Abstract
Background
Preserving the nipple-areolar complex (NAC) in breast cancer surgery improves patient satisfaction and quality of life. The oncologic safety of NSM in tumors < 2 cm from the nipple remains in question. We conducted a systematic review to determine whether TND < 2 cm was associated with increased risk of LRR in patients undergoing NSM.
Methods
We included studies of invasive or in situ breast cancer < 2 cm from NAC undergoing NSM which reported LRR rates. LRR rates were stratified by TND and culminated across studies. Cohort study quality was assessed using Newcastle–Ottawa Criteria. Meta-analysis was not possible due to heterogeneity in reporting survival outcomes.
Results
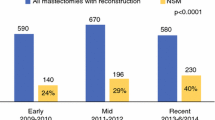
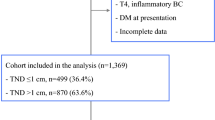
We identified seven retrospective cohort studies with 2295 patients and 18 case series with 3507 patients. Direct tumor involvement of NAC was considered an absolute contraindication to NSM in all studies. In cohort studies, median follow-up was 31–112 (range 14–204) months. Cohorts with TND < 2 cm did not have a significantly higher rate of LRR. Amongst case series, 275 patients had TND < 2 cm. Combined LRR in case series was 2.6%, with median follow-up 10.4–71 (range 0–158) months.
Conclusions
Our systematic review did not identify TND < 2 cm as a significant risk factor for LRR. NSM appears oncologically safe in select patients with TND < 2 cm. Given the improved quality of life associated with NSM compared to skin-sparing mastectomy, we suggest NSM as the procedure of choice in appropriately selected patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coopey SB, Tang R, Lei L, et al. Increasing eligibility for nipple-sparing mastectomy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(10):3218–22. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-3152-x.
Bailey CR, Ogbuagu O, Baltodano PA, et al. Quality-of-life outcomes improve with nipple-sparing mastectomy and breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;140(2):219–26. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000003505.
Mallon P, Feron JG, Couturaud B, et al. The role of nipple-sparing mastectomy in breast cancer: a comprehensive review of the literature. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131(5):969–84. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182865a3c.
NCCN Guidelines Version 2.2022 Breast Cancer. Accessed 26 April 2022. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf
Kim S, Lee S, Bae Y, Lee S. Nipple-sparing mastectomy for breast cancer close to the nipple: a single institution’s 11-year experience. Breast Cancer. 2020;27(5):999–1006. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-020-01104-0.
de Alcantara Filho P, Capko D, Barry JM, Morrow M, Sacchini VS, Pusic A. Nipple-sparing mastectomy for breast cancer and risk-reducing surgery: the memorial sloan-kettering cancer center experience. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(11):3117–22. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-011-1974-y.
Tang R, Coopey SB, Merrill AL, et al. Positive nipple margins in nipple-sparing mastectomies: rates, management, and oncologic safety. J Am Coll Surg. 2016;222(6):1149–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2016.02.016.
Peled AW, Foster RD, Stover AC, et al. Outcomes after total skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate reconstruction in 657 breasts. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19(11):3402–9. https://doi.org/10.1245/S10434-012-2362-Y/FIGURES/2.
Alsharif E, Ryu JM, Choi HJ, et al. Oncologic outcomes of nipple-sparing mastectomy with immediate breast reconstruction in patients with tumor-nipple distance less than 2.0 cm. J Breast Cancer. 2019;22(4):613–23. https://doi.org/10.4048/JBC.2019.22.E48.
Balci FL, Kara H, Dulgeroglu O, Uras C. Oncologic safety of nipple-sparing mastectomy in patients with short tumor-nipple distance. Breast J. 2019;25(4):612–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbj.13289.
Fregatti P, Gipponi M, Zoppoli G, et al. Tumor-to-nipple distance should not preclude nipple-sparing mastectomy in breast cancer patients. Personal experience and literature review. Anticancer Res. 2020;40(6):3543–50. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.14343.
Frey JD, Salibian AA, Lee J, et al. Oncologic trends, outcomes, and risk factors for locoregional recurrence: an analysis of tumor-to-nipple distance and critical factors in therapeutic nipple-sparing mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;143(6):1575–85. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000005600.
Wu ZY, Kim HJ, Lee J, et al. Recurrence outcomes after nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction in patients with pure ductal carcinoma in situ. Ann Surg Oncol. 2020;27(5):1627–35. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-019-08184-z.
Wu ZY, Kim HJ, Lee J, et al. Oncologic safety of nipple-sparing mastectomy in patients with breast cancer and tumor-to-nipple distance ≤ 1 cm: a matched cohort study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2021;28(8):4284–91. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-020-09427-0.
Lanitis S, Tekkis PP, Sgourakis G, Dimopoulos N, Al Mufti R, Hadjiminas DJ. Comparison of skin-sparing mastectomy versus non-skin-sparing mastectomy for breast cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann Surg. 2010;251(4):632–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0B013E3181D35BF8.
Burdge EC, Yuen J, Hardee M, et al. Nipple skin-sparing mastectomy is feasible for advanced disease. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(10):3294–302. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-3174-4.
Dent BL, Miller JA, Eden DJ, Swistel A, Talmor M. Tumor-to-nipple distance as a predictor of nipple involvement: expanding the inclusion criteria for nipple-sparing mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;140(1):1e–8e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000003414.
Fortunato L, Loreti A, Andrich R, et al. When mastectomy is needed: is the nipple-sparing procedure a new standard with very few contraindications? J Surg Oncol. 2013;108(4):207–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.23390.
Jun S, Bae SJ, Cha YJ, et al. Significance of non-mass enhancement in the subareolar region on preoperative breast magnetic resonance imaging for nipple-sparing mastectomy. Clin Breast Cancer. 2020;20(4):e458–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clbc.2020.02.005.
Krajewski AC, Boughey JC, Degnim AC, et al. Expanded indications and improved outcomes for nipple-sparing mastectomy over time. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22(10):3317–23. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4737-3.
Paepke S, Schmid R, Fleckner S, et al. Subcutaneous mastectomy with conservation of the nipple-areola skin: broadening the indications. Ann Surg. 2009;250(2):288–92. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181b0c7d8.
Ozkurt E, Tukenmez M, Guven E, et al. Favorable outcome with close margins in patients undergoing nipple/skin sparing mastectomy with immediate breast reconstruction: 5-year follow-up. Balkan Med J. 2018;35(1):84–92. https://doi.org/10.4274/balkanmedj.2017.0029.
Sacchini V, Pinotti JA, Barros ACSD, et al. Nipple-sparing mastectomy for breast cancer and risk reduction: oncologic or technical problem? J Am Coll Surg. 2006;203(5):704–14.
Santoro S, Loreti A, Cavaliere F, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is not a contraindication for nipple sparing mastectomy. Breast. 2015;24(5):661–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2015.08.001.
Shimo A, Tsugawa K, Tsuchiya S, et al. Oncologic outcomes and technical considerations of nipple-sparing mastectomies in breast cancer: experience of 425 cases from a single institution. Breast Cancer. 2016;23(6):851–60.
Valero MG, Muhsen S, Moo TA, et al. Increase in utilization of nipple-sparing mastectomy for breast cancer: indications, complications, and oncologic outcomes. Ann Surg Oncol. 2020;27(2):344–51. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-019-07948-x.
Yamashita Y, Nagura N, Kajiura Y, et al. Long-term oncologic safety of nipple-sparing mastectomy with immediate reconstruction. Clin Breast Cancer. 2021;21(4):352–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clbc.2021.01.002.
Chan YHY, Yau WM, Cheung PSY. Oncological safety and technical feasibility of nipple-sparing mastectomy for breast cancer: the Hong Kong experience. World J Surg. 2018;42(5):1375–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-017-4197-y.
Mesdag V, Regis C, Tresch E, et al. Nipple sparing mastectomy for breast cancer is associated with high patient satisfaction and safe oncological outcomes. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2017;46(8):637–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jogoh.2017.07.003.
Poruk KE, Ying J, Chidester JR, et al. Breast cancer recurrence after nipple-sparing mastectomy: one institution’s experience. Am J Surg. 2015;209(1):212–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2014.04.001.
Holleczek B, Stegmaier C, Radosa JC, Solomayer EF, Brenner H. Risk of loco-regional recurrence and distant metastases of patients with invasive breast cancer up to ten years after diagnosis-results from a registry-based study from Germany. BMC Cancer. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-5710-5.
Moran MS, Schnitt SJ, Giuliano AE, et al. SSO-ASTRO consensus guideline on margins for breast-conserving surgery with whole breast irradiation in stage I and II invasive breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;88(3):553. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJROBP.2013.11.012.
Acknowledgement
SY, NR, and DL designed the search protocol. SY and EL conducted the literature search, reviewed articles, extracted data from selected articles, and performed quality assessments. NR, DL, DO, and LP provided manuscript review and editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
DISCLOSURE
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix 1: Search Criteria Applied to Medline and EMBASE Databases. Date of Last Search December 4, 2021
-
1.
Exp Recurrence/ or exp Neoplasm Recurrence, Local/or recurrence.mp.
-
2.
Exp recurrent disease/
-
3.
1 or 2
-
4.
Nipples/
-
5.
Tumor-nipple distance.mp. [mp=ti, ab, ot, nm, hw, fx, kf, ox, px, rx, ui, sy, tn, dm, mf, dv, dq]
-
6.
Nipple-areol*.mp. [mp=ti, ab, ot, nm, hw, fx, kf, ox, px, rx, ui, sy, tn, dm, mf, dv, dq]
-
7.
Nipple-sparing.mp. [mp=ti, ab, ot, nm, hw, fx, kf, ox, px, rx, ui, sy, tn, dm, mf, dv, dq]
-
8.
Exp nipple/ or nipple.mp. or exp nipple-sparing mastectomy/
-
9.
4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8
-
10.
exp Breast Neoplasms/su [Surgery]
-
11.
Exp breast cancer/su [Surgery]
-
12.
10 or 11
-
13.
3 and 9 and 12
-
14.
Limit 14 to yr = “2000–2021”
Appendix 2: Study Quality Scoring System Based on Newcastle–Ottawa Cohort Study Criteria
-
A.
Representativeness of exposed cohort: 1 point if included all consecutive patients with TND < 2 cm in cohort of patients undergoing nipple-sparing mastectomy
-
B.
Selection of nonexposed cohort: 1 point patients with TND > 2 cm selected from same community as patients with TND ≤ 2 cm
-
C.
Ascertainment of exposure: 1 point if TND measured on preoperative imaging
-
D.
Demonstrating that outcome of interest was not present at beginning of study: 1 point if study excluded patients with previous breast cancers or recurrent breast cancer.
-
E.
Comparability of cohorts: 2 points if matched by T-stage, nodal status, and hormone receptor and HER2 status; 1 point if adjusted for age and pathology; 0 points if no comparison data provided
-
F.
Assessment of outcome: 1 point if surveillance protocol included imaging and physical exam.
-
G.
Follow-up long enough for study outcomes to occur: 1 point if median follow-up at least 3 years
-
H.
Adequacy of follow-up for cohorts: 1 point if < 10% of patients lost to follow-up
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Youn, S., Lee, E., Peiris, L. et al. Spare the Nipple: A Systematic Review of Tumor Nipple-Distance and Oncologic Outcomes in Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy. Ann Surg Oncol 30, 8381–8388 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-023-14143-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-023-14143-6