Abstract
Background
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have shown great promise in treating late-stage gastric cancer, but their efficacy in the neoadjuvant setting has not been studied in large cohorts. Here, we explored the efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant ICI-based therapy in locally advanced gastric cancer.
Patients and Methods
We included studies containing patients with locally advanced gastric/gastroesophageal cancer who received ICI-based neoadjuvant therapy. We searched PubMed, Embase, Cochrane library, and abstracts from major international oncology conferences. We performed this meta-analysis using the META package in R.3.6.1.
Results
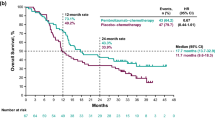
Twenty-one prospective phase I/II studies comprising 687 patients were identified. The pathological complete response (pCR) rate was 0.21 (95% CI 0.18–0.24), major pathological response (MPR) rate was 0.41 (95% CI 0.31–0.52), and R0 resection rate was 0.94 (95% CI 0.92–0.96). The efficacy was highest with ICI plus radiochemotherapy, lowest with ICI alone, and in the middle with ICI and chemotherapy ± anti-angiogenesis. dMMR/MSI-H and PD-L1-high patients benefited more than pMMR/MSS and PD-L1-low patients. Grade 3 or higher toxicity rate was 0.23 (95% CI 0.13–0.38). These results exceeded those in trials of neoadjuvant chemotherapy, where the rate of pCR was 0.08 (95% CI 0.06–0.11), MPR was 0.22 (95% CI 0.19–0.26), R0 section was 0.84 (95% CI 0.80–0.87), and overall grade 3 or higher toxicity was 0.28 (95% CI 0.13–0.47) in 4800 patients across 21 studies.
Conclusions
In summary, the integrated results show promising efficacy and safety of ICI-based neoadjuvant therapy for locally advanced gastric cancer and support further investigation in large multicenter randomized trials.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49.
In H, Solsky I, Palis B, Langdon-Embry M, Ajani J, Sano T. Validation of the 8th edition of the AJCC TNM staging system for gastric cancer using the national cancer database. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017;24(12):3683–91.
Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, van Grieken NC, Lordick F. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2020;396(10251):635–48.
Cunningham D, Allum WH, Stenning SP, et al. Perioperative chemotherapy versus surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(1):11–20.
Ychou M, Boige V, Pignon JP, et al. Perioperative chemotherapy compared with surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma: an FNCLCC and FFCD multicenter phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(13):1715–21.
Al-Batran SE, Homann N, Pauligk C, et al. Perioperative chemotherapy with fluorouracil plus leucovorin, oxaliplatin, and docetaxel versus fluorouracil or capecitabine plus cisplatin and epirubicin for locally advanced, resectable gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (FLOT4): a randomised, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet. 2019;393(10184):1948–57.
Hayashi M, Fujita T, Matsushita H. Prognostic value of tumor regression grade following the administration of neoadjuvant chemotherapy as treatment for gastric/gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma: a meta-analysis of 14 published studies. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2021;47(8):1996–2003.
An JY, Kim KM, Kim YM, Cheong JH, Hyung WJ, Noh SH. Surgical complications in gastric cancer patients preoperatively treated with chemotherapy: their risk factors and clinical relevance. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19(8):2452–8.
Fuchs CS, Doi T, Jang RW, et al. Safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab monotherapy in patients with previously treated advanced gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer: phase 2 clinical KEYNOTE-059 trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(5):e180013.
Kang YK, Boku N, Satoh T, et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer refractory to, or intolerant of, at least two previous chemotherapy regimens (ONO-4538-12, ATTRACTION-2): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2017;390(10111):2461–71.
Janjigian YY, Shitara K, Moehler M, et al. First-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric, gastro-oesophageal junction, and oesophageal adenocarcinoma (CheckMate 649): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;398(10294):27–40.
Janjigian YY, Kawazoe A, Yanez P, et al. The KEYNOTE-811 trial of dual PD-1 and HER2 blockade in HER2-positive gastric cancer. Nature. 2021;600(7890):727–730.
Forde PM, Chaft JE, Smith KN, et al. Neoadjuvant PD-1 blockade in resectable lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(21):1976–86.
Amaria RN, Reddy SM, Tawbi HA, et al. Neoadjuvant immune checkpoint blockade in high-risk resectable melanoma. Nat Med. 2018;24(11):1649–54.
Liu J, Blake SJ, Yong MC, et al. Improved efficacy of neoadjuvant compared to adjuvant immunotherapy to eradicate metastatic disease. Cancer Discov. 2016;6(12):1382–99.
Blank CU, Rozeman EA, Fanchi LF, et al. Neoadjuvant versus adjuvant ipilimumab plus nivolumab in macroscopic stage III melanoma. Nat Med. 2018;24(11):1655–61.
Slim K, Nini E, Forestier D, Kwiatkowski F, Panis Y, Chipponi J. Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J Surg. 2003;73(9):712–6.
DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7(3):177–88.
Liu N, Liu Z, Zhou Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of camrelizumab combined with FLOT versus FLOT alone as neoadjuvant therapy in patients with resectable locally advanced gastric and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma who received D2 radical gastrectomy. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(15_suppl):e16020.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557–60.
Li S, Yu W, Xie F, et al. A prospective, phase II, single-arm study of neoadjuvant/conversion therapy with camrelizumab, apatinib, S-1 ± oxaliplatin for locally advanced cT4a/bN+ gastric cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(15_suppl):4061.
Wei J, Lu X, Liu Q, et al. SHARED: efficacy and safety of sintilimab in combination with concurrent chemoradiotherapy (cCRT) in patients with locally advanced gastric (G) or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(15_suppl):4040.
Spicer J, Wang C, Tanaka F, et al. Surgical outcomes from the phase 3 CheckMate 816 trial: nivolumab (NIVO) + platinum-doublet chemotherapy (chemo) vs chemo alone as neoadjuvant treatment for patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(15_suppl):8503–8503.
Duan H, Wang T, Luo Z, et al. Neoadjuvant programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitors combined with chemotherapy in resectable non-small cell lung cancer: an open-label, multicenter, single-arm study. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021;10(2):1020–8.
Shitara K, Ozguroglu M, Bang YJ, et al. Pembrolizumab versus paclitaxel for previously treated, advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (KEYNOTE-061): a randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2018;392(10142):123–33.
Galluzzi L, Humeau J, Buque A, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G. Immunostimulation with chemotherapy in the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020;17(12):725–41.
Liu Y, Han G, Li H, et al. Camrelizumab combined with FLOFOX as neoadjuvant therapy for resectable locally advanced gastric and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma: updated results of efficacy and safety. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(15_suppl):4036.
Versluis JM, Long GV, Blank CU. Learning from clinical trials of neoadjuvant checkpoint blockade. Nat Med. 2020;26(4):475–84.
Pietrantonio F, Randon G, Di Bartolomeo M, et al. Predictive role of microsatellite instability for PD-1 blockade in patients with advanced gastric cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. ESMO Open. 2021;6(1):100036.
Chalabi M, Fanchi LF, Dijkstra KK, et al. Neoadjuvant immunotherapy leads to pathological responses in MMR-proficient and MMR-deficient early-stage colon cancers. Nat Med. 2020;26(4):566–76.
Bang Y-J, Cutsem EV, Fuchs CS, et al. KEYNOTE-585: phase 3 study of chemotherapy (chemo) + pembrolizumab (pembro) vs chemo + placebo as neoadjuvant/adjuvant treatment for patients (pts) with gastric or gastroesophageal junction (G/GEJ) cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(15_suppl):4136.
Acknowledgement
Alexandra H. Marshall (Marshall Medical Communications) edited the manuscript. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (82173305); Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2017MH005); Foundation of Shandong University Clinical Research Center (2020SDUCRCC011); Chinese Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M652406).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Xu, Q., Dai, X. et al. Neoadjuvant Therapy with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann Surg Oncol 30, 3594–3602 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-023-13143-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-023-13143-w