. Boeckl, Nanomaterials 7, 301 (2017).
C. Xiong, A.E. Aliev, B. Gnade and K.J. Balkus Jr. ACS Nano 2, 293 (2008).
E. H. Lee, M. B. Lewis, P. J. Blau, and L. K. Mansur, J. Mater. Res. 6, 610 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, S., Walden, J., Banaszak, A. et al. Facile Synthesis of Water-Soluble Graphene Quantum Dots/Graphene for Efficient Photodetector. MRS Advances 3, 817–824 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2018.14
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2018.14